Covalent Bonding-compounds & Structures
... The amount of sharing can change depending on how strongly an atom holds onto its electrons. We use the periodic table and values of electronegativity to determine how strongly an atom will pull electrons in a bond. The electronegativity of the atoms was assigned by Linus Pauling when he studi ...
... The amount of sharing can change depending on how strongly an atom holds onto its electrons. We use the periodic table and values of electronegativity to determine how strongly an atom will pull electrons in a bond. The electronegativity of the atoms was assigned by Linus Pauling when he studi ...
Ionic bonding
... Nonmetal atoms have relatively high ionization energies, so it is difficult to remove electrons from them When nonmetals bond together, it is better in terms of potential energy for the atoms to share valence electrons Potential energy lowest when the electron is between the nuclei, holding the atom ...
... Nonmetal atoms have relatively high ionization energies, so it is difficult to remove electrons from them When nonmetals bond together, it is better in terms of potential energy for the atoms to share valence electrons Potential energy lowest when the electron is between the nuclei, holding the atom ...
Chem 200 Dr. Saidane
... b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound. c) The Law of Multiple Proportions, which states that, if two or more compounds are composed of ...
... b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound. c) The Law of Multiple Proportions, which states that, if two or more compounds are composed of ...
Name January 5, 2017 Period Bio-Chem Unit 2 Review (Chapters
... C. 1808 John Dalton was first to publish Atomic Theory a. All matter composed of indivisible particles called atoms, which retain their identity during chemical reactions b. All atoms of the same element have identical properties, which differ from other elements. c. Atoms cannot be created nor dest ...
... C. 1808 John Dalton was first to publish Atomic Theory a. All matter composed of indivisible particles called atoms, which retain their identity during chemical reactions b. All atoms of the same element have identical properties, which differ from other elements. c. Atoms cannot be created nor dest ...
File - Mr. Holz`s Website
... Ionic Bond – Transfer of electrons to create a bond between two ions that are attracted by opposite charges Covalent Bond – Bond that forms when electrons are shared between atoms Ion – Charged atoms that form from ionic bonds; atoms in which the number of electrons does not equal the number of prot ...
... Ionic Bond – Transfer of electrons to create a bond between two ions that are attracted by opposite charges Covalent Bond – Bond that forms when electrons are shared between atoms Ion – Charged atoms that form from ionic bonds; atoms in which the number of electrons does not equal the number of prot ...
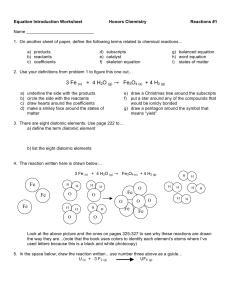
Equation Intro Worksheet 1213
... Look at the above picture and the ones on pages 325-327 to see why these reactions are drawn the way they are…(note that the book uses colors to identify each element’s atoms where I’ve used letters because this is a black and white photocopy) 5. In the space below, draw the reaction written…use num ...
... Look at the above picture and the ones on pages 325-327 to see why these reactions are drawn the way they are…(note that the book uses colors to identify each element’s atoms where I’ve used letters because this is a black and white photocopy) 5. In the space below, draw the reaction written…use num ...
Chapter 18 Power Point
... atoms but there was no evidence. John Dalton said that atoms were indestructible spheres of solid matter (the billiard ball model). They can be joined together to form molecules. He had evidence. In 1913, Niels Bohr decided that the atom was like a solar system where the planets were the electrons a ...
... atoms but there was no evidence. John Dalton said that atoms were indestructible spheres of solid matter (the billiard ball model). They can be joined together to form molecules. He had evidence. In 1913, Niels Bohr decided that the atom was like a solar system where the planets were the electrons a ...
representing chemical compounds
... • Use experimental data to show that a compound obeys the law of definite proportions ...
... • Use experimental data to show that a compound obeys the law of definite proportions ...
5 - atomic structure ppt
... 1.9 understand that atoms consist of a central nucleus, composed of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons, orbiting in shells 1.10 recall the relative mass and relative charge of a proton, neutron and electron 1.11 understand the terms atomic number, mass number, isotopes and relative atom ...
... 1.9 understand that atoms consist of a central nucleus, composed of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons, orbiting in shells 1.10 recall the relative mass and relative charge of a proton, neutron and electron 1.11 understand the terms atomic number, mass number, isotopes and relative atom ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... four elements: earth, fire, air and water. These four elements were supposedly blended in different proportions to make up all the various types substances in the world. • Aristotle had such a great reputation as a thinker that many of his ideas were simply accepted as true without any experimental ...
