Incorrect…try again
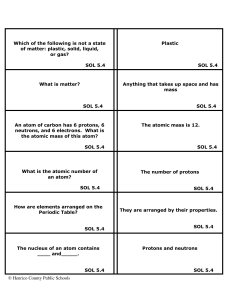
... • The protons (atomic #) indicate the element name: • 12 protons = Magnesium • The Mass # is found by adding the protons and neutrons. You only used the protons (12). You must add the neutrons (8) to this number. ...
... • The protons (atomic #) indicate the element name: • 12 protons = Magnesium • The Mass # is found by adding the protons and neutrons. You only used the protons (12). You must add the neutrons (8) to this number. ...
Amidine: Structure, Reactivity and Complexation Behaviour
... Chemical species containing the N-H bond form an important class of compounds with a large variety of applications, from pharmaceutical agents[27-29] to toxic substances[30,31]. These compounds may be found in the building blocks of bio-molecules as well as in a large number of chemical industry pro ...
... Chemical species containing the N-H bond form an important class of compounds with a large variety of applications, from pharmaceutical agents[27-29] to toxic substances[30,31]. These compounds may be found in the building blocks of bio-molecules as well as in a large number of chemical industry pro ...
ap 2005 chemistry_b scoring guidelines - AP Central
... mass of the sample after heating is less than the mass before heating. Explain. KAl(SO4)2·12H2O(s) is a hydrate. For the mass of the sample to be less after heating, the water of hydration must be lost. Heating the sample of KAl(SO4)2·12H2O(s) crystals will drive off the water first, decreasing the ...
... mass of the sample after heating is less than the mass before heating. Explain. KAl(SO4)2·12H2O(s) is a hydrate. For the mass of the sample to be less after heating, the water of hydration must be lost. Heating the sample of KAl(SO4)2·12H2O(s) crystals will drive off the water first, decreasing the ...
231. - Department of Chemistry
... (c-C5H5)Fe⫹ in He bath gas at 0.35 Torr with a variety of inorganic ligands containing hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Previous measurements in our laboratory have shown that the presence of a cyclopentadienyl ligand has a dramatic effect on the reactivity of Fe⫹. For example, we have shown ...
... (c-C5H5)Fe⫹ in He bath gas at 0.35 Torr with a variety of inorganic ligands containing hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Previous measurements in our laboratory have shown that the presence of a cyclopentadienyl ligand has a dramatic effect on the reactivity of Fe⫹. For example, we have shown ...
Matter Flashcards 5 - Henrico County Public Schools
... No, the properties of the compound are different from those of the elements that make it up. For instance, Sodium (Na) is an explosive substance and Chlorine (Cl) is a poisonous gas, but combined together, they make NaCl, or table salt, which is not poisonous or explosive. SOL 5.4 ...
... No, the properties of the compound are different from those of the elements that make it up. For instance, Sodium (Na) is an explosive substance and Chlorine (Cl) is a poisonous gas, but combined together, they make NaCl, or table salt, which is not poisonous or explosive. SOL 5.4 ...
Untitled
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without either the prior written permission of the publisher or a licence permitting restricted ...
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without either the prior written permission of the publisher or a licence permitting restricted ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions - An Introduction to Chemistry
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. When fluorine atoms are combined with atoms of other elements, their oxidation number is ‒1. When oxygen atoms are combined with atoms of other elements, their oxidation number is ‒2, except in peroxides, such as hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 ...
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. When fluorine atoms are combined with atoms of other elements, their oxidation number is ‒1. When oxygen atoms are combined with atoms of other elements, their oxidation number is ‒2, except in peroxides, such as hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 ...
Chemistry - College Catalog
... performance on the mathematics/calculus and chemistry placement tests. Enrollment by placement only. The first two courses in this sequence meet the general education requirement in the physical sciences. This three-quarter sequence is a comprehensive survey of modern descriptive, inorganic, and phy ...
... performance on the mathematics/calculus and chemistry placement tests. Enrollment by placement only. The first two courses in this sequence meet the general education requirement in the physical sciences. This three-quarter sequence is a comprehensive survey of modern descriptive, inorganic, and phy ...
Chapter 22 - 2012 Book Archive
... Group 13 is the first group to span the dividing line between metals and nonmetals, so its chemistry is more diverse than that of groups 1 and 2, which include only metallic elements. Except for the lightest element (boron), the group 13 elements are all relatively electropositive; that is, they ten ...
... Group 13 is the first group to span the dividing line between metals and nonmetals, so its chemistry is more diverse than that of groups 1 and 2, which include only metallic elements. Except for the lightest element (boron), the group 13 elements are all relatively electropositive; that is, they ten ...
Chapter 4: Experimental Techniques
... applications of some of these methods are detailed. We focus on the techniques used to determine the identity and spectroscopic properties of a compound, and will not be concerned with determining the amounts of trace elements or compounds in, for example, water and air samples.† Analytical methods ...
