Synthesis of Inorganic Nanostructures in Reverse Micelles
... can self-assemble into a rich variety of organized structures in solution, such as normal and reverse micelles, microemulsions, vesicles, and lyotropic liquid crystals.[5] Specifically, reverse micelles are globular aggregates formed by the self-assembly of surfactants in apolar solvents, whereas nor ...
... can self-assemble into a rich variety of organized structures in solution, such as normal and reverse micelles, microemulsions, vesicles, and lyotropic liquid crystals.[5] Specifically, reverse micelles are globular aggregates formed by the self-assembly of surfactants in apolar solvents, whereas nor ...
Information on measuring ammonia in water
... Some typical applications of ammonia sensors that may be mentioned are: Monitoring for leaks in cooling plant, e. g. large cold stores for storing food, ice rinks, refrigeration installations in supermarkets. Ammonia measurement: - in freshwater, salt water and seawater, - in boiler feed water, ...
... Some typical applications of ammonia sensors that may be mentioned are: Monitoring for leaks in cooling plant, e. g. large cold stores for storing food, ice rinks, refrigeration installations in supermarkets. Ammonia measurement: - in freshwater, salt water and seawater, - in boiler feed water, ...
الشريحة 1
... - Warm lakes and streams have less O2 dissolved in them than cool lakes (thermal pollution), fish may suffocate and die under these conditions. ...
... - Warm lakes and streams have less O2 dissolved in them than cool lakes (thermal pollution), fish may suffocate and die under these conditions. ...
Integrated Chemical Systems
... isotropic ESR spectrum, I, with a g value of 1.9604 and a line width of 16 G at room temperature (Figure 1A). Since the ESR spectrum of the Ti(II1) ion in Nafion is readily observable at room temperature, the configuration of ligands around Ti(II1) in Nafion clearly deviates from a species with perf ...
... isotropic ESR spectrum, I, with a g value of 1.9604 and a line width of 16 G at room temperature (Figure 1A). Since the ESR spectrum of the Ti(II1) ion in Nafion is readily observable at room temperature, the configuration of ligands around Ti(II1) in Nafion clearly deviates from a species with perf ...
Ch 12 Solutions
... - If the supersaturated solution comes in contact with the solid particles, then the solute will be able to leave the solution. The solute will continue to separate and become solid until equilibrium is reached and the solution is no longer supersaturated. Solubility of Gases - All gases are miscibl ...
... - If the supersaturated solution comes in contact with the solid particles, then the solute will be able to leave the solution. The solute will continue to separate and become solid until equilibrium is reached and the solution is no longer supersaturated. Solubility of Gases - All gases are miscibl ...
Chapter 7: Solutions
... There were solvated cations and anions in each the two solutions before mixing, then the solutions were mixed and the cations and anions remained solvated in the mixture. ...
... There were solvated cations and anions in each the two solutions before mixing, then the solutions were mixed and the cations and anions remained solvated in the mixture. ...
Mixtures
... and spread evenly throughout a mixture is known as dissolving. In solutions, the solute is the substance that is dissolved, and the solvent is the substance in which the solute is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve, in the solvent. A substance that is insoluble, or unable to dissolv ...
... and spread evenly throughout a mixture is known as dissolving. In solutions, the solute is the substance that is dissolved, and the solvent is the substance in which the solute is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve, in the solvent. A substance that is insoluble, or unable to dissolv ...
full text pdf
... BrO3– and 63% of Br– using NF membrane for the treatment of river water at the initial concentration of BrO3– amounted to 300 µg/dm3. It was found that the NF was more economical in terms of cost, mainly as a result of lower pressure applied. The disadvantages of the discussed techniques include dee ...
... BrO3– and 63% of Br– using NF membrane for the treatment of river water at the initial concentration of BrO3– amounted to 300 µg/dm3. It was found that the NF was more economical in terms of cost, mainly as a result of lower pressure applied. The disadvantages of the discussed techniques include dee ...
Chapter 7 lecture notes: Solutions
... This particular gas producing reaction is important in medicine because sodium bicarbonate is used as an over-the-counter therapeutic agent to treat acid indigestion (heartburn). Sodium bicarbonate is the primary active ingredient in many antacids, such as alka-seltzer. Sodium bicarbonate “neutraliz ...