... four elements: earth, fire, air and water. These four elements were supposedly blended in different proportions to make up all the various types substances in the world. • Aristotle had such a great reputation as a thinker that many of his ideas were simply accepted as true without any experimental ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... A model has been devised to explain this phenomena Think of the model as a bookcase with each succeeding shelf getting closer and closer Depending on the element, different electronic transitions can be observed. The emphasis her is electronic, the electrons are being excited to different levels ...
... A model has been devised to explain this phenomena Think of the model as a bookcase with each succeeding shelf getting closer and closer Depending on the element, different electronic transitions can be observed. The emphasis her is electronic, the electrons are being excited to different levels ...
atomic number
... normal conditions, protons and neutrons stick together in the nucleus. During radioactive decay, they may be knocked out of there. Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and electron together. If there are many atoms of an element that are ...
... normal conditions, protons and neutrons stick together in the nucleus. During radioactive decay, they may be knocked out of there. Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and electron together. If there are many atoms of an element that are ...
are made up of
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
Lesson Outline - WordPress.com
... 1. Boron has two isotopes. The first, has a mass of 10.01 u and makes up 19.78%. The second, has a mass of 11.01 u and makes up 80.22%. What is the average atomic mass of Boron? 2. Silver has two isotopes, the first has a mass of 106.9 u and an abundance of 51.8%, the second has a mass of 108.9 u an ...
... 1. Boron has two isotopes. The first, has a mass of 10.01 u and makes up 19.78%. The second, has a mass of 11.01 u and makes up 80.22%. What is the average atomic mass of Boron? 2. Silver has two isotopes, the first has a mass of 106.9 u and an abundance of 51.8%, the second has a mass of 108.9 u an ...
Atomic Structure
... Niels Bohr studied under Rutherford at the Victoria University in Manchester. Bohr refined Rutherford's idea by adding that the electrons were in orbits. Rather like planets orbiting the sun. With each orbit only able to contain a set number of electrons. ...
... Niels Bohr studied under Rutherford at the Victoria University in Manchester. Bohr refined Rutherford's idea by adding that the electrons were in orbits. Rather like planets orbiting the sun. With each orbit only able to contain a set number of electrons. ...
BS5-Ch 2.
... • elements and compounds • Free elements are not combined with another element in a compound. Examples: Fe (iron), Na (sodium), and K (potassium) Many non-metals occur in groups of 2 (as diatomic molecules)- H, O, N, F, Cl, I, Br Some elements occur as molecules: P4, S, S8, P10, O3 , ...
... • elements and compounds • Free elements are not combined with another element in a compound. Examples: Fe (iron), Na (sodium), and K (potassium) Many non-metals occur in groups of 2 (as diatomic molecules)- H, O, N, F, Cl, I, Br Some elements occur as molecules: P4, S, S8, P10, O3 , ...
Text Related to Segment 7.01 ©2002 Claude E. Wintner To make a
... It needs to be emphasized that the foregoing discussion properly cannot be termed an explanation of the phenomenon of covalent bonding; rather, we have developed a model — but one which has proved to have very significant predictive value. Indeed, these ideas can be extended nicely to rationalize th ...
... It needs to be emphasized that the foregoing discussion properly cannot be termed an explanation of the phenomenon of covalent bonding; rather, we have developed a model — but one which has proved to have very significant predictive value. Indeed, these ideas can be extended nicely to rationalize th ...
Lecture 3: Matter: What it is Slide 2: What does it Matter? What is a
... What are the four states of matter? Can you list them from low temperature to high temperature? Which state of matter is the most common in the universe? Can you name some examples of each for ...
... What are the four states of matter? Can you list them from low temperature to high temperature? Which state of matter is the most common in the universe? Can you name some examples of each for ...
Bonding Web Practice Trupia - Trupia
... reddish-brown liquid, volatilizing readily at room temperature to a red vapor with a strong disagreeable odor, resembling chlorine, and having a very irritating effect on the eyes and throat; it is readily soluble in water or carbon disulfide, forming a red solution, is less active than chlorine but ...
... reddish-brown liquid, volatilizing readily at room temperature to a red vapor with a strong disagreeable odor, resembling chlorine, and having a very irritating effect on the eyes and throat; it is readily soluble in water or carbon disulfide, forming a red solution, is less active than chlorine but ...
Self-Quiz - mrsgooyers
... Gold and silver are easily shaped to fill a hole in a tooth. Neither metal will react with water or any food someone might eat. Gold and silver are very expensive metals. Using them in dental fillings would cost more than using other materials with similar properties. ...
... Gold and silver are easily shaped to fill a hole in a tooth. Neither metal will react with water or any food someone might eat. Gold and silver are very expensive metals. Using them in dental fillings would cost more than using other materials with similar properties. ...
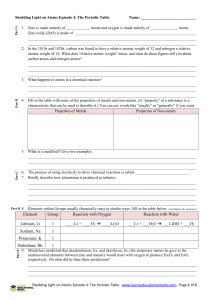
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.