TEKS 8.6A
... air pressure changing during the process of inhaling and exhaling (respiration)? The air pressure is greater during exhalation and less during inhalation. Breathing occurs because of changes in air pressure. At rest, the air pressure inside the lungs is equal to the atmospheric pressure outside of t ...
... air pressure changing during the process of inhaling and exhaling (respiration)? The air pressure is greater during exhalation and less during inhalation. Breathing occurs because of changes in air pressure. At rest, the air pressure inside the lungs is equal to the atmospheric pressure outside of t ...
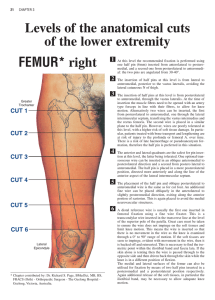
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the lower extremity
... motion. Alternatively two wires can be inserted, the first from posterolateral to anteromedial, one through the lateral intermuscular septum, transfixing the vastus intermedius and the rectus femoris. The second wire is placed in a similar plane to the half pin. However, wires are poorly tolerated a ...
... motion. Alternatively two wires can be inserted, the first from posterolateral to anteromedial, one through the lateral intermuscular septum, transfixing the vastus intermedius and the rectus femoris. The second wire is placed in a similar plane to the half pin. However, wires are poorly tolerated a ...
PART II - LWW.com
... muscle, referral sensation projects to the angle of the neck/ shoulder (crook of the neck area), with a spillover zone next to the vertebral border of the scapula and across the posterior shoulder. Referrals from these trigger points are some of the most important causes of neck pain and, at times, ...
... muscle, referral sensation projects to the angle of the neck/ shoulder (crook of the neck area), with a spillover zone next to the vertebral border of the scapula and across the posterior shoulder. Referrals from these trigger points are some of the most important causes of neck pain and, at times, ...
Biomechanics Kinesiology
... o Anteversion: greater than 15 (compensates by internally rotating tibia) o Retroversion: less than 8 (may present with ext. rotated limb) Neutral Pelvis: ASIS and pubic symphysis should be in a vertical line, PSIS is lower than ASIS in horizontal plane Anterior Pelvic Tilt: ASIS in front of pubic ...
... o Anteversion: greater than 15 (compensates by internally rotating tibia) o Retroversion: less than 8 (may present with ext. rotated limb) Neutral Pelvis: ASIS and pubic symphysis should be in a vertical line, PSIS is lower than ASIS in horizontal plane Anterior Pelvic Tilt: ASIS in front of pubic ...
CAT DISSECTION A LABORATORY GUIDE
... platysma, are attached to the undersurface of the skin and will be removed as you peel away the skin. 6. Continue peeling the skin until it is only attached at the face and the tail. Cut around the base of the tail, leaving the skin on the tail. Cut the skin around the face of the cat, leaving the s ...
... platysma, are attached to the undersurface of the skin and will be removed as you peel away the skin. 6. Continue peeling the skin until it is only attached at the face and the tail. Cut around the base of the tail, leaving the skin on the tail. Cut the skin around the face of the cat, leaving the s ...
Two Part Pterional Craniotomy
... approach elegantly provides access to the optic nerves, chiasm, lamina terminalis, cavernous sinus, as well as the circle of Willis. Further testament to its versatility is how commonly and easily it can be combined with other approaches. Nowhere is this highlighted better, than the orbitozygomatic ...
... approach elegantly provides access to the optic nerves, chiasm, lamina terminalis, cavernous sinus, as well as the circle of Willis. Further testament to its versatility is how commonly and easily it can be combined with other approaches. Nowhere is this highlighted better, than the orbitozygomatic ...
Morphology of the melon and its tendinous connections
... upon by facial muscles (rostral, pars anterointernus, and nasal plug muscles). The goals of this study were to investigate the gross morphology of the melon in the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) and to describe how it is tendinously connected to these facial muscles. Standard gross dissecti ...
... upon by facial muscles (rostral, pars anterointernus, and nasal plug muscles). The goals of this study were to investigate the gross morphology of the melon in the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) and to describe how it is tendinously connected to these facial muscles. Standard gross dissecti ...
