Chapter 9 Orthopedics: Muscular Chapter 9 Word List
... a flat, wide, white fibrous sheet of connective tissue, sometimes composed of several tendons incoordination of muscle movement of a mild type or character that does not threaten health or life of the arm (Latin) short in length (Latin) a thin sac of synovial membrane filled with synovial fluid ...
... a flat, wide, white fibrous sheet of connective tissue, sometimes composed of several tendons incoordination of muscle movement of a mild type or character that does not threaten health or life of the arm (Latin) short in length (Latin) a thin sac of synovial membrane filled with synovial fluid ...
Bones and Muscles - OYR Raiders Ice Hockey
... mourning.(The lacrimal bone forms half of the receptacle, which holds the lacrimal sac, a structure that receives the tears and directs them into the nasal cavity. That explains why we blow our noses in cold weather, or when we cry, we are blowing out the tears that have drained into the cavity. The ...
... mourning.(The lacrimal bone forms half of the receptacle, which holds the lacrimal sac, a structure that receives the tears and directs them into the nasal cavity. That explains why we blow our noses in cold weather, or when we cry, we are blowing out the tears that have drained into the cavity. The ...
Nasal cavity
... — they are divided into three groups: (i) anterior: opens into the depth of anterior part of the semilunar hiatus (ii) middle: opens into the ethmoidal bulla (iii) posterior: opens into the superior meatus of the nose — nerve supply by anterior and posterior ethmoidal n. Sphenoidal sinuses — paired, ...
... — they are divided into three groups: (i) anterior: opens into the depth of anterior part of the semilunar hiatus (ii) middle: opens into the ethmoidal bulla (iii) posterior: opens into the superior meatus of the nose — nerve supply by anterior and posterior ethmoidal n. Sphenoidal sinuses — paired, ...
Bones of the Back Region - Listed in Superior to Inferior Order
... coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its body part of the pelvis forms 1/5 of the acetabulum; its symphyseal surface unites with the pubis of the opposite side to form the pubic symphysis; the superior and inferior pubic rami participate in the formation of the obturator foramen ...
... coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its body part of the pelvis forms 1/5 of the acetabulum; its symphyseal surface unites with the pubis of the opposite side to form the pubic symphysis; the superior and inferior pubic rami participate in the formation of the obturator foramen ...
Diaphragm C L I N I C A L N O T E S
... the crura the diaphragm arises from the medial and lateral arcuate ligaments (see Fig. 2.16). The medial arcuate ligament extends from the side of the body of the second lumbar vertebra to the tip of the transverse process of the first lumbar vertebra. The lateral arcuate ligament extends from the t ...
... the crura the diaphragm arises from the medial and lateral arcuate ligaments (see Fig. 2.16). The medial arcuate ligament extends from the side of the body of the second lumbar vertebra to the tip of the transverse process of the first lumbar vertebra. The lateral arcuate ligament extends from the t ...
Osteology and cranial musculature of Caiman latirostris
... proceeded from the most superficial muscles to the deepest ones, removing the jugal and quadratojugal bones, the postorbital processes, and finally part of the maxilla. We follow Romer (1956) for osteological nomenclature and Sedlmayr (2002) for the nomenclature of nerves and blood vessels. The main c ...
... proceeded from the most superficial muscles to the deepest ones, removing the jugal and quadratojugal bones, the postorbital processes, and finally part of the maxilla. We follow Romer (1956) for osteological nomenclature and Sedlmayr (2002) for the nomenclature of nerves and blood vessels. The main c ...
The Skeletal System
... •Articulates with the sternum medially and with the scapula laterally •Scapula—shoulder blade •Articulates with the clavicle at the acromioclavicular joint •Articulates with the arm bone at the glenoid cavity •These bones allow the upper limb to have exceptionally free movement © 2012 Pearson Educat ...
... •Articulates with the sternum medially and with the scapula laterally •Scapula—shoulder blade •Articulates with the clavicle at the acromioclavicular joint •Articulates with the arm bone at the glenoid cavity •These bones allow the upper limb to have exceptionally free movement © 2012 Pearson Educat ...
morphology of the larynx of corvus brachyrhynchos (passeriformes
... quite correct as it most likely does not originate from the cricoid cartilage. Insertion of the M. d. glottidis is along the laterodorsal surface of the anterior end of the arytenoid ...
... quite correct as it most likely does not originate from the cricoid cartilage. Insertion of the M. d. glottidis is along the laterodorsal surface of the anterior end of the arytenoid ...
C- Spine Adult vs pediatric - Calgary Emergency Medicine
... water. He was pulled semiconscious from the water by lifeguards. While maintaining his airway, the lifeguards placed the patient in full C-spine immobilization. When the patient became more alert, he complained of pain to his upper neck region. Paramedics transported the patient to the ED. ...
... water. He was pulled semiconscious from the water by lifeguards. While maintaining his airway, the lifeguards placed the patient in full C-spine immobilization. When the patient became more alert, he complained of pain to his upper neck region. Paramedics transported the patient to the ED. ...
C- Spine Adult vs pediatric
... water. He was pulled semiconscious from the water by lifeguards. While maintaining his airway, the lifeguards placed the patient in full C-spine immobilization. When the patient became more alert, he complained of pain to his upper neck region. Paramedics transported the patient to the ED. ...
... water. He was pulled semiconscious from the water by lifeguards. While maintaining his airway, the lifeguards placed the patient in full C-spine immobilization. When the patient became more alert, he complained of pain to his upper neck region. Paramedics transported the patient to the ED. ...
landmarksforradiology
... technique, when the x-ray beam is directed at an upward angle through the ridges. ...
... technique, when the x-ray beam is directed at an upward angle through the ridges. ...
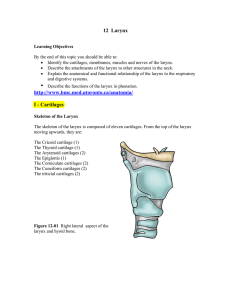
Anatomy of phonation (related topic 1)
... neck call ed the laryngeal prominence or Adam’s apple. The thyroid laminae meet at an angle of 80 degrees in males and 90 degrees in females. The posterior border of each lamina is prolonged upward and downward as the superior and inferior thyroid horns. The superior thyroid horns are directed somew ...
... neck call ed the laryngeal prominence or Adam’s apple. The thyroid laminae meet at an angle of 80 degrees in males and 90 degrees in females. The posterior border of each lamina is prolonged upward and downward as the superior and inferior thyroid horns. The superior thyroid horns are directed somew ...
study of two unusual separate biceps brachii muscle
... brachialis. It usually enters the forearm between the heads of the pronator teres, crossing to the lateral side of the ulnar artery and separated from it by the deep head of pronator teres [1]. Anomalous pattern of the median nerve can be explained on the basis of embryological development The upper ...
... brachialis. It usually enters the forearm between the heads of the pronator teres, crossing to the lateral side of the ulnar artery and separated from it by the deep head of pronator teres [1]. Anomalous pattern of the median nerve can be explained on the basis of embryological development The upper ...
Wrist & Hand - members.iinet.com.au
... Diagram of a cross section of Radius, Ulna and tubes provided with the caption: “At the lower end of the forearm there is an extensor retinaculum. Septa attach the retinaculum to the radius and ulna forming six osseofascial tunnels for the extensor tendons”. List the tendons corresponding to each of ...
... Diagram of a cross section of Radius, Ulna and tubes provided with the caption: “At the lower end of the forearm there is an extensor retinaculum. Septa attach the retinaculum to the radius and ulna forming six osseofascial tunnels for the extensor tendons”. List the tendons corresponding to each of ...
live anatomy - University of New England
... Follow the clavicle from its lateral end to medial end. This bone is concave laterally and convex medially. Between the elevated medial ends of the clavicle is the jugular notch (suprasternal notch). Palpate the sternoclavicular joint. Determine how the clavicle shifts during elevation and depressio ...
... Follow the clavicle from its lateral end to medial end. This bone is concave laterally and convex medially. Between the elevated medial ends of the clavicle is the jugular notch (suprasternal notch). Palpate the sternoclavicular joint. Determine how the clavicle shifts during elevation and depressio ...
Iv>XUlna - The BMJ
... Check bone margins and density-The cortex of the radial neck and head should form a smooth continuous concave arc extending from the radial shaft to the base of the radial head. The cortical margin of the radial head should be sharply defined. About half of radial head fractures are undisplaced, mak ...
... Check bone margins and density-The cortex of the radial neck and head should form a smooth continuous concave arc extending from the radial shaft to the base of the radial head. The cortical margin of the radial head should be sharply defined. About half of radial head fractures are undisplaced, mak ...
15 The muscles of the head and neck.
... +the transverse and alar parts -the transverse and vertical parts -the medial and lateral parts -the external and internal parts ...
... +the transverse and alar parts -the transverse and vertical parts -the medial and lateral parts -the external and internal parts ...
Chapter 7 and 9 PowerPoint
... bones are held together by dense irregular connective tissue that is rich in collagen fibers (between bones of skull) • Cartilaginous joints – no synovial cavity and bones are held together by cartilage. (hip joint) • Synovial Joints – synovial cavity and bones are united by the dense irregular conn ...
... bones are held together by dense irregular connective tissue that is rich in collagen fibers (between bones of skull) • Cartilaginous joints – no synovial cavity and bones are held together by cartilage. (hip joint) • Synovial Joints – synovial cavity and bones are united by the dense irregular conn ...
Gluteal region, thigh & leg
... It extends from the apex of the femoral triangle, where the sartorius crosses over the adductor longus, to the adductor hiatus in the tendon of the adductor magnus. ...
... It extends from the apex of the femoral triangle, where the sartorius crosses over the adductor longus, to the adductor hiatus in the tendon of the adductor magnus. ...
A BIOKINETIC APPROACH TO THE PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION OF SHOULDER INJURIES
... The players were then divided into a control group and an experimental group. Both groups completed a series of physical scientific tests, consisting of posture analysis, body composition, flexibility, functional strength of the upper body; and isokinetic power and endurance of the shoulder muscles. ...
... The players were then divided into a control group and an experimental group. Both groups completed a series of physical scientific tests, consisting of posture analysis, body composition, flexibility, functional strength of the upper body; and isokinetic power and endurance of the shoulder muscles. ...
Advanced Reconstruction Spine_frontmatter.indd
... of the mandible can be problematic. In such cases, a handheld retractor can be used for superior exposure. It is important to note the amount of head rotation, if any, at this stage to avoid coursing too far laterally during the dissection and removing too much of the lateral arch of C1 or the later ...
... of the mandible can be problematic. In such cases, a handheld retractor can be used for superior exposure. It is important to note the amount of head rotation, if any, at this stage to avoid coursing too far laterally during the dissection and removing too much of the lateral arch of C1 or the later ...
L11- Forearm
... the interosseous membrane. This membrane allows movement of Pronation and Supination while the two bones are connected together. Also it gives origin for the deep muscles. ...
... the interosseous membrane. This membrane allows movement of Pronation and Supination while the two bones are connected together. Also it gives origin for the deep muscles. ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.