Study Island
... 5. The elements on the periodic table are arranged in rows, or periods, by increasing atomic mass. Along each row of the periodic table, atomic mass increases from left to right. 6. The number of protons in an atom gives the atom its identity. For example, all atoms with six protons found in their n ...
... 5. The elements on the periodic table are arranged in rows, or periods, by increasing atomic mass. Along each row of the periodic table, atomic mass increases from left to right. 6. The number of protons in an atom gives the atom its identity. For example, all atoms with six protons found in their n ...
Webquest: Atomic Theories and Models
... couldn't) ultimately you would see individual atoms - objects that could not be divided further (that was the definition of atom). ...
... couldn't) ultimately you would see individual atoms - objects that could not be divided further (that was the definition of atom). ...
Atomic Structure 1. Historical perspective of the model of the atom a
... a.) In 1803, John Dalton proposed the atomic theory which stated that all matter is made of atoms, atoms of the same type of element have the same chemical properties, compounds are formed by two or more different types of atoms, and that a chemical reaction involves either, joining, separating, or ...
... a.) In 1803, John Dalton proposed the atomic theory which stated that all matter is made of atoms, atoms of the same type of element have the same chemical properties, compounds are formed by two or more different types of atoms, and that a chemical reaction involves either, joining, separating, or ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry comes alive
... Valence shell – outermost energy level containing chemically active electrons Octet rule – except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in their valence shell ...
... Valence shell – outermost energy level containing chemically active electrons Octet rule – except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in their valence shell ...
File
... An element is a pure substance which cannot be split up into two or more simpler substances by physical or chemical means. ...
... An element is a pure substance which cannot be split up into two or more simpler substances by physical or chemical means. ...
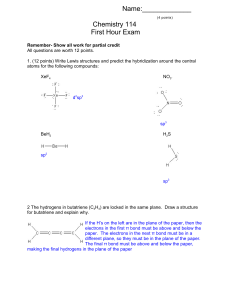
Name:______ Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
... 5.Draw the structures for the following organic compounds. Some the given names may be incorrect. If a name is not correct, give the correct name for the compound 2-methyl-6-ethylhexane ...
... 5.Draw the structures for the following organic compounds. Some the given names may be incorrect. If a name is not correct, give the correct name for the compound 2-methyl-6-ethylhexane ...
Remember Question words
... Atomic structure nucleus (protons, neutrons) shells (electrons) shell = a particular region where electrons can orbit the nucleus of an atom valence electron = an electron in the outermost shell of an atom charges (positive = proton; neutral = neutron; negative = ...
... Atomic structure nucleus (protons, neutrons) shells (electrons) shell = a particular region where electrons can orbit the nucleus of an atom valence electron = an electron in the outermost shell of an atom charges (positive = proton; neutral = neutron; negative = ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory Atomic Theory II
... negatively charged electrons moved around the nucleus. ...
... negatively charged electrons moved around the nucleus. ...
Cahpter 19 – Properties of Atoms and the Periodic table
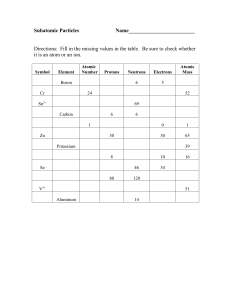
... Protons (p+) = positive charged particles Neutrons (no) = uncharged particles Electrons (e-)= negative charged particles ...
... Protons (p+) = positive charged particles Neutrons (no) = uncharged particles Electrons (e-)= negative charged particles ...
Ch 4 Review
... ____ 22. Physical properties of matter are characteristics that a. can be observed without changing the composition of substances. b. describe reactions between substances. c. describe reactions between unreactive substances. d. can be observed only after changing the composition of substances. ____ ...
... ____ 22. Physical properties of matter are characteristics that a. can be observed without changing the composition of substances. b. describe reactions between substances. c. describe reactions between unreactive substances. d. can be observed only after changing the composition of substances. ____ ...
Comprehensive Science 3 Module 4 Practice Test
... 8. How many Neutrons would an element have with an atomic number of 4 and an atomic mass of 16? ...
... 8. How many Neutrons would an element have with an atomic number of 4 and an atomic mass of 16? ...
Answer = 1.81 x 10 24 molecules
... • Chemists also agreed that elements could combine to form compounds that have different physical and chemical properties than those of the elements used to form them Ex. NaCl has different physical and chemical properties than chlorine (Cl) and Sodium (Na) • There was controversy over whether ele ...
... • Chemists also agreed that elements could combine to form compounds that have different physical and chemical properties than those of the elements used to form them Ex. NaCl has different physical and chemical properties than chlorine (Cl) and Sodium (Na) • There was controversy over whether ele ...
Atomic Models - South Houston High School
... 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 2. Understand Conclusions Show that you understand the conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory by describing how Democritus’s idea of the atom was ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 2. Understand Conclusions Show that you understand the conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory by describing how Democritus’s idea of the atom was ...
3 Atoms
... o Explain the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions, and the law of multiple proportions o Summarize the five essential points of Dalton’s atomic theory o Explain the relationship between Dalton’s atomic theory and the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportio ...
... o Explain the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions, and the law of multiple proportions o Summarize the five essential points of Dalton’s atomic theory o Explain the relationship between Dalton’s atomic theory and the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportio ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... Development of Atomic Theory 1. Democritus named atoms from the Greek word that means ____________________. 2. During Aristotle’s it was believed that all substances were built from the four elements ________________, air, _____________________ and water. 3. By the 1800s Dalton’s ideas replaced the ...
... Development of Atomic Theory 1. Democritus named atoms from the Greek word that means ____________________. 2. During Aristotle’s it was believed that all substances were built from the four elements ________________, air, _____________________ and water. 3. By the 1800s Dalton’s ideas replaced the ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONS
... Elements in Groups 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18 are called the Main Group elements; those in the centre (Groups 3 to 12) are called the Transition Metals. Elements in Groups 13, 14 and 15 are sometimes termed Post ...
... Elements in Groups 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18 are called the Main Group elements; those in the centre (Groups 3 to 12) are called the Transition Metals. Elements in Groups 13, 14 and 15 are sometimes termed Post ...
File
... Atoms are made up of 3 main subatomic particles The nucleus is located at the center of the atom The nucleus contains protons that are positively charged and neutrons which have no charge Electrons are located outside the nucleus in specific energy ...
... Atoms are made up of 3 main subatomic particles The nucleus is located at the center of the atom The nucleus contains protons that are positively charged and neutrons which have no charge Electrons are located outside the nucleus in specific energy ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... He asked: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided? ...
... He asked: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided? ...
Unit 4
... ● Atoms are made up of 3 subatomic particles; protons, neutrons, and electrons. ● The history of atomic development shaped the way scientists have constructed the current model of the atom. ...
... ● Atoms are made up of 3 subatomic particles; protons, neutrons, and electrons. ● The history of atomic development shaped the way scientists have constructed the current model of the atom. ...
Atomic Structure
... History B.C. – Democritus proposed all matter was made up of small particles called atoms Atomic numbers were assigned to elements by Henry Moseley 1913- Niels Bohr described the planetary model of the atom ...
... History B.C. – Democritus proposed all matter was made up of small particles called atoms Atomic numbers were assigned to elements by Henry Moseley 1913- Niels Bohr described the planetary model of the atom ...
Chemical Reactions - TSHSChemistry
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
File
... • atoms that are covalently bonded form molecules • when two atoms form a covalent bond the sharing of electrons allows each to satisfy the octet rule ...
... • atoms that are covalently bonded form molecules • when two atoms form a covalent bond the sharing of electrons allows each to satisfy the octet rule ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.