ite and - Smithycroft Secondary School
... I can explain what an atomic number and a mass number are in an atom I can state the mass of subatomic particles Look at the periodic table on page 8 of chemistry data book. Notice that each element has a number above it - this is its unique ATOMIC NUMBER. The atomic number used to be called the pro ...
... I can explain what an atomic number and a mass number are in an atom I can state the mass of subatomic particles Look at the periodic table on page 8 of chemistry data book. Notice that each element has a number above it - this is its unique ATOMIC NUMBER. The atomic number used to be called the pro ...
Warm-up #11 Jan. 25
... Bohr got closer than we had been so far, but it was still not right. He gave us the idea of energy levels for electrons. BUT his idea only worked for one atom ...
... Bohr got closer than we had been so far, but it was still not right. He gave us the idea of energy levels for electrons. BUT his idea only worked for one atom ...
The Atom - Fairfield Public Schools
... and electrons (-) is opposite but equal so when there is the same number of protons and electrons they cancel each other out and an atom has no overall charge. It is neutral! Atoms have a net charge of zero (neutral). Therefore: ...
... and electrons (-) is opposite but equal so when there is the same number of protons and electrons they cancel each other out and an atom has no overall charge. It is neutral! Atoms have a net charge of zero (neutral). Therefore: ...
Unit 1. Materials: Formulating Matter A. How do chemists describe
... 31. You melted and burned paraffin wax in the Lab Investigating Matter. Write the chemical formula of paraffin wax given its model below. (Note: The carbon and hydrogen atoms are smaller than in the key so that this molecule can fit on the page.) ...
... 31. You melted and burned paraffin wax in the Lab Investigating Matter. Write the chemical formula of paraffin wax given its model below. (Note: The carbon and hydrogen atoms are smaller than in the key so that this molecule can fit on the page.) ...
The Atom
... John Dalton 1803, ____________ studied experiments and concluded that the properties of matter could be atoms explained in terms of _____. ...
... John Dalton 1803, ____________ studied experiments and concluded that the properties of matter could be atoms explained in terms of _____. ...
IX Chemistry Chapter 03
... Daltons atomic theory assumed that atoms of elements are indivisible ' and that no particles smaller than atoms existed. But as the time passed new experimental facts led to the modification and extension of Dalton's atomic theory. Atom is a complex organization, composed of even smaller particles c ...
... Daltons atomic theory assumed that atoms of elements are indivisible ' and that no particles smaller than atoms existed. But as the time passed new experimental facts led to the modification and extension of Dalton's atomic theory. Atom is a complex organization, composed of even smaller particles c ...
Synopses - Mindfiesta
... The formal charge is a factor based on a pure covalent view of bonding in which electron pairs are shared equally by neighbouring atoms. Drawbacks of the octet theory : (1) It is clear that octet rule is based upon the chemical inertness of noble gases. However, some noble gases (for example xenon a ...
... The formal charge is a factor based on a pure covalent view of bonding in which electron pairs are shared equally by neighbouring atoms. Drawbacks of the octet theory : (1) It is clear that octet rule is based upon the chemical inertness of noble gases. However, some noble gases (for example xenon a ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... 1. Identify the scientist responsible for each of the following: (a) first to propose that matter is composed of atoms (b) identified matter as being composed of either elements or compounds (c) showed that mass is conserved during chemical reactions (d) proposed that compounds always contain the sa ...
... 1. Identify the scientist responsible for each of the following: (a) first to propose that matter is composed of atoms (b) identified matter as being composed of either elements or compounds (c) showed that mass is conserved during chemical reactions (d) proposed that compounds always contain the sa ...
Atomic Structure - Madison County Schools
... Electrons are negatively charged particles that surround the atom's nucleus. Electrons were discovered by J. J. Thomson in 1897. Electrons determine properties of the atom. Chemical reactions involve sharing or exchanging electrons. ...
... Electrons are negatively charged particles that surround the atom's nucleus. Electrons were discovered by J. J. Thomson in 1897. Electrons determine properties of the atom. Chemical reactions involve sharing or exchanging electrons. ...
Atomic Structure
... The atoms of any particular element always have the same number of protons. For example: hydrogen atoms always contain 1 proton carbon atoms always contain 6 protons magnesium atoms always contain 12 protons. ...
... The atoms of any particular element always have the same number of protons. For example: hydrogen atoms always contain 1 proton carbon atoms always contain 6 protons magnesium atoms always contain 12 protons. ...
ionization energies
... Noble Gas Configurations • The inner-most electrons of an element comprise what is known as a noble gas core. • At the close of each shell, you have a noble gas configuration. Noble gases are chemically inactive because they have completely filled shells. • Lithium, for example, has a two electron ...
... Noble Gas Configurations • The inner-most electrons of an element comprise what is known as a noble gas core. • At the close of each shell, you have a noble gas configuration. Noble gases are chemically inactive because they have completely filled shells. • Lithium, for example, has a two electron ...
Subatomic Particles
... Discovery of the Particles Purpose of the Neutron (cont.) • Neutrons also possess this strong force but with no charge. • This allows them to hold the nucleus together more tightly than the protons alone can accomplish. • As a nucleus gets larger, it gets more electric force pushing out the protons ...
... Discovery of the Particles Purpose of the Neutron (cont.) • Neutrons also possess this strong force but with no charge. • This allows them to hold the nucleus together more tightly than the protons alone can accomplish. • As a nucleus gets larger, it gets more electric force pushing out the protons ...
