Patellar instability
... The majority of patients with complaints of patellar instability will have abnormalities of the extensor mechanism and patella‐femoral joint. These include 1. A shallow trochlea 2. An increased quadriceps angle (Q‐angle) 3. Patella alta or infera 4. A vastus medialis obliquus (VMO) deficiency ...
... The majority of patients with complaints of patellar instability will have abnormalities of the extensor mechanism and patella‐femoral joint. These include 1. A shallow trochlea 2. An increased quadriceps angle (Q‐angle) 3. Patella alta or infera 4. A vastus medialis obliquus (VMO) deficiency ...
Antebrachium, Hand, and Joints
... POSTERIOR ANTEBRACHIUM Identify the superficial and deep muscles located in the posterior compartment of the forearm. Describe the attachment points of all of the posterior antebrachial muscles. Describe the primary action of each of these muscles. Identify the primary source of innervation and vasc ...
... POSTERIOR ANTEBRACHIUM Identify the superficial and deep muscles located in the posterior compartment of the forearm. Describe the attachment points of all of the posterior antebrachial muscles. Describe the primary action of each of these muscles. Identify the primary source of innervation and vasc ...
Arthroscopic Capsular Plication And Capsular
... for articular damage when the arthroscope sheath is inserted. The posterior incision is made, and the blunt trocar and sheath are introduced into the joint, with backflow of fluid noted to confirm placement. The arthroscope is introduced and the diagnostic portion of the arthroscopy is begun. The a ...
... for articular damage when the arthroscope sheath is inserted. The posterior incision is made, and the blunt trocar and sheath are introduced into the joint, with backflow of fluid noted to confirm placement. The arthroscope is introduced and the diagnostic portion of the arthroscopy is begun. The a ...
***t***t***u***u***u***u***u***u***u***u***u** u** u***u***u** u***u
... paranasal sinuses The sinuses are air-filled bony cavities located in the face and skull adjacent to the nose. ...
... paranasal sinuses The sinuses are air-filled bony cavities located in the face and skull adjacent to the nose. ...
Cervical Spine joints
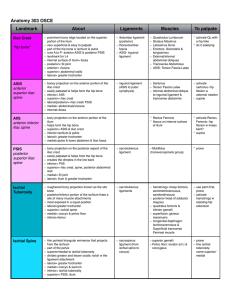
... Posterior inner Approximately Branches of lip of the iliac on half the T12, L1 nerves crest length of the lower border of the 12th rib and the transverse process of the upper four lumbar vertebrae Sternocleidomast Anterrolateral neck, Manubrium of Mastoid Spinal oid (both sides) diagonally between s ...
... Posterior inner Approximately Branches of lip of the iliac on half the T12, L1 nerves crest length of the lower border of the 12th rib and the transverse process of the upper four lumbar vertebrae Sternocleidomast Anterrolateral neck, Manubrium of Mastoid Spinal oid (both sides) diagonally between s ...
7. The Tongue - UCLA Linguistics
... to a point on the mandible about halfway between the chin and the lower incisors (front teeth). (Check by feeling with a forefinger down behind the lower front teeth in your own mouth, and ...
... to a point on the mandible about halfway between the chin and the lower incisors (front teeth). (Check by feeling with a forefinger down behind the lower front teeth in your own mouth, and ...
CAW-4703
... Proximal Humerus Pathophysiology of displaced 4-part fractures involves each muscle or muscle group pulling the fragments in various directions. The diaphysis (1) is drawn medially by the pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi muscles and is separated from the epiphysis at the surgical neck. The less ...
... Proximal Humerus Pathophysiology of displaced 4-part fractures involves each muscle or muscle group pulling the fragments in various directions. The diaphysis (1) is drawn medially by the pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi muscles and is separated from the epiphysis at the surgical neck. The less ...
technical information 3.3.1. - ING corporation, spol. s ro
... of the upper extremity - the adjustment of the angle of shoulder abduction, the adjustment of the horizontal flexion in shoulder and elbow joints. The Modular Arm Abduction Orthosis is provided as an assembly for individual treatment. The orthosis is prescribed by a medical doctor, fabrication and f ...
... of the upper extremity - the adjustment of the angle of shoulder abduction, the adjustment of the horizontal flexion in shoulder and elbow joints. The Modular Arm Abduction Orthosis is provided as an assembly for individual treatment. The orthosis is prescribed by a medical doctor, fabrication and f ...
Chapter 8: Joints of the Skeletal System
... A. Joints are also called articulations. B. Joints bind parts of the skeletal system, make possible bone growth, permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth and enable the body to move in response to skeletal muscle contractions. II. Classification of Joints A. Introduction 1. Thr ...
... A. Joints are also called articulations. B. Joints bind parts of the skeletal system, make possible bone growth, permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth and enable the body to move in response to skeletal muscle contractions. II. Classification of Joints A. Introduction 1. Thr ...
Anatomy and physiology of the nose and paranasal sinuses 1
... It supplied by branches of internal and external carotid arteries. i branches of the internal carotid artery that supply the nose are the anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries. While the external carotid artery supplies the nose through it`s maxillary branch and small contribution of the facial ...
... It supplied by branches of internal and external carotid arteries. i branches of the internal carotid artery that supply the nose are the anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries. While the external carotid artery supplies the nose through it`s maxillary branch and small contribution of the facial ...
Region 7: Oral Cavity and Larynx Oral Cavity -
... attachment to vocal process of the arytenoid is moveable *epithelial coverings over the vocal ligament form the vocal folds/true vocal cords --Joints of the Larynx a. cricothyroid joint: synovial joints on both sides b/w cricoid and inferior horns of the thyroid cartilages --Interior of the Larynx ...