Anatomical variations and congenital anomalies of the
... Hemivertebra is one of the most common vertebral anomalies. It results from unilateral failure of vertebral formation, in witch only one half of the vertebra body develops. Hemivertebra is a common cause of congenital scoliosis. It can associate with other anomalies of the spine, ribs, heart and gen ...
... Hemivertebra is one of the most common vertebral anomalies. It results from unilateral failure of vertebral formation, in witch only one half of the vertebra body develops. Hemivertebra is a common cause of congenital scoliosis. It can associate with other anomalies of the spine, ribs, heart and gen ...
how voices work - James Daugherty
... connect to the cricoid cartilage via the cricoarytenoid joints. Each of the three-sided, pyramidshaped arytenoid cartilages has four surfaces: anterior, lateral, medial, and a base. The arytenoid cartilages can move rather rapidly on two planes: (a) sideways, or laterally, to and from a midline poin ...
... connect to the cricoid cartilage via the cricoarytenoid joints. Each of the three-sided, pyramidshaped arytenoid cartilages has four surfaces: anterior, lateral, medial, and a base. The arytenoid cartilages can move rather rapidly on two planes: (a) sideways, or laterally, to and from a midline poin ...
Neuraxial Blockade Anatomy and Landmarks
... Posterior spinal arteries are formed by posterior cerebellar arteries and travel down the dorsal surface of the spinal cord just medial to the dorsal nerve roots. They supply 1/3rd of the posterior cord. Additional blood flow is contributed by the anterior and posterior spinal arteries from the inte ...
... Posterior spinal arteries are formed by posterior cerebellar arteries and travel down the dorsal surface of the spinal cord just medial to the dorsal nerve roots. They supply 1/3rd of the posterior cord. Additional blood flow is contributed by the anterior and posterior spinal arteries from the inte ...
Anatomy and Injuries of the Knee - Wright Wonders
... immobilize in position you find it Ice ER visit After reduction, immobilize in extension about 4 weeks—use crutches Strengthen muscles of knee, thigh and hip ...
... immobilize in position you find it Ice ER visit After reduction, immobilize in extension about 4 weeks—use crutches Strengthen muscles of knee, thigh and hip ...
Orthopaedic trauma - Home - Qassim College of Medicine
... CHANGE IN ANATOMICAL POSITION Length Distraction Shortening over-riding impacted ...
... CHANGE IN ANATOMICAL POSITION Length Distraction Shortening over-riding impacted ...
physicianlecture day 2015
... ▸ Fibers run from 1 transverse process to the spinous process superior to them ...
... ▸ Fibers run from 1 transverse process to the spinous process superior to them ...
Thigh & Popliteal fossa
... Passes under the inguinal ligament. Enters the femoral triangle midpoint of the inguinal ligament (midway between ASIS & pubic tubercle). Continues down the thigh in the adductor canal. ...
... Passes under the inguinal ligament. Enters the femoral triangle midpoint of the inguinal ligament (midway between ASIS & pubic tubercle). Continues down the thigh in the adductor canal. ...
FREE Sample Here
... 24) In describing the relationship between the patellar and popliteal regions: A) the patellar region is superior to the popliteal region B) the patellar region is proximal to the popliteal region C) the patellar region is distal to the popliteal region D) the patellar region is lateral to the popli ...
... 24) In describing the relationship between the patellar and popliteal regions: A) the patellar region is superior to the popliteal region B) the patellar region is proximal to the popliteal region C) the patellar region is distal to the popliteal region D) the patellar region is lateral to the popli ...
Investigation of Insufficient Lumbopelvic Stability in Low Back Pain
... There are different definitions of low back pain depending on the choice of the source. According to the European Guidelines for prevention of low back pain, low back pain is defined as “pain and discomfort, localized below de costal margin and above the inferior gluteal folds, with or without leg p ...
... There are different definitions of low back pain depending on the choice of the source. According to the European Guidelines for prevention of low back pain, low back pain is defined as “pain and discomfort, localized below de costal margin and above the inferior gluteal folds, with or without leg p ...
