Lower Extremity Anatomy
... – Calcaneus – Largest tarsal, prominence of the heel, tuberosity which is insertion for ligaments and tendons (Achilles) • Sustentaculum Tali – medial surface which supports the talus • Sinus Tarsi – canal from articulation between talus and calcaneous ...
... – Calcaneus – Largest tarsal, prominence of the heel, tuberosity which is insertion for ligaments and tendons (Achilles) • Sustentaculum Tali – medial surface which supports the talus • Sinus Tarsi – canal from articulation between talus and calcaneous ...
chapter 25 section 2 notes
... established hundreds of millions of years ago. Ever since that time, each phylum’s evolutionary history has shown variations in body plan as species have adapted to changing conditions. If the changes have enabled members of a phylum to survive and reproduce, the phylum still exists. If the body pla ...
... established hundreds of millions of years ago. Ever since that time, each phylum’s evolutionary history has shown variations in body plan as species have adapted to changing conditions. If the changes have enabled members of a phylum to survive and reproduce, the phylum still exists. If the body pla ...
Anatomy of the insertion of the tibialis posterior tendon
... C. Stukenborg-Colsman1, A. Schmiedl2 ...
... C. Stukenborg-Colsman1, A. Schmiedl2 ...
The Appendicular Skeleton
... • Deeper of the two bones – Always on the outside of the lower leg ...
... • Deeper of the two bones – Always on the outside of the lower leg ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
... (horizontal) plane. Each plane also describes a section taken of an organism or of an organ within the organism. Understanding these sections enables understanding of images and slides used to describe the body and its parts. ...
... (horizontal) plane. Each plane also describes a section taken of an organism or of an organ within the organism. Understanding these sections enables understanding of images and slides used to describe the body and its parts. ...
Skeletal - OnCourse
... ◦ first 7 pairs are true ribs – articulate with the sternum by costal cartilage ◦ next 5 pairs are false ribs – articulate indirectly to sternum or not at all (last 2 pair lack articulation and are floating ribs) ...
... ◦ first 7 pairs are true ribs – articulate with the sternum by costal cartilage ◦ next 5 pairs are false ribs – articulate indirectly to sternum or not at all (last 2 pair lack articulation and are floating ribs) ...
Lumbar Spine Fluoroscopy and Needle Placement
... • Bone is our friend: – When you are on bone you cannot be in a blood vessel, nervous tissue or intrathecal space – Touching a bone offers a unique opportunity to know needle tip position – You must understand skeletal and fluoroscopic anatomy Medical Advanced Pain Specialists David Schultz MD ...
... • Bone is our friend: – When you are on bone you cannot be in a blood vessel, nervous tissue or intrathecal space – Touching a bone offers a unique opportunity to know needle tip position – You must understand skeletal and fluoroscopic anatomy Medical Advanced Pain Specialists David Schultz MD ...
Dissecting Basilar Artery Aneurysm in Marfan Syndrome: Case Report
... The lumen (L), internal elastic membrane (straight arrow), and media (M) are marked. Note that the thrombus splits the media (curved arrow) and extends to the adventitial layer (arrowhead). (H and E stain) D, Histologic section of basilar artery shows small vacuoles and blue-staining mucosubstance w ...
... The lumen (L), internal elastic membrane (straight arrow), and media (M) are marked. Note that the thrombus splits the media (curved arrow) and extends to the adventitial layer (arrowhead). (H and E stain) D, Histologic section of basilar artery shows small vacuoles and blue-staining mucosubstance w ...
JOINTS - amber
... larger forearm bone (ulna), its knob-like head articulates with a notch of the radius (ulnar notch) laterally and with a disk of fibrocartilage below. This disk, in turn, joins a wrist bone (the triquetrum). A medial "styloid process" at the lower end of the ulna provides attachments for ligaments ( ...
... larger forearm bone (ulna), its knob-like head articulates with a notch of the radius (ulnar notch) laterally and with a disk of fibrocartilage below. This disk, in turn, joins a wrist bone (the triquetrum). A medial "styloid process" at the lower end of the ulna provides attachments for ligaments ( ...
The Skeletal System
... Cervical Vertebrae: The Axis (C2) The axis has a body, spine, and vertebral arches as do other cervical vertebrae Unique to the axis is the dens, or odontoid process, which projects superiorly from the body and is cradled in the anterior arch of the atlas The dens is a pivot for the rotation of ...
... Cervical Vertebrae: The Axis (C2) The axis has a body, spine, and vertebral arches as do other cervical vertebrae Unique to the axis is the dens, or odontoid process, which projects superiorly from the body and is cradled in the anterior arch of the atlas The dens is a pivot for the rotation of ...
Cranial nerves made ridiculously simple
... hand-in-hand in a. Visit http://www.brainwashedsoftware.com for more information. This is the corticospinal tract as seen in Axiom Neuro, a new interactive functional atlas. Free neuro exam videos made simple for medical students, residents, nurses, physician assistants, nurse practioners. Neuro exa ...
... hand-in-hand in a. Visit http://www.brainwashedsoftware.com for more information. This is the corticospinal tract as seen in Axiom Neuro, a new interactive functional atlas. Free neuro exam videos made simple for medical students, residents, nurses, physician assistants, nurse practioners. Neuro exa ...
Skeletal System Gross Anatomy
... Which of the following is not a part of the axial division of the skeletal system? A. Vertebral column B. Hyoid bone C. Skull D. Auditory ossicles E. Pectoral girdle ***** ...
... Which of the following is not a part of the axial division of the skeletal system? A. Vertebral column B. Hyoid bone C. Skull D. Auditory ossicles E. Pectoral girdle ***** ...
