Chapter 4- Atomic Structure
... If an atom gains enough energy, one of its electrons can move to an orbital with a higher energy level. This configuration is referred to as an excited state. At an excited state the atom is less stable than at ground state. Eventually the electron loses energy and the atom returns to the ground ...
... If an atom gains enough energy, one of its electrons can move to an orbital with a higher energy level. This configuration is referred to as an excited state. At an excited state the atom is less stable than at ground state. Eventually the electron loses energy and the atom returns to the ground ...
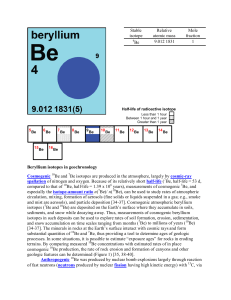
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... cosmic rays – extremely high-energy radiation, mainly originating outside the Solar System, consisting of one or more charged particles, such as protons, alpha particles, and larger atomic nuclei. [return] cosmogenic – produced by the interaction of Earth materials (soil, rock, and atmosphere) and m ...
... cosmic rays – extremely high-energy radiation, mainly originating outside the Solar System, consisting of one or more charged particles, such as protons, alpha particles, and larger atomic nuclei. [return] cosmogenic – produced by the interaction of Earth materials (soil, rock, and atmosphere) and m ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1 The Atom
... • An ______is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same element. • Scientists now know that atoms are made of even smaller particles, but the atom is the smallest unit that has the chemical properties of an element. • There are many types of atoms that combi ...
... • An ______is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same element. • Scientists now know that atoms are made of even smaller particles, but the atom is the smallest unit that has the chemical properties of an element. • There are many types of atoms that combi ...
Atomic Structure Guided Notes
... The ___________________ of an element contain equal numbers of protons and electrons and so have no overall charge, so if you can find it on the Periodic Table, it means it has a charge of __________________!!! Atomic Number The atoms of any particular element always contain the same number of _ ...
... The ___________________ of an element contain equal numbers of protons and electrons and so have no overall charge, so if you can find it on the Periodic Table, it means it has a charge of __________________!!! Atomic Number The atoms of any particular element always contain the same number of _ ...
Parts of the Atom - Dalton Local Schools
... a. Two protons push each other away or repel. b. Two protons push each other away or repel. c. Protons and electrons are attracted to each other because the have opposite charges. d. All three of the above statements are true. e. All of the answers are false. ...
... a. Two protons push each other away or repel. b. Two protons push each other away or repel. c. Protons and electrons are attracted to each other because the have opposite charges. d. All three of the above statements are true. e. All of the answers are false. ...
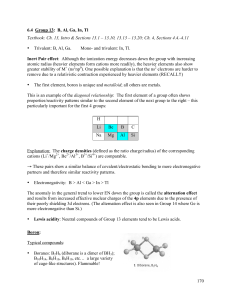
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
CHM 130 Final Exam Review Chapter 1 Scientific method Theory
... Oxidation and reduction, the agents Writing products Chapter 16 Increasing the rate of a reaction Energy profiles Chapter 9 The mole and Avogadro’s number Molar mass Converting between grams and moles and atoms/molecules Molar volume Converting between liters and moles at STP Chapter 10 Mole mole ra ...
... Oxidation and reduction, the agents Writing products Chapter 16 Increasing the rate of a reaction Energy profiles Chapter 9 The mole and Avogadro’s number Molar mass Converting between grams and moles and atoms/molecules Molar volume Converting between liters and moles at STP Chapter 10 Mole mole ra ...
Development of Atomic Theory
... developed by (7). It was later proposed that the atom is not indivisible, but is made These up of smaller particles, each of which is called a(n) (8). particles include the negatively charged 0, discovered by (10);the positively charged ( ...
... developed by (7). It was later proposed that the atom is not indivisible, but is made These up of smaller particles, each of which is called a(n) (8). particles include the negatively charged 0, discovered by (10);the positively charged ( ...
4.Chemical bonding and Molecular Structure
... electrons, the covalent bond between them is called a double bond. e.g O2 If two atoms share three electron pairs of electrons, the covalent bond between them is called a double bond. e.g N2 ...
... electrons, the covalent bond between them is called a double bond. e.g O2 If two atoms share three electron pairs of electrons, the covalent bond between them is called a double bond. e.g N2 ...
Atoms FlexBook Atoms FlexBook
... orbiting the nucleus and German scientist Max Planck’s idea of a quantum, which Planck published in 1901. A quantum (plural, quanta) is the minimum amount of energy that can be absorbed or released by matter. It is a discrete, or distinct, amount of energy. If energy were water and you wanted to add ...
... orbiting the nucleus and German scientist Max Planck’s idea of a quantum, which Planck published in 1901. A quantum (plural, quanta) is the minimum amount of energy that can be absorbed or released by matter. It is a discrete, or distinct, amount of energy. If energy were water and you wanted to add ...
atomic number - Teacher Pages
... These atoms typically gain or share two atoms in a reaction. The Oxygen we breath is O2 and Ozone = O3. Group 17 is known as the Halogen Family. All but one of these elements in the Halogen Family are nonmetals. A halogen atom has 7 valence electrons and typically gains or shares one electron when i ...
