Elements, Isotopes, and Ions
... – Is the total mass of a certain ISOTOPE of an element. 1. How to calculate mass #: # of protons + # of neutrons = mass # 2. How to calculate # of neutrons from mass #: (Mass #) ...
... – Is the total mass of a certain ISOTOPE of an element. 1. How to calculate mass #: # of protons + # of neutrons = mass # 2. How to calculate # of neutrons from mass #: (Mass #) ...
What are atoms? Notes - Riverdale Middle School
... Scientific method is a series of steps that scientists use when performing an experiment. Hypothesis is an explanation that can be tested with a scientific investigation. Data are information that is gathered during an investigation. Data can be recorded in the form of descriptions, tables, charts, ...
... Scientific method is a series of steps that scientists use when performing an experiment. Hypothesis is an explanation that can be tested with a scientific investigation. Data are information that is gathered during an investigation. Data can be recorded in the form of descriptions, tables, charts, ...
File
... The law of conservation of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, it is conserved. ...
... The law of conservation of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, it is conserved. ...
Chapter Two:
... When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers. ...
... When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers. ...
Document
... Four electron pairs around an atom assume tetrahedral arrangement. When there are not enough electrons for single bonds the molecule forms multiple bonds and the structure differs. VSEPR theory treats each multiple bond as a single electron group, because it occupies roughly the same region of space ...
... Four electron pairs around an atom assume tetrahedral arrangement. When there are not enough electrons for single bonds the molecule forms multiple bonds and the structure differs. VSEPR theory treats each multiple bond as a single electron group, because it occupies roughly the same region of space ...
100 Greatest Discoveries - Mr-Hubeny
... Einstein recognizes that light always travels at a constant speed, no matter the speed of the measurer. What did the ancient people think the universe was made of? Earth, air, fire, and water What was Newton’s main contribution to the understanding of light? He found out that white light is really m ...
... Einstein recognizes that light always travels at a constant speed, no matter the speed of the measurer. What did the ancient people think the universe was made of? Earth, air, fire, and water What was Newton’s main contribution to the understanding of light? He found out that white light is really m ...
Atomic Number - Manhasset Schools
... The protons and neutrons have a much greater mass than the electrons. ...
... The protons and neutrons have a much greater mass than the electrons. ...
atoms - Moodle
... If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. When two or more compounds exist from the same elements, they can not h ...
... If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. When two or more compounds exist from the same elements, they can not h ...
Inside the Atom
... While studying the atom, Rutherford discovered that the number of protons he could detect coming from atoms often did not seem to match the mass of the atom. This led him to propose that there was another particle inside the atom which also had mass but no charge. He could find no experimental proof ...
... While studying the atom, Rutherford discovered that the number of protons he could detect coming from atoms often did not seem to match the mass of the atom. This led him to propose that there was another particle inside the atom which also had mass but no charge. He could find no experimental proof ...
Introduction to the Atom
... • The masses of all other atoms are compared with the mass of this type of carbon atom. According to this definition, an atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon12 atom. ...
... • The masses of all other atoms are compared with the mass of this type of carbon atom. According to this definition, an atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon12 atom. ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _A__ 43) Which of the following occurs in an ionic bond? (electrostatic forces between charged ions) a. Oppositely charged ions attract. c. Two atoms share more than two electrons. b. Two atoms share two electrons. d. Like-charged ions attract. _A__ 44) Which of the following pairs of elements is mo ...
... _A__ 43) Which of the following occurs in an ionic bond? (electrostatic forces between charged ions) a. Oppositely charged ions attract. c. Two atoms share more than two electrons. b. Two atoms share two electrons. d. Like-charged ions attract. _A__ 44) Which of the following pairs of elements is mo ...
Second Semester Notes 09-10
... Nonmetals – everything to the right of the stairstep; includes hydrogen ...
... Nonmetals – everything to the right of the stairstep; includes hydrogen ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
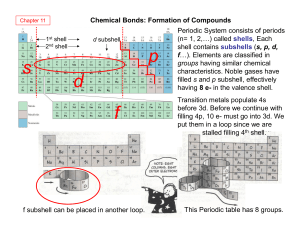
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
History Atomic Theory
... and how it relates to the study of chemistry; be aware of how it differs from the currently accepted modern Atomic Theory. • Know the basic details of how each subatomic particle was discovered, and what information was determined about protons, neutrons, and electrons in these experiments ...
... and how it relates to the study of chemistry; be aware of how it differs from the currently accepted modern Atomic Theory. • Know the basic details of how each subatomic particle was discovered, and what information was determined about protons, neutrons, and electrons in these experiments ...
CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, IONS, AND COMPOUNDS
... CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, IONS, AND COMPOUNDS (Topics to Review) Early Models Democritus (462-370 B.C.): proposed that all matter was made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atomos (meaning “not to cut) or atoms. Empedocles (490-430 B.C.): suggested all matter was composed of four basic elements: air, ...
... CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, IONS, AND COMPOUNDS (Topics to Review) Early Models Democritus (462-370 B.C.): proposed that all matter was made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atomos (meaning “not to cut) or atoms. Empedocles (490-430 B.C.): suggested all matter was composed of four basic elements: air, ...
SLE133 – “Chemistry in Our World” Summary Notes Week 1
... A chemical change is a change that affects the chemical makeup of a substance. A reaction occurs during a chemical change and the reacting compounds are changed into new compounds. A chemical change cannot be reversed. Eg: 1. Frying an egg (bonds break and new bonds form, cannot change the fried egg ...
... A chemical change is a change that affects the chemical makeup of a substance. A reaction occurs during a chemical change and the reacting compounds are changed into new compounds. A chemical change cannot be reversed. Eg: 1. Frying an egg (bonds break and new bonds form, cannot change the fried egg ...
Intro to Chemistry
... other matter; end matter is different than original matter and has unique physical properties ...
... other matter; end matter is different than original matter and has unique physical properties ...
Unit Test: Atomic Structure
... A. Methane is a compound of carbon and hydrogen. A sample contains 1.2 g of carbon and 0.40 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in methane? B. Benzene is another compound of carbon and hydrogen. A 78 g sample of bnzene contains 72 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in benzene? 6 ...
... A. Methane is a compound of carbon and hydrogen. A sample contains 1.2 g of carbon and 0.40 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in methane? B. Benzene is another compound of carbon and hydrogen. A 78 g sample of bnzene contains 72 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in benzene? 6 ...
Chemical Formulas and Composition Stoichiometry
... among elements in compounds (composition stoichiometry) and among substances as they undergo chemical changes (reaction stoichiometry). ...
... among elements in compounds (composition stoichiometry) and among substances as they undergo chemical changes (reaction stoichiometry). ...
electrons - River Dell Regional School District
... Should include He but helium has the properties of the noble gases. - its outer shell is filled with the maximum number of electrons allowed for the first shell (2) ...
... Should include He but helium has the properties of the noble gases. - its outer shell is filled with the maximum number of electrons allowed for the first shell (2) ...
Chapter 3 - Whitwell High School
... that the iron forms in the liquid state. A certain welding operation requires at least 86.0 g of Fe be produced. What is the minimum mass in grams of Fe2O3 needed? How much Al2O3 is produced? ? (MM of Fe2O3 = 159.489 g/mol, MM of Al2O3 = 101.961 g/mol) ...
... that the iron forms in the liquid state. A certain welding operation requires at least 86.0 g of Fe be produced. What is the minimum mass in grams of Fe2O3 needed? How much Al2O3 is produced? ? (MM of Fe2O3 = 159.489 g/mol, MM of Al2O3 = 101.961 g/mol) ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.