... This particular gas producing reaction is important in medicine because sodium bicarbonate is used as an over-the-counter therapeutic agent to treat acid indigestion (heartburn). Sodium bicarbonate is the primary active ingredient in many antacids, such as alka-seltzer. Sodium bicarbonate “neutraliz ...
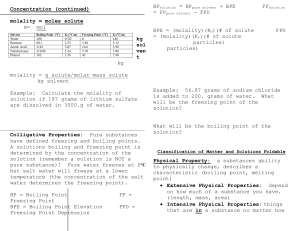
Solutions Foldable
... Example: 56.87 grams of sodium chloride is added to 200. grams of water. What will be the freezing point of the solution? What will be the boiling point of the solution? ...
... Example: 56.87 grams of sodium chloride is added to 200. grams of water. What will be the freezing point of the solution? What will be the boiling point of the solution? ...
Chapter 13: Properties of Solutions
... ΔTf=Kfm o ΔTf - freezing point of pure solvent o Kf- molal freezing-point-depression ...
... ΔTf=Kfm o ΔTf - freezing point of pure solvent o Kf- molal freezing-point-depression ...
std 6 review12ans
... b. How many grams of NaClO3 will dissolve in 100 g of water at 60 °C? about 150-155 c. How many grams of NaClO3 will dissolve in 400g of water at 20°C? 400g in 400g of water d. Which molecule is a gas? How do you know? X or CO2 since curve goes down e. How many more grams of KNO3 will dissolve if I ...
... b. How many grams of NaClO3 will dissolve in 100 g of water at 60 °C? about 150-155 c. How many grams of NaClO3 will dissolve in 400g of water at 20°C? 400g in 400g of water d. Which molecule is a gas? How do you know? X or CO2 since curve goes down e. How many more grams of KNO3 will dissolve if I ...
water - Portal UniMAP
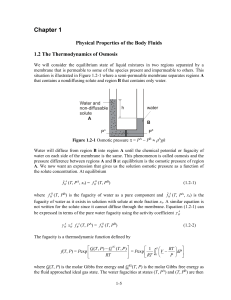
... (e.g. water) molecules pass through a semi permeable membrane from a solution of lower solute (e.g. chemical) concentration to a solution of higher solute concentration. Osmosis is the movement of solvent from a region of ...
... (e.g. water) molecules pass through a semi permeable membrane from a solution of lower solute (e.g. chemical) concentration to a solution of higher solute concentration. Osmosis is the movement of solvent from a region of ...
water - Portal UniMAP
... (e.g. water) molecules pass through a semi permeable membrane from a solution of lower solute (e.g. chemical) concentration to a solution of higher solute concentration. Osmosis is the movement of solvent from a region of ...
... (e.g. water) molecules pass through a semi permeable membrane from a solution of lower solute (e.g. chemical) concentration to a solution of higher solute concentration. Osmosis is the movement of solvent from a region of ...
Solutions, Acids, and Bases
... solute to a liquid solvent will usually raise the boiling point of the solvent. Adding salt to boil water when cooking ...
... solute to a liquid solvent will usually raise the boiling point of the solvent. Adding salt to boil water when cooking ...
Metathesis Problems (and Some Solutions) Identified Through
... • Semipermeable membrane: allows solvent molecules to pass but large solute molecules cannot • Osmosis: flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane to equalize solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane • π = MRT (M = molar conc., R = gas constant, T = absolute temperature) • Reverse o ...
... • Semipermeable membrane: allows solvent molecules to pass but large solute molecules cannot • Osmosis: flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane to equalize solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane • π = MRT (M = molar conc., R = gas constant, T = absolute temperature) • Reverse o ...
Salt Marshes II
... • Defn: Osmosis is the diffusion of a solvent through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration, or in other words, from a high water concentration to a low water concentration. The selectively-permeable membrane is permeable ...
... • Defn: Osmosis is the diffusion of a solvent through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration, or in other words, from a high water concentration to a low water concentration. The selectively-permeable membrane is permeable ...
