Slide 1 ______
... Energy continued Energy can change form. Chemical potential energy in gasoline becomes mechanical energy driving the pistons and radiant energy in heat, Chemical energy in foods are converted to usable mechanical energy in our bodies or stored as other forms of potential energy. ...
... Energy continued Energy can change form. Chemical potential energy in gasoline becomes mechanical energy driving the pistons and radiant energy in heat, Chemical energy in foods are converted to usable mechanical energy in our bodies or stored as other forms of potential energy. ...
File - Meissnerscience.com
... a water solution and has _____ molecules incorporated into their crystal structure. Hydrates have a ________________ of water molecules ___________ bonded to each _________________. Compounds that have no water molecules incorporated into them are called _________________ to distinguish them from th ...
... a water solution and has _____ molecules incorporated into their crystal structure. Hydrates have a ________________ of water molecules ___________ bonded to each _________________. Compounds that have no water molecules incorporated into them are called _________________ to distinguish them from th ...
Atomic mass
... Distinguishing Among Atoms • The atomic number (Z) identifies the atom – protons in the nucleus ...
... Distinguishing Among Atoms • The atomic number (Z) identifies the atom – protons in the nucleus ...
C:\usb key\sch3u\unit 1\chapter 2 test answers.wpd
... In a co-ordinate bond, both electrons come from the same atom. 2) Draw a Lewis diagram for the molecule HO. Label one of each of the following types of electrons: lone pair, bonded pair, and unpaired (3 points). ...
... In a co-ordinate bond, both electrons come from the same atom. 2) Draw a Lewis diagram for the molecule HO. Label one of each of the following types of electrons: lone pair, bonded pair, and unpaired (3 points). ...
Synthesis, Crystal-Structure Determination and Magnetic Properties
... radiation, linear position-sensitive detector, range of measurement: 8-110° in 2θ with individual steps of 0.01°) with a flatsample (CoNCN) and a glass-capillary (0.3 mm diameter) holder (NiNCN). The X-ray powder diagrams were indexed using primitive hexagonal unit cells, and the primary structural ...
... radiation, linear position-sensitive detector, range of measurement: 8-110° in 2θ with individual steps of 0.01°) with a flatsample (CoNCN) and a glass-capillary (0.3 mm diameter) holder (NiNCN). The X-ray powder diagrams were indexed using primitive hexagonal unit cells, and the primary structural ...
Electron Configuration
... • Orbital- is a region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found. • An electron cloud is a good approximation of how electrons behave in their orbitals • The level in which an electron has the least energy—the lowest energy level—has only one orbital. Higher energy levels h ...
... • Orbital- is a region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found. • An electron cloud is a good approximation of how electrons behave in their orbitals • The level in which an electron has the least energy—the lowest energy level—has only one orbital. Higher energy levels h ...
Atomic Theory: Skeleton Notes
... explained ________________ ______ (e.g. The maximum number of electrons in each level is given by the number of elements in each period of the periodic table; that is, 2, 8, 8, 18 etc.) completely explained the atomic spectrum for _______________ (could not completely explain the atomic spectra ...
... explained ________________ ______ (e.g. The maximum number of electrons in each level is given by the number of elements in each period of the periodic table; that is, 2, 8, 8, 18 etc.) completely explained the atomic spectrum for _______________ (could not completely explain the atomic spectra ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... Periodic properties (e.g., metal/nonmetal/metalloid behavior, electrical/heat conductivity, electronegativity, electron affinity, ionization energy, atomic/covalent/ionic radius) 2e. Compare the properties of compounds according to their type of bonding. (DOK 1) Covalent, ionic, and metallic bon ...
... Periodic properties (e.g., metal/nonmetal/metalloid behavior, electrical/heat conductivity, electronegativity, electron affinity, ionization energy, atomic/covalent/ionic radius) 2e. Compare the properties of compounds according to their type of bonding. (DOK 1) Covalent, ionic, and metallic bon ...