... These atoms typically gain or share two atoms in a reaction. The Oxygen we breath is O2 and Ozone = O3. Group 17 is known as the Halogen Family. All but one of these elements in the Halogen Family are nonmetals. A halogen atom has 7 valence electrons and typically gains or shares one electron when i ...
homework_#1_10
... 1. Tiny Tike has decided to make 288 tricycles a day. How many tricycle seats, wheels, and pedals are needed? ...
... 1. Tiny Tike has decided to make 288 tricycles a day. How many tricycle seats, wheels, and pedals are needed? ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Molecules
... The beauty of this is that since one mass id divided by another mass, the units cancel out, and the Atomic Mass ratio is a unitless number Using these ratios we can make a mass system that relates the mass of all the atoms on the periodic table to any other atom. All we have to do is to chose one to ...
... The beauty of this is that since one mass id divided by another mass, the units cancel out, and the Atomic Mass ratio is a unitless number Using these ratios we can make a mass system that relates the mass of all the atoms on the periodic table to any other atom. All we have to do is to chose one to ...
Atomic Theory Lecture Notes
... • Matter is composed of atoms too small to be seen. • Believed atoms could not be created, destroyed or further divided. • Atoms are solid and homogeneous with empty space between them. • Different atoms have different sizes and shapes which determine the properties of matter. ...
... • Matter is composed of atoms too small to be seen. • Believed atoms could not be created, destroyed or further divided. • Atoms are solid and homogeneous with empty space between them. • Different atoms have different sizes and shapes which determine the properties of matter. ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... Look at the atomic weights of a few different elements on your periodic table. Do you notice that very few of the elements have atomic weights that are close to being nice whole numbers? Do you know why this is? After all, for our purposes, the mass of both the proton and the neutron are almost exac ...
... Look at the atomic weights of a few different elements on your periodic table. Do you notice that very few of the elements have atomic weights that are close to being nice whole numbers? Do you know why this is? After all, for our purposes, the mass of both the proton and the neutron are almost exac ...
Chapter_5_Notes_Atom - Chemistry
... Dalton proposed that: An element is composed of tiny, indivisible, indestructible particles called atoms. All atoms of an element are identical and have the same properties. Atoms of different elements combine to form compounds. Compounds contain atoms in small whole number ratios. Atoms c ...
... Dalton proposed that: An element is composed of tiny, indivisible, indestructible particles called atoms. All atoms of an element are identical and have the same properties. Atoms of different elements combine to form compounds. Compounds contain atoms in small whole number ratios. Atoms c ...
Atomic Timeline There are small, negatively charged particles inside
... Atomic Timeline The table below contains a number of statements connected to major discoveries in the development of the atomic theory. ...
... Atomic Timeline The table below contains a number of statements connected to major discoveries in the development of the atomic theory. ...
Intro To Atomic Theory
... The molar mass of Cl-35 is 34.968852g and Cl-37 is 36.965903. If 75.77% of chlorine is Cl-35 and 24.23% of chlorine is Cl-37, what is the average molar mass of the chlorine atom in such a mixture? Take the percent average Mass of Cl-35= 75.77% x 34.968852 = 26.4959 Mass of Cl-37= 24.23% x 36.965803 ...
... The molar mass of Cl-35 is 34.968852g and Cl-37 is 36.965903. If 75.77% of chlorine is Cl-35 and 24.23% of chlorine is Cl-37, what is the average molar mass of the chlorine atom in such a mixture? Take the percent average Mass of Cl-35= 75.77% x 34.968852 = 26.4959 Mass of Cl-37= 24.23% x 36.965803 ...
The Structure of Matter
... The concept of matter was first introduced by Aristotle as “something out of which that has the capacity or potentiality to be.”[1] Another way the Greeks explained what matter is “the immense variety of different substances forming the world results from a combination of comparatively few simple el ...
... The concept of matter was first introduced by Aristotle as “something out of which that has the capacity or potentiality to be.”[1] Another way the Greeks explained what matter is “the immense variety of different substances forming the world results from a combination of comparatively few simple el ...
Chp 4 Review - MagicSquare
... Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom The tiny positive core of an atom; contains proton ...
... Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom The tiny positive core of an atom; contains proton ...
Condition - Future Website of mrbentley2
... 6. Draw the Lewis dot structures of the following ionic compounds. Then, using a different colored pen, show how one element “steals” the other’s electrons, resulting in two ions. (Hint: Some of the compounds may require multiple numbers of one type of element - be sure to draw in the extra element ...
... 6. Draw the Lewis dot structures of the following ionic compounds. Then, using a different colored pen, show how one element “steals” the other’s electrons, resulting in two ions. (Hint: Some of the compounds may require multiple numbers of one type of element - be sure to draw in the extra element ...
Name Magic Square Atomic Structure and Theory Directions: Put the
... Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom The tiny positive core of an atom; contains proton ...
... Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom The tiny positive core of an atom; contains proton ...
Name Magic Square Atomic Structure and Theory
... Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom The tiny positive core of an atom; contains proton ...
... Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom The tiny positive core of an atom; contains proton ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.