Production of stable isotopes by membrane method
... Heavy water (HDO, D2O) is used in nuclear technology and research and the increasing market demand is expected in future if nuclear fusion will be used for energy production. Water enriched in 18O is used in research and medicine in trace experiments, as is water enriched in 17O. Recently there appe ...
... Heavy water (HDO, D2O) is used in nuclear technology and research and the increasing market demand is expected in future if nuclear fusion will be used for energy production. Water enriched in 18O is used in research and medicine in trace experiments, as is water enriched in 17O. Recently there appe ...
File
... more strongly than other molecular compounds that are non-polar • polar substances act as good solutes for other polar molecules and for all ionic compounds. ...
... more strongly than other molecular compounds that are non-polar • polar substances act as good solutes for other polar molecules and for all ionic compounds. ...
Ch1-2
... of solutes or osmolarity, then the establishment of osmotic equilibrium requires the osmosis of water into the cell resulting in swelling of the cell. If the cell is placed in a hypertonic solution with a higher concentration of solutes or osmolarity, then osmotic equilibrium requires osmosis of wat ...
... of solutes or osmolarity, then the establishment of osmotic equilibrium requires the osmosis of water into the cell resulting in swelling of the cell. If the cell is placed in a hypertonic solution with a higher concentration of solutes or osmolarity, then osmotic equilibrium requires osmosis of wat ...
Reactive polymer membrane for water disinfection and - ICTP-CSIC
... An industrial partner interested in manufacturing this membrane under a license agreement for its application in industrial water treatment plants is sought. Improved biocidal effect at high flux The invention is related to a porous polymer membrane consisting in a matrix of polyvinylidene fluoride ...
... An industrial partner interested in manufacturing this membrane under a license agreement for its application in industrial water treatment plants is sought. Improved biocidal effect at high flux The invention is related to a porous polymer membrane consisting in a matrix of polyvinylidene fluoride ...
Packet 2- Chemistry of Life
... A. Conclusion: Osmolarity describes the solution, but not how WATER will affect the cell…what the water does depends on: i. Osmolarity of both “sides” ii. Qualities of the MEMBRANE separating the sides. iii. What particles can pass through, and what particles cannot?! a. # Penetrating solutes o ...
... A. Conclusion: Osmolarity describes the solution, but not how WATER will affect the cell…what the water does depends on: i. Osmolarity of both “sides” ii. Qualities of the MEMBRANE separating the sides. iii. What particles can pass through, and what particles cannot?! a. # Penetrating solutes o ...
Reverse Osmosis As A Solution For Water Shortage In Iran
... The domestic and industrial wastewater may be used as resources for producing water. This is scientifically possible using appropriate technologies such as membrane processes in general and reverse osmosis in particular. The produced water is a great resource for industrial and agricultural applicat ...
... The domestic and industrial wastewater may be used as resources for producing water. This is scientifically possible using appropriate technologies such as membrane processes in general and reverse osmosis in particular. The produced water is a great resource for industrial and agricultural applicat ...
Reverse osmosis

Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification technology that uses a semipermeable membrane to remove larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property, that is driven by chemical potential, a thermodynamic parameter. Reverse osmosis can remove many types of molecules and ions from solutions, including bacteria, and is used in both industrial processes and the production of potable water. The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and the pure solvent is allowed to pass to the other side. To be ""selective"", this membrane should not allow large molecules or ions through the pores (holes), but should allow smaller components of the solution (such as the solvent) to pass freely.In the normal osmosis process, the solvent naturally moves from an area of low solute concentration (high water potential), through a membrane, to an area of high solute concentration (low water potential). The movement of a pure solvent is driven to reduce the free energy of the system by equalizing solute concentrations on each side of a membrane, generating osmotic pressure. Applying an external pressure to reverse the natural flow of pure solvent, thus, is reverse osmosis. The process is similar to other membrane technology applications. However, key differences are found between reverse osmosis and filtration. The predominant removal mechanism in membrane filtration is straining, or size exclusion, so the process can theoretically achieve perfect exclusion of particles regardless of operational parameters such as influent pressure and concentration. Moreover, reverse osmosis involves a diffusive mechanism, so that separation efficiency is dependent on solute concentration, pressure, and water flux rate. Reverse osmosis is most commonly known for its use in drinking water purification from seawater, removing the salt and other effluent materials from the water molecules.