Chemistry Syllabus - Madison County Schools
... Periodic properties (e.g., metal/nonmetal/metalloid behavior, electrical/heat conductivity, electronegativity, electron affinity, ionization energy, atomic/covalent/ionic radius) 2e. Compare the properties of compounds according to their type of bonding. (DOK 1) Covalent, ionic, and metallic bon ...
... Periodic properties (e.g., metal/nonmetal/metalloid behavior, electrical/heat conductivity, electronegativity, electron affinity, ionization energy, atomic/covalent/ionic radius) 2e. Compare the properties of compounds according to their type of bonding. (DOK 1) Covalent, ionic, and metallic bon ...
Many-electron atoms
... With K and Ca, successive electrons go into the 4s orbital, and Ca has the electronic configuration [Ar]4s2. At this point, the pattern changes. To a first approximation, the 10 electrons for the next 10 elements (Sc to Zn) enter the 3d orbitals, giving Zn the electronic configuration 4s23d10. Ther ...
... With K and Ca, successive electrons go into the 4s orbital, and Ca has the electronic configuration [Ar]4s2. At this point, the pattern changes. To a first approximation, the 10 electrons for the next 10 elements (Sc to Zn) enter the 3d orbitals, giving Zn the electronic configuration 4s23d10. Ther ...
Chapter 3 Molecules Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical
... elements found in the compound, compound the numbers of their atoms, the order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment. They do not directly describe the three-dimensional shape but an experienced chemist can make a good shape, guess at it. use lines to represent covalent bonds Each lin ...
... elements found in the compound, compound the numbers of their atoms, the order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment. They do not directly describe the three-dimensional shape but an experienced chemist can make a good shape, guess at it. use lines to represent covalent bonds Each lin ...
Openstax - Chemistry - Answer Key
... spheres and two purple spheres. This violates Dalton’s postulate that that atoms are not created during a chemical change, but are merely redistributed. 3. This statement violates Dalton’s fourth postulate: In a given compound, the numbers of atoms of each type (and thus also the percentage) always ...
... spheres and two purple spheres. This violates Dalton’s postulate that that atoms are not created during a chemical change, but are merely redistributed. 3. This statement violates Dalton’s fourth postulate: In a given compound, the numbers of atoms of each type (and thus also the percentage) always ...
ch02 lecture 7e
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any other element. Co ...
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any other element. Co ...
13.1 Fundamental Particles and Forces
... What if there are Almost all elements have one or more isotopes that are stable. too many “Stable” means the nucleus stays together. For complex reasons, the neutrons? nucleus of an atom becomes unstable if it contains too many or too few neutrons relative to the number of protons. If the nucleus is ...
... What if there are Almost all elements have one or more isotopes that are stable. too many “Stable” means the nucleus stays together. For complex reasons, the neutrons? nucleus of an atom becomes unstable if it contains too many or too few neutrons relative to the number of protons. If the nucleus is ...
what`s ahead - Al Akhawayn University
... because electrons contribute only a very small fraction of an atom’s mass they probably were responsible for an equally small fraction of the atom’s size. He proposed that the atom consisted of a uniform positive sphere of matter in which the electrons were embedded like raisins in a pudding or seed ...
... because electrons contribute only a very small fraction of an atom’s mass they probably were responsible for an equally small fraction of the atom’s size. He proposed that the atom consisted of a uniform positive sphere of matter in which the electrons were embedded like raisins in a pudding or seed ...
Chemistry - Edgbarrow School
... I can name the main I can represent chemical reactions out simple techniques for changes of state, there are Periodic Table was materials are more reactive elements that make up the using word equations separating mixtures energy changes developed by Mendeleev than others composition of the Earth ...
... I can name the main I can represent chemical reactions out simple techniques for changes of state, there are Periodic Table was materials are more reactive elements that make up the using word equations separating mixtures energy changes developed by Mendeleev than others composition of the Earth ...