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... → The properties of specific atoms determine the properties of matter with those atoms. There are currently 91 naturally occurring elements and 20 man-made elements. 4.2 Indivisible: The Atomic Theory Greek philosophers were the first to propose explanations for what was observed in nature. – Surpri ...
... → The properties of specific atoms determine the properties of matter with those atoms. There are currently 91 naturally occurring elements and 20 man-made elements. 4.2 Indivisible: The Atomic Theory Greek philosophers were the first to propose explanations for what was observed in nature. – Surpri ...
for-unit-test-4-atomic-scientists-and-atoms
... • Aristotle, another Greek philosopher, disagreed with Democritus’s ideas. He believed that you would never end up with a particle that could not be cut. ...
... • Aristotle, another Greek philosopher, disagreed with Democritus’s ideas. He believed that you would never end up with a particle that could not be cut. ...
Glowing Tubes for Signs, Television Sets, and Computers
... case the electrons are directed onto a screen containing chemical compounds that glow when struck by fast-moving electrons. The use of various compounds that emit different colors when they are struck by the electrons makes color pictures possible on the screens of these CRTs. ...
... case the electrons are directed onto a screen containing chemical compounds that glow when struck by fast-moving electrons. The use of various compounds that emit different colors when they are struck by the electrons makes color pictures possible on the screens of these CRTs. ...
atom
... Isotopes, continued • Naming Isotopes To identify a specific isotope of an element, write the name of the element followed by a hyphen and the mass number of the isotope. • Calculating the Mass of an Element The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the naturally occ ...
... Isotopes, continued • Naming Isotopes To identify a specific isotope of an element, write the name of the element followed by a hyphen and the mass number of the isotope. • Calculating the Mass of an Element The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the naturally occ ...
CHAPTER 3 - THE ATOM answer key
... and the Law of Definite composition could only be explained if atoms existed. Wrote Dalton’s Atomic Theory, which was mostly right. 1. Matter is composed extremely small particles called atoms 2. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and ch ...
... and the Law of Definite composition could only be explained if atoms existed. Wrote Dalton’s Atomic Theory, which was mostly right. 1. Matter is composed extremely small particles called atoms 2. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and ch ...
Question to answer… - Rochester Century High School
... chemical reaction (what you start with) On the right side of the equation New substances created as a result of a chemical reaction (what you end up with) ...
... chemical reaction (what you start with) On the right side of the equation New substances created as a result of a chemical reaction (what you end up with) ...
Tendencies of ionic/atomic radii in the periodic table
... 1. The atomic radii increase down a group (e.g. first group 157 – 272 pm) and within the s and p blocks, decrease from left to right across a period (e.g. second period 157 – 64 pm). 2. The atomic radii for elements following the f block decrease because of the lanthanide contractions 3. All anions ...
... 1. The atomic radii increase down a group (e.g. first group 157 – 272 pm) and within the s and p blocks, decrease from left to right across a period (e.g. second period 157 – 64 pm). 2. The atomic radii for elements following the f block decrease because of the lanthanide contractions 3. All anions ...
unit plan template
... The properties of an element are determined by the composition of its atoms. As a result of this composition, elements can be classified into three main types—metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Culminating Assessment: Using the knowledge of atomic structure, build and label a 3D model of the atom. ...
... The properties of an element are determined by the composition of its atoms. As a result of this composition, elements can be classified into three main types—metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Culminating Assessment: Using the knowledge of atomic structure, build and label a 3D model of the atom. ...
Trends in the periodic table - Brigham Young University
... Ionization energy: the energy required to remove one electron from an atom • what do you think will happen with the ionization energy, based on what you have learned about atomic radius? ...
... Ionization energy: the energy required to remove one electron from an atom • what do you think will happen with the ionization energy, based on what you have learned about atomic radius? ...
Chapter 3 : Simple Bonding Theory Why do they make chemical
... possibilities of Lewis structure. 1. Structures with small FC (-2,+2 or less) are more likely. 2. Nonzero FCs on adjacent atoms are usually of opposite sign. 3. More electronegative atoms should have negative FC. 4. FCs of opposite signs separated by large distance are unlikely. 5. The largest sum o ...
... possibilities of Lewis structure. 1. Structures with small FC (-2,+2 or less) are more likely. 2. Nonzero FCs on adjacent atoms are usually of opposite sign. 3. More electronegative atoms should have negative FC. 4. FCs of opposite signs separated by large distance are unlikely. 5. The largest sum o ...
Chemistry can be defined as the study of the composition, structure
... Phosphorous is one of the most abundant minerals in the human body, second only to calcium. This essential mineral is required for the healthy formation of bones and teeth, and is necessary for our bodies to process many of the foods that we eat. It is also a part of the body's energy storage system ...
... Phosphorous is one of the most abundant minerals in the human body, second only to calcium. This essential mineral is required for the healthy formation of bones and teeth, and is necessary for our bodies to process many of the foods that we eat. It is also a part of the body's energy storage system ...
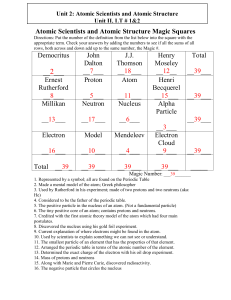
Atomic Scientists and Atomic Structure Magic Squares
... 5. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom. (Not a fundamental particle) 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons. 7. Credited with the first atomic theory model of the atom which had four main postulates. 8. Discovered the nucleus using his gold foil experiment. 9 ...
... 5. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom. (Not a fundamental particle) 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons. 7. Credited with the first atomic theory model of the atom which had four main postulates. 8. Discovered the nucleus using his gold foil experiment. 9 ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.