Visceral motor Nerves
... The regularity of the distribution of the preganglionic and postganglionic fibers. ①After the preganglionic fibers from the intermediolateral nuclei of the 1st to 5th thoracic segments of spinal cord interchange neurons, the postgnglionic fibers are distributed in the visceral organs of the head, ne ...
... The regularity of the distribution of the preganglionic and postganglionic fibers. ①After the preganglionic fibers from the intermediolateral nuclei of the 1st to 5th thoracic segments of spinal cord interchange neurons, the postgnglionic fibers are distributed in the visceral organs of the head, ne ...
Peritoneum and Intraperitoneal Viscera
... 3.1.1 Development of the Digestive Tube Until the end of the second gestational week, the embryonic disk (blastodisk) consists of two germ layers, the endoderm and ectoderm, separated from each other by a basal membrane. Both germ layers participate in forming the third layer, the mesoderm, which d ...
... 3.1.1 Development of the Digestive Tube Until the end of the second gestational week, the embryonic disk (blastodisk) consists of two germ layers, the endoderm and ectoderm, separated from each other by a basal membrane. Both germ layers participate in forming the third layer, the mesoderm, which d ...
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb)
... 25) In describing the relationship of the thoracic and spinal cavities: A) the thoracic cavity is superior to the spinal cavity B) the thoracic cavity is inferior to the spinal cavity C) the thoracic cavity is proximal to the spinal cavity D) the thoracic cavity is medial to the spinal cavity E) the ...
... 25) In describing the relationship of the thoracic and spinal cavities: A) the thoracic cavity is superior to the spinal cavity B) the thoracic cavity is inferior to the spinal cavity C) the thoracic cavity is proximal to the spinal cavity D) the thoracic cavity is medial to the spinal cavity E) the ...
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb)
... 25) In describing the relationship of the thoracic and spinal cavities: A) the thoracic cavity is superior to the spinal cavity B) the thoracic cavity is inferior to the spinal cavity C) the thoracic cavity is proximal to the spinal cavity D) the thoracic cavity is medial to the spinal cavity E) the ...
... 25) In describing the relationship of the thoracic and spinal cavities: A) the thoracic cavity is superior to the spinal cavity B) the thoracic cavity is inferior to the spinal cavity C) the thoracic cavity is proximal to the spinal cavity D) the thoracic cavity is medial to the spinal cavity E) the ...
Branches of axillary artery for PDF 13.5.11
... divides branches. (i)side clavicular, up over subclavius ; (ii) pectoral largesurface and runs into two, one goes toruns the side of the chest, the other to theisdeep of The axillary artery across thewith superior aspect ofanterior the axilla is marked by the latissimus down between with the runs th ...
... divides branches. (i)side clavicular, up over subclavius ; (ii) pectoral largesurface and runs into two, one goes toruns the side of the chest, the other to theisdeep of The axillary artery across thewith superior aspect ofanterior the axilla is marked by the latissimus down between with the runs th ...
ORBIT MBBS QAD Series 1. Which of the following statement is true
... The animal which sexes can be differentiated from external morphology is: Taenia (b) Krait (c) Ascaris (d) Sea anemone Filaria can be eradicated if the population of following is exterminated Cockroach (b) Housefly (c) Culex mosquito (d)Anopheles mosquito Which one of the following is true for Ascar ...
... The animal which sexes can be differentiated from external morphology is: Taenia (b) Krait (c) Ascaris (d) Sea anemone Filaria can be eradicated if the population of following is exterminated Cockroach (b) Housefly (c) Culex mosquito (d)Anopheles mosquito Which one of the following is true for Ascar ...
mandible — clinically revisited
... Development of the chin is then a symptom of general phylogenetic adaptation of the skull. Widening of the brain box, especially in its anterior part cause in a consequence change in the face width, i.e. upper jaws and palate, and the mandible had to follow these changes. Development of the mandible ...
... Development of the chin is then a symptom of general phylogenetic adaptation of the skull. Widening of the brain box, especially in its anterior part cause in a consequence change in the face width, i.e. upper jaws and palate, and the mandible had to follow these changes. