PROPERTIES_OF_MATTER
... chemically combined in a fixed proportion. – for example: • Common table salt is a one to one combination of sodium atoms (Na) and chlorine atoms (Cl) = NaCl ...
... chemically combined in a fixed proportion. – for example: • Common table salt is a one to one combination of sodium atoms (Na) and chlorine atoms (Cl) = NaCl ...
Electrons - biospaces
... strongly it pulls shared electrons toward itself • Electronegativity increases within the periodic table from left to right and from bottom to top! ...
... strongly it pulls shared electrons toward itself • Electronegativity increases within the periodic table from left to right and from bottom to top! ...
Name
... ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PHYSICAL SCIENCE I. Atomic Structure A. Objectives 1. Explain _________________________ and describes why it was more successful than _________________________________________ 2. State the ______________________ of each part of an atom according to the _______ ...
... ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLE PHYSICAL SCIENCE I. Atomic Structure A. Objectives 1. Explain _________________________ and describes why it was more successful than _________________________________________ 2. State the ______________________ of each part of an atom according to the _______ ...
Chapter 2 – Fundamental Building Blocks: Chemistry, Water, and pH
... simple set of component substances through chemical processes – Gold is an example of an element o The thing that defines each element is the number of protons it has in its nucleus o Protons and neutrons are components of atoms but they are not component substances because they cannot exist by them ...
... simple set of component substances through chemical processes – Gold is an example of an element o The thing that defines each element is the number of protons it has in its nucleus o Protons and neutrons are components of atoms but they are not component substances because they cannot exist by them ...
Unit 1 – Physical Science and Chemical Reactions
... When metals (cations) and non-metals (anions) join, the net electrical charge of an ionic compound must be zero. - ie. The sum of all positive charges must equal the sum of all negative charges Never change the charge on an ion from the Periodic Table - To find the net charge, multiply the charg ...
... When metals (cations) and non-metals (anions) join, the net electrical charge of an ionic compound must be zero. - ie. The sum of all positive charges must equal the sum of all negative charges Never change the charge on an ion from the Periodic Table - To find the net charge, multiply the charg ...
History of Atomic Theories Worksheet Answers
... particles, each of which was called a(n) __(1)__. The theory that such particles existed was supported, much later, by __(2)__, who proposed, in his law of __(3)__, that matter cannot be created or destroyed. Then __(4)__ proposed, in his law of __(5)__, that the ratio of the masses of elements in a ...
... particles, each of which was called a(n) __(1)__. The theory that such particles existed was supported, much later, by __(2)__, who proposed, in his law of __(3)__, that matter cannot be created or destroyed. Then __(4)__ proposed, in his law of __(5)__, that the ratio of the masses of elements in a ...
Chapter 3 – Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter - Hatboro
... thought of an _______ as something that could not be broken down and that could _________ with other elements to form __________. 1800’s combine ...
... thought of an _______ as something that could not be broken down and that could _________ with other elements to form __________. 1800’s combine ...
Chapter 30 - The Chemical Basis of Animal Life
... present in trace amounts include sodium, sulfur, manganese, magnesium, copper, iodine, iron, and chlorine. Elements are composed of units of matter called atoms. An atom (Gr. atomos, indivisible) is the smallest part of an element that can enter into a chemical reaction. Atoms vary in size, weight, ...
... present in trace amounts include sodium, sulfur, manganese, magnesium, copper, iodine, iron, and chlorine. Elements are composed of units of matter called atoms. An atom (Gr. atomos, indivisible) is the smallest part of an element that can enter into a chemical reaction. Atoms vary in size, weight, ...
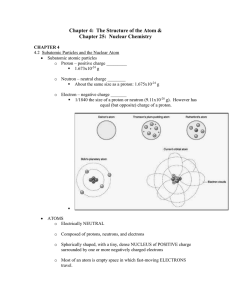
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... Characteristics or Chemical and Nuclear Reactions CHEMICAL 1. Occur when bonds are broken and formed 2. Atoms remain unchanged, though they may be rearranged 3. Involve only valence electrons 4. Associated with small energy changes 5. Reaction rate is influenced by temperature, pressure, concentra ...
... Characteristics or Chemical and Nuclear Reactions CHEMICAL 1. Occur when bonds are broken and formed 2. Atoms remain unchanged, though they may be rearranged 3. Involve only valence electrons 4. Associated with small energy changes 5. Reaction rate is influenced by temperature, pressure, concentra ...
atomic number
... Neutral atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Ions are charged atoms. -cations – have more protons than electrons and are positively charged -anions – have more electrons than protons and are negatively charged ...
... Neutral atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Ions are charged atoms. -cations – have more protons than electrons and are positively charged -anions – have more electrons than protons and are negatively charged ...
Periodic Table Jeopardy
... A substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. All atoms in this substance have the same atomic #. ...
... A substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. All atoms in this substance have the same atomic #. ...
Chemistry Fall Semester Review Sheet
... 7. Which phase is the most structured? The least? Solids are the most structured, Gases are the least 8. Label the following on the phase diagram on the right. Gas Liquid Solid Triple point Critical point Freezing ...
... 7. Which phase is the most structured? The least? Solids are the most structured, Gases are the least 8. Label the following on the phase diagram on the right. Gas Liquid Solid Triple point Critical point Freezing ...
The Atom - Magoffin County Schools
... • Over the years since Dalton’s time the idea of the atoms has been TESTED and REVISED many times as new information was obtained. ...
... • Over the years since Dalton’s time the idea of the atoms has been TESTED and REVISED many times as new information was obtained. ...
2 Types of Chemical Bonds
... • A chemical bond is formed when atoms of elements change the number of valence electrons they have to get 8 or 2 • A chemical bond combines elements together to form a compound! ...
... • A chemical bond is formed when atoms of elements change the number of valence electrons they have to get 8 or 2 • A chemical bond combines elements together to form a compound! ...
ATOMS - Mr. Deets
... Showed atoms could emit negative particles “plum pudding” model Electrons were embedded in a positively charged spherical cloud ...
... Showed atoms could emit negative particles “plum pudding” model Electrons were embedded in a positively charged spherical cloud ...
Unit 3 - MaxStudy.org
... • Alchemy – atoms of one element can change to another element • Robert Boyle – element is when can longer break down substances • Lavoisier – law of conservation of mass – mass is neither created nor destroyed • Proust – law of definite proportion – a given compound always contains exactly the same ...
... • Alchemy – atoms of one element can change to another element • Robert Boyle – element is when can longer break down substances • Lavoisier – law of conservation of mass – mass is neither created nor destroyed • Proust – law of definite proportion – a given compound always contains exactly the same ...
Tutorial - Brock physics
... orbital quantum number `. This rule is called a selection rule and states that ∆` = ±1. In other words, when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, the value of ` can only increase or decrease by one. The value of ` may not remain the same or increase or decrease by more than one. Acc ...
... orbital quantum number `. This rule is called a selection rule and states that ∆` = ±1. In other words, when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, the value of ` can only increase or decrease by one. The value of ` may not remain the same or increase or decrease by more than one. Acc ...
Atomic theory gallery walk
... Chemistry Unit 2 Topic 1 Atomic Structure Station 4—Lord Ernest Rutherford 1. What is the charge of an alpha particle?______________________________________________________ 2. Why is Rutherford’s experiment called the gold foil experiment? __________________________________ ...
... Chemistry Unit 2 Topic 1 Atomic Structure Station 4—Lord Ernest Rutherford 1. What is the charge of an alpha particle?______________________________________________________ 2. Why is Rutherford’s experiment called the gold foil experiment? __________________________________ ...
SCSD Physical Science 9th - Shenandoah Community Schools
... Atoms are composed of even smaller components (I,D,M) That have measurable properties Mass (I,D,M) Electrical charge (I,D,M) o Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons (I, D, M) • Understand the composition and size of atomic nucleus (I,D,M) o Is composed ...
... Atoms are composed of even smaller components (I,D,M) That have measurable properties Mass (I,D,M) Electrical charge (I,D,M) o Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons (I, D, M) • Understand the composition and size of atomic nucleus (I,D,M) o Is composed ...
ATOMS
... THOMPSON’S & MILLIKAN’S IDEAS ATOMS ARE IN FACT DIVISIBLE. ELECTRONS ARE PRESENT IN ATOMS OF ALL ELEMENTS. ONE OF THE ATOM’S FUNDAMENTAL PARTICLES IS NEGATIVE CHARGED. ATOMS ARE ELECTRICALLY NEUTRAL, SO THERE MUST BE A (+) CHARGE TO BALANCE OUT THE (–). ...
... THOMPSON’S & MILLIKAN’S IDEAS ATOMS ARE IN FACT DIVISIBLE. ELECTRONS ARE PRESENT IN ATOMS OF ALL ELEMENTS. ONE OF THE ATOM’S FUNDAMENTAL PARTICLES IS NEGATIVE CHARGED. ATOMS ARE ELECTRICALLY NEUTRAL, SO THERE MUST BE A (+) CHARGE TO BALANCE OUT THE (–). ...
The Atom PPT - WordPress.com
... • Rip or cut a standard piece of paper in half as many times as you can. Class Discussion: • How many cuts were we able to make? ____ • Do you think we could keep cutting the paper forever? Why or why not? • You would have to cut the paper in half around thirty-one (31) times to get to the size of a ...
... • Rip or cut a standard piece of paper in half as many times as you can. Class Discussion: • How many cuts were we able to make? ____ • Do you think we could keep cutting the paper forever? Why or why not? • You would have to cut the paper in half around thirty-one (31) times to get to the size of a ...
File - Mr. L`s Room
... Characterisitcs of Science: Each of these items were covered on the previous study guides: Safety, Scientific Method (Process), Experimental Design, Lab Equipment, and Measurements (including SI Units). S8P1a Atoms and Molecules: See Atoms and the Periodic Table as well. 1. Define atom, element, mol ...
... Characterisitcs of Science: Each of these items were covered on the previous study guides: Safety, Scientific Method (Process), Experimental Design, Lab Equipment, and Measurements (including SI Units). S8P1a Atoms and Molecules: See Atoms and the Periodic Table as well. 1. Define atom, element, mol ...
Basic Atomic Structure
... has a mass of 1 amu Neutron- neutral/no charge, in the nucleus, has a mass of 1 amu Electron- negative charge, towards the outside of the atom, has no mass ...
... has a mass of 1 amu Neutron- neutral/no charge, in the nucleus, has a mass of 1 amu Electron- negative charge, towards the outside of the atom, has no mass ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.