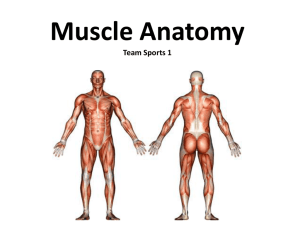
Muscle Anatomy Team Sports 1
... • Skeletal/Voluntary- Skeletal muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. Those muscles that can be moved by our thoughts and actions. • Smooth/Involuntary MuscleMuscles that moves internal organs, such as the bowels, and vessels. Reflex action is made without our thought. • ...
... • Skeletal/Voluntary- Skeletal muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. Those muscles that can be moved by our thoughts and actions. • Smooth/Involuntary MuscleMuscles that moves internal organs, such as the bowels, and vessels. Reflex action is made without our thought. • ...
Ponce Lecture-Skeleton of the Face and the Soft Tissue of the Skull
... CAT SCAN-Can check missing parts of bone with 3-D image, and can create a prosthetic piece to replace the missing bone. Missing hair. In the countryside, the women let their hair grow and ask for favors from the virgins. If their requests are granted, they will offer their hair to the virgin. One pa ...
... CAT SCAN-Can check missing parts of bone with 3-D image, and can create a prosthetic piece to replace the missing bone. Missing hair. In the countryside, the women let their hair grow and ask for favors from the virgins. If their requests are granted, they will offer their hair to the virgin. One pa ...
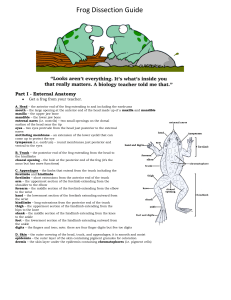
Frog Dissection Guide
... kidneys – long, flat structures along the dorsal surface of the coelom near the posterior end of the cavity; dark brown fat bodies/ovaries – yellow or brown wormlike structures in the mid abdominal area (ovaries are too small to see) fat bodies/testes – yellow or brown wormlike structures in the mid ...
... kidneys – long, flat structures along the dorsal surface of the coelom near the posterior end of the cavity; dark brown fat bodies/ovaries – yellow or brown wormlike structures in the mid abdominal area (ovaries are too small to see) fat bodies/testes – yellow or brown wormlike structures in the mid ...
Margin = edge Foramen = hole Sinus = empty space Sutures = joints
... This area is composed of the sternum and 12 pairs of ribs. The first seven are the TRUE RIBS because they connect to the sternum via their own cartilage. Ribs 8-12 are the FALSE RIBS because they share cartilage to connect to the sternum. Ribs 11 & 12 are further classified as FLOATING RIBS because ...
... This area is composed of the sternum and 12 pairs of ribs. The first seven are the TRUE RIBS because they connect to the sternum via their own cartilage. Ribs 8-12 are the FALSE RIBS because they share cartilage to connect to the sternum. Ribs 11 & 12 are further classified as FLOATING RIBS because ...
CHAPTER 4 copy - WordPress.com
... In some animals, the body is externally and internally divided into segments with a serial repetition of at least some organs. The body shows this pattern called metameric segmentation and the phenomenon is known as metamerism. e.g., in earthworm. ...
... In some animals, the body is externally and internally divided into segments with a serial repetition of at least some organs. The body shows this pattern called metameric segmentation and the phenomenon is known as metamerism. e.g., in earthworm. ...
Period 7 Lower Limb
... leverage that the tendon can exert on the femur by increasing the angle at which it acts. ...
... leverage that the tendon can exert on the femur by increasing the angle at which it acts. ...
An Introduction to Exercise and Sport Physiology
... Increasing your physical capabilities by loading beyond the point to which you are normally used to Example: – A short distance runner would run slightly longer distances every week until he can run a marathon. ...
... Increasing your physical capabilities by loading beyond the point to which you are normally used to Example: – A short distance runner would run slightly longer distances every week until he can run a marathon. ...
Chapter 7 Practice Questions
... vertebrae together. 38) The atlas or C1 vertebra has no body. It articulates with the skull with large curved articular surfaces to allow the skull to rock in a "yes" motion. The axis or C2 vertebra has a dens that allows the axis to pivot, giving the head the "no" motion. The vertebral foramen of t ...
... vertebrae together. 38) The atlas or C1 vertebra has no body. It articulates with the skull with large curved articular surfaces to allow the skull to rock in a "yes" motion. The axis or C2 vertebra has a dens that allows the axis to pivot, giving the head the "no" motion. The vertebral foramen of t ...
Spongy Bone
... Remodeling of Bones Bone is continually being broken down and built up again Osteoclasts remove worn cells and deposit calcium in the blood Osteoblasts remove calcium from the blood and form new bone Three important hormones regulating bone growth ...
... Remodeling of Bones Bone is continually being broken down and built up again Osteoclasts remove worn cells and deposit calcium in the blood Osteoblasts remove calcium from the blood and form new bone Three important hormones regulating bone growth ...
Forensic Anthropology Center - Texas State Living Donor Paperwork
... Trauma and advanced research request: Your initials indicate that you permit your remains to be used for trauma and other advanced research that benefits the biomedical, medicolegal, and anthropological communities. Research of this type will help increase our knowledge of the processes of trauma, w ...
... Trauma and advanced research request: Your initials indicate that you permit your remains to be used for trauma and other advanced research that benefits the biomedical, medicolegal, and anthropological communities. Research of this type will help increase our knowledge of the processes of trauma, w ...
Body snatching
Body snatching is the secret disinterment of corpses from graveyards or other burial sites. A common purpose of body snatching, especially in the 19th century, was to sell the corpses for dissection or anatomy lectures in medical schools. Those who practiced body snatching were often called ""resurrectionists"" or ""resurrection-men"". A related act is grave robbery, uncovering a tomb or crypt to steal artifacts or personal effects rather than corpses.