... applications of some of these methods are detailed. We focus on the techniques used to determine the identity and spectroscopic properties of a compound, and will not be concerned with determining the amounts of trace elements or compounds in, for example, water and air samples.† Analytical methods ...
Midterm 3 NY Regents Practice Questions
... b. 15 mL of HCl(aq) at 20 C d. 15 mL of H2O(l) at 30oC ____ 71. Which sample at STP has the same number of molecules as 5 liters of NO2(g) at STP? a. 5 grams of H2(g) c. 5 moles of O2(g) b. 5 liters of CH4(g) d. 5 x 1023 molecules of CO2(g) ____ 72. Under which conditions of temperature and pressur ...
... b. 15 mL of HCl(aq) at 20 C d. 15 mL of H2O(l) at 30oC ____ 71. Which sample at STP has the same number of molecules as 5 liters of NO2(g) at STP? a. 5 grams of H2(g) c. 5 moles of O2(g) b. 5 liters of CH4(g) d. 5 x 1023 molecules of CO2(g) ____ 72. Under which conditions of temperature and pressur ...
CSEC Chemistry Revision Guide Answers.indd
... 5. The magnesium atoms are packed tightly together in rows to form a metal lattice and their valence electrons become delocalised. This forms positive magnesium cations and a sea of mobile electrons. The metal lattice is held together by the electrostatic forces of attraction between the delocalised ...
... 5. The magnesium atoms are packed tightly together in rows to form a metal lattice and their valence electrons become delocalised. This forms positive magnesium cations and a sea of mobile electrons. The metal lattice is held together by the electrostatic forces of attraction between the delocalised ...
CHAPTER 23 THE TRANSITION ELEMENTS AND THEIR
... a) One would expect that the elements would increase in size as they increase in mass from Period 5 to 6. Because 14 additional elements lie between Periods 5 and 6, the effective nuclear charge increases significantly. As effective charge increases, the atomic size decreases or “contracts.” This ef ...
... a) One would expect that the elements would increase in size as they increase in mass from Period 5 to 6. Because 14 additional elements lie between Periods 5 and 6, the effective nuclear charge increases significantly. As effective charge increases, the atomic size decreases or “contracts.” This ef ...
Chapter 4 Elements and the Periodic Table
... Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain six protons and six electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon12 is the most common isotope. ...
... Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain six protons and six electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon12 is the most common isotope. ...
Chapter 4 Elements and the Periodic Table
... Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain six protons and six electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon12 is the most common isotope. ...
... Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain six protons and six electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon12 is the most common isotope. ...
Chemical Reactions
... Sometimes you are given quantities of more than one reactant, and asked to calculate the amount of product formed. The quantities of reactants might be such that both react completely, or one might react completely, and the other(s) might be in excess. These are called limiting reagent problems, sin ...
... Sometimes you are given quantities of more than one reactant, and asked to calculate the amount of product formed. The quantities of reactants might be such that both react completely, or one might react completely, and the other(s) might be in excess. These are called limiting reagent problems, sin ...
Review - gbschemphys
... Suppose that a student wishes to solve a problem involving the determination of the mass of product produced if a given amount of moles of reactant was reacted. Which quantities would be essential in order to solve such a problem? Bubble in all that apply - but only those that are essential to this ...
... Suppose that a student wishes to solve a problem involving the determination of the mass of product produced if a given amount of moles of reactant was reacted. Which quantities would be essential in order to solve such a problem? Bubble in all that apply - but only those that are essential to this ...
Defining the Atom
... The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. – 370 B.C.) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms (from the Greek word “atomos”) He ...
... The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. – 370 B.C.) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms (from the Greek word “atomos”) He ...
A different quantum physics of the atom had been found
... served to ingrain in him a profound respect for classical tradition. His boo~ Nature and the Greeks, published in I 948, is an elegant exposition ol ancient physical theories and their relevance. Schrodinger developed a I ift• long interest in philosophy, which would lead to more than casual reading ...
... served to ingrain in him a profound respect for classical tradition. His boo~ Nature and the Greeks, published in I 948, is an elegant exposition ol ancient physical theories and their relevance. Schrodinger developed a I ift• long interest in philosophy, which would lead to more than casual reading ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • By definition, this is the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol) – The molar mass of an element is the mass number for the element that we find on the periodic table – The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol) Stoichiometry ...
... • By definition, this is the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol) – The molar mass of an element is the mass number for the element that we find on the periodic table – The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol) Stoichiometry ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical
... • By definition, this is the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol) – The molar mass of an element is the mass number for the element that we find on the periodic table – The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol) Stoichiometry ...
... • By definition, this is the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol) – The molar mass of an element is the mass number for the element that we find on the periodic table – The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol) Stoichiometry ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.