Green Chemistry: Principles and Practice
... – Treatment for Type II diabetes, controls blood sugar without significant side effects – Transaminase-based process with broad applications for converting ketones to chiral amines F ...
... – Treatment for Type II diabetes, controls blood sugar without significant side effects – Transaminase-based process with broad applications for converting ketones to chiral amines F ...
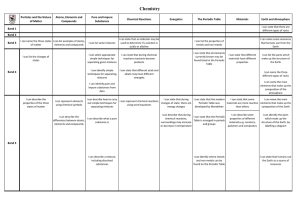
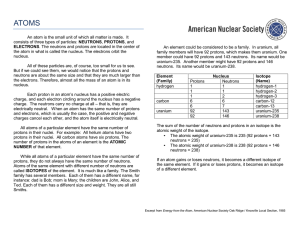
An atom is the small unit of which all matter is made. It consists of
... ELECTRONS. The neutrons and protons are located in the center of the atom in what is called the nucleus. The electrons orbit the nucleus. All of these particles are, of course, too small for us to see. But if we could see them, we would notice that the protons and neutrons are about the same size an ...
... ELECTRONS. The neutrons and protons are located in the center of the atom in what is called the nucleus. The electrons orbit the nucleus. All of these particles are, of course, too small for us to see. But if we could see them, we would notice that the protons and neutrons are about the same size an ...
b. Elements as Mixtures - Isotopes
... Elements are made from atoms having the same atomic number, protons Are all atoms of one particular atom the same or are they mixtures? 1) All atom nuclei for an element have the same number of protons. 2) Every atom in an element has the same number of protons & electrons 3) However, elements are ...
... Elements are made from atoms having the same atomic number, protons Are all atoms of one particular atom the same or are they mixtures? 1) All atom nuclei for an element have the same number of protons. 2) Every atom in an element has the same number of protons & electrons 3) However, elements are ...
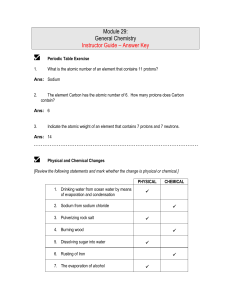
Module 29: General Chemistry Instructor Guide – Answer Key
... Ans: A physical change in matter is a change in the form of matter but not in its chemical identity. A chemical change in matter is a change in which one or more kinds of matter transform into a new kind of matter. ...
... Ans: A physical change in matter is a change in the form of matter but not in its chemical identity. A chemical change in matter is a change in which one or more kinds of matter transform into a new kind of matter. ...
periodic table
... • Protons and neutrons are made up of smaller particles called quarks. • So far, scientists have confirmed the existence of six uniquely different quarks. ...
... • Protons and neutrons are made up of smaller particles called quarks. • So far, scientists have confirmed the existence of six uniquely different quarks. ...
Unit #3: ATOMIC STRUCTURE - Miss Virga`s Chemistry Class
... as helium on the Sun, which is exactly the same as helium from the most distant start we can detect. The elements are the common building blocks of the Universe. Each element also leaves a characteristic “fingerprint” that we can detect as an atom moves from the excited state back down to the ground ...
... as helium on the Sun, which is exactly the same as helium from the most distant start we can detect. The elements are the common building blocks of the Universe. Each element also leaves a characteristic “fingerprint” that we can detect as an atom moves from the excited state back down to the ground ...
Chapter 12
... at noon to drive four blocks to get some lunch. The gasoline that fuels the car is composed of many different organic compounds, including some belonging to the category of organic compounds called alkanes and a fuel additive called methyl t-butyl ether (MTBE). When they get to the restaurant, Stuart ...
... at noon to drive four blocks to get some lunch. The gasoline that fuels the car is composed of many different organic compounds, including some belonging to the category of organic compounds called alkanes and a fuel additive called methyl t-butyl ether (MTBE). When they get to the restaurant, Stuart ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.