... attachment to vocal process of the arytenoid is moveable *epithelial coverings over the vocal ligament form the vocal folds/true vocal cords --Joints of the Larynx a. cricothyroid joint: synovial joints on both sides b/w cricoid and inferior horns of the thyroid cartilages --Interior of the Larynx ...
English
... The sternocleidomastoid muscle is a muscle that divides the side of the neck into anterior and posterior triangles. It is an important surgical landmark as it is related to many neurovascular structures in the neck. It originates from two heads. The sternal head is rounded and tendinous. It originat ...
... The sternocleidomastoid muscle is a muscle that divides the side of the neck into anterior and posterior triangles. It is an important surgical landmark as it is related to many neurovascular structures in the neck. It originates from two heads. The sternal head is rounded and tendinous. It originat ...
152
... • head is small & round w circulate facet that articulates wi T1 (neck/tubercle- costotransverse) • articulates with manubirum anteriorly (via costal ...
... • head is small & round w circulate facet that articulates wi T1 (neck/tubercle- costotransverse) • articulates with manubirum anteriorly (via costal ...
SKELETAL SYSTEM LAB
... can be identified. These Haversian systems resemble tree stumps and are also known as osteons. Osteocytes (bone cells) can be seen inside small hollow spaces called lacunae. Description: A network of osteons makes ground compact bone resemble a field of tree stumps. Location: Makes up the bones of t ...
... can be identified. These Haversian systems resemble tree stumps and are also known as osteons. Osteocytes (bone cells) can be seen inside small hollow spaces called lacunae. Description: A network of osteons makes ground compact bone resemble a field of tree stumps. Location: Makes up the bones of t ...
50 jmscr
... with meralgia paraesthetica. It is commonly seen in the adolescent age group. Avulsion fractures results due to sudden or repetitive contraction or pull by the muscle or tendon attached to the bone. Treatment is mainly conservative depending on the displacement of the fragment, depending on the disp ...
... with meralgia paraesthetica. It is commonly seen in the adolescent age group. Avulsion fractures results due to sudden or repetitive contraction or pull by the muscle or tendon attached to the bone. Treatment is mainly conservative depending on the displacement of the fragment, depending on the disp ...
Potential Contribution of Abnormal Talar Dome Lateral
... Introduction/Purpose: Abnormal tibial plafond geometry, varus deformity and insufficient talar anterior coverage in particular, is well recognized as congenital factors predisposing ankles to osteoarthritis (OA), both primarily and after lateral ligament injury. Presumably, abnormal geometry of the ...
... Introduction/Purpose: Abnormal tibial plafond geometry, varus deformity and insufficient talar anterior coverage in particular, is well recognized as congenital factors predisposing ankles to osteoarthritis (OA), both primarily and after lateral ligament injury. Presumably, abnormal geometry of the ...
occulsion 1
... The Arterio-venous shunt:We talked before that patients can feel the pain from the TMJ, through the following: 1- The synovial fluid and free nerve endings surrounding the capsule. 2- The oto-mandibular ligament that transmit the pain to the ear. 3- The Arterio-venous shunt, that is located behind t ...
... The Arterio-venous shunt:We talked before that patients can feel the pain from the TMJ, through the following: 1- The synovial fluid and free nerve endings surrounding the capsule. 2- The oto-mandibular ligament that transmit the pain to the ear. 3- The Arterio-venous shunt, that is located behind t ...
Anatomy, Joint Orientation and Arthrokinematics
... The superficial fires extend across several vertebrae Fibres only connect to the intervertebral discs and adjacent margins The posterior ligament is considerably weaker than the anterior ligament The ligament is thicker when over the intervertebral discs ...
... The superficial fires extend across several vertebrae Fibres only connect to the intervertebral discs and adjacent margins The posterior ligament is considerably weaker than the anterior ligament The ligament is thicker when over the intervertebral discs ...
Arteries of the Arm - Deranged Physiology
... The Anterior circumflex humeral artery The Posteror circumflex humeral artery The Subscapular artery Axillary nerve Posterior circumflex humeral artery ...
... The Anterior circumflex humeral artery The Posteror circumflex humeral artery The Subscapular artery Axillary nerve Posterior circumflex humeral artery ...
TYPES OF THE JOINTS: 1
... Rotator Cuff muscles: [SITS] supraspinatus (above), infraspinatus(posterior), teres minor(posterior), suprascapularis(anterior) Supraspinatus abduction till (15-18) degree. Deltoid (middle fibers) abduction till 90 degree. Nerve Supply: Most of the nerves that pass through the joint give innervati ...
... Rotator Cuff muscles: [SITS] supraspinatus (above), infraspinatus(posterior), teres minor(posterior), suprascapularis(anterior) Supraspinatus abduction till (15-18) degree. Deltoid (middle fibers) abduction till 90 degree. Nerve Supply: Most of the nerves that pass through the joint give innervati ...
functional anatomy of the mammal
... sectional planes. Aspects are surfaces offered to space and are named with reference to the direction from "rhich a body is viewed. The aspects or views are (1) cranial (head), (2) caudal (tail), (3) dorsal (back), (4) ventral (belly), and (5) right and (6) left lateral (sides). On appendages, the a ...
... sectional planes. Aspects are surfaces offered to space and are named with reference to the direction from "rhich a body is viewed. The aspects or views are (1) cranial (head), (2) caudal (tail), (3) dorsal (back), (4) ventral (belly), and (5) right and (6) left lateral (sides). On appendages, the a ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.