Bones and bone markings list
... - Alveoli = sockets - Ramus – two rami extend upward at the posterior end of the body - Mandibular condyle - Coronoid process - Mandibular notch - Mental foramina - Mandibular foramina D. Middle Ear Bones a) Malleus = hammer (2) b) Incus = anvil (2) c) Stapes = stirrup (2) E. Hyoid Bone (1) - U-shap ...
... - Alveoli = sockets - Ramus – two rami extend upward at the posterior end of the body - Mandibular condyle - Coronoid process - Mandibular notch - Mental foramina - Mandibular foramina D. Middle Ear Bones a) Malleus = hammer (2) b) Incus = anvil (2) c) Stapes = stirrup (2) E. Hyoid Bone (1) - U-shap ...
Biomech MS System (cont'd), Upper Extremity
... • Pectoralis minor (underneath pectoralis major) – downward rotation, abduction, or protraction ...
... • Pectoralis minor (underneath pectoralis major) – downward rotation, abduction, or protraction ...
Thieme: Locomotor System
... all the carpal bones of the proximal row are in continual contact with the socketshaped articular facet of the radius and the disk. The triquetrum (3), only makes close contact with the disk during ulnar abduction and loses contact on radial abduction. The capsule of the wrist joint is lax, dorsally ...
... all the carpal bones of the proximal row are in continual contact with the socketshaped articular facet of the radius and the disk. The triquetrum (3), only makes close contact with the disk during ulnar abduction and loses contact on radial abduction. The capsule of the wrist joint is lax, dorsally ...
Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
... Humerus Lateral epicondyle Medial epicondyle More prominent than lateral one Trochlea (“pulley” or “spool”) In center of condyle (middle “knuckle) Where trochlear notch of ulna rotates during forearm flexion Capitulum Forms a “cap” over the radius Figure 8–4 ...
... Humerus Lateral epicondyle Medial epicondyle More prominent than lateral one Trochlea (“pulley” or “spool”) In center of condyle (middle “knuckle) Where trochlear notch of ulna rotates during forearm flexion Capitulum Forms a “cap” over the radius Figure 8–4 ...
PRACTICAL-Upper limb
... They are numbered from medial (big toe) to lateral. 1st metatarsal bone is large and lies medially. Each metatarsal bone has a base (proximal). a shaft and a head (distal). ...
... They are numbered from medial (big toe) to lateral. 1st metatarsal bone is large and lies medially. Each metatarsal bone has a base (proximal). a shaft and a head (distal). ...
lateral - Dr. Par Mohammadian
... (Sally left the party to take Cindy home.); carpel tunnel syndrome: overuse of tendons causes inflammation-> swelling->compression of nerve ...
... (Sally left the party to take Cindy home.); carpel tunnel syndrome: overuse of tendons causes inflammation-> swelling->compression of nerve ...
Dislocated Shoulder
... Your doctor will examine your shoulder and may order an X-ray. It's important for you to tell your doctor how it happened. Was it an injury? Have you ever dislocated your shoulder before? Your doctor will place the ball of the upper arm bone (humerus) back into the joint socket. This process is call ...
... Your doctor will examine your shoulder and may order an X-ray. It's important for you to tell your doctor how it happened. Was it an injury? Have you ever dislocated your shoulder before? Your doctor will place the ball of the upper arm bone (humerus) back into the joint socket. This process is call ...
SA04su2a
... e) none of the above Which of the following classifications is INCORRECT. a) atlanto-occipital joint - ginglymus b) sacroiliac joint - diarthrodial c) temporomandibular joint -multiaxial d) costotransverse joint - plane e) manubriosternal joint - synchondrosis 23) Choose the INCORRECT statement. a) ...
... e) none of the above Which of the following classifications is INCORRECT. a) atlanto-occipital joint - ginglymus b) sacroiliac joint - diarthrodial c) temporomandibular joint -multiaxial d) costotransverse joint - plane e) manubriosternal joint - synchondrosis 23) Choose the INCORRECT statement. a) ...
doc - CLAS Users
... the mandibular condyles fit. mastoid process: A pyramid-shaped prominence of cancelous bone on the temporal bone behind the external auditory meatus. Muscles that extend and turn the head attach on it. nasal spine (anterior): The thin projection of bone at the midline on the lower nasal margin, hold ...
... the mandibular condyles fit. mastoid process: A pyramid-shaped prominence of cancelous bone on the temporal bone behind the external auditory meatus. Muscles that extend and turn the head attach on it. nasal spine (anterior): The thin projection of bone at the midline on the lower nasal margin, hold ...
Diagnosis and Treatment of Scapular Injuries
... • Anterior/Posterior Tilt • Upward/Downward Glide ...
... • Anterior/Posterior Tilt • Upward/Downward Glide ...
curriculum
... o Extension of humerus: Latissimus dorsi, teres major, posterior deltoid, triceps brachii ...
... o Extension of humerus: Latissimus dorsi, teres major, posterior deltoid, triceps brachii ...
FORM A
... a) in the petrous portion of the temporal bone b) lateral to the tympanic membrane c) rostral to the glabella d) inferior to the foramen magnum e) two of the above 2) Choose the TRUE statement. a) cranial nerve 8 exits the skull via the stylomastoid foramen b) the internal acoustic meatus is located ...
... a) in the petrous portion of the temporal bone b) lateral to the tympanic membrane c) rostral to the glabella d) inferior to the foramen magnum e) two of the above 2) Choose the TRUE statement. a) cranial nerve 8 exits the skull via the stylomastoid foramen b) the internal acoustic meatus is located ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
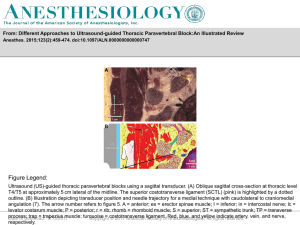
... From: Different Approaches to Ultrasound-guided Thoracic Paravertebral Block:An Illustrated Review Anesthes. 2015;123(2):459-474. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000000747 ...
... From: Different Approaches to Ultrasound-guided Thoracic Paravertebral Block:An Illustrated Review Anesthes. 2015;123(2):459-474. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000000747 ...
Bone Diversity
... • More stable but less flexible than shoulder girdle • “Pelvis” is actually three separate bones ...
... • More stable but less flexible than shoulder girdle • “Pelvis” is actually three separate bones ...
Fall 231 2013 Supplemental package
... gloves or goggles, etc. Upon request, detailed written information is available on every chemical used (MSDS). Ask your instructor. 5. No pen or pencil is to be used at any time on any model or bone. The bones are fragile, hard to replace and used by hundreds of students every year. To protect them ...
... gloves or goggles, etc. Upon request, detailed written information is available on every chemical used (MSDS). Ask your instructor. 5. No pen or pencil is to be used at any time on any model or bone. The bones are fragile, hard to replace and used by hundreds of students every year. To protect them ...
Bio103Lab6-82008Bone..
... explain many of them while helping you with the skeleton. Please inquire about any that you do not understand. Acromion process ...
... explain many of them while helping you with the skeleton. Please inquire about any that you do not understand. Acromion process ...
2C Worksheet KEY
... that subdivide a synovial cavity is referred to as menisci. 2 C 2-3 9) Movements at synovial joints are caused by muscle contraction. The origin of the muscle is attached to less movable bone, which is usually located more medially while the insertion is where it attaches to moveable bone is usually ...
... that subdivide a synovial cavity is referred to as menisci. 2 C 2-3 9) Movements at synovial joints are caused by muscle contraction. The origin of the muscle is attached to less movable bone, which is usually located more medially while the insertion is where it attaches to moveable bone is usually ...
Bio103Lab6-82008Bone..
... explain many of them while helping you with the skeleton. Please inquire about any that you do not understand. Acromion process ...
... explain many of them while helping you with the skeleton. Please inquire about any that you do not understand. Acromion process ...
Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
... - a broad pubic angle (greater than 100 degrees) - less curvature of sacrum and coccyx - a wider, circular pelvic inlet - a broad, low pelvis - ilia that project farther laterally, rather than upwards ...
... - a broad pubic angle (greater than 100 degrees) - less curvature of sacrum and coccyx - a wider, circular pelvic inlet - a broad, low pelvis - ilia that project farther laterally, rather than upwards ...
Ulnar Bone - By Dr Nand Lal Dhomeja ( Anatomy Department )
... begins above at the medial angle of the coronoid process ...
... begins above at the medial angle of the coronoid process ...
Slide ()
... The extraocular muscles and their innervation. The medial rectus muscle has been sectioned and retracted in this drawing of the right eye to show the position of the extraocular muscles. The course of cranial nerves (CNs) III (oculomotor, superior and inferior divisions), IV (trochlear), and VI (abd ...
... The extraocular muscles and their innervation. The medial rectus muscle has been sectioned and retracted in this drawing of the right eye to show the position of the extraocular muscles. The course of cranial nerves (CNs) III (oculomotor, superior and inferior divisions), IV (trochlear), and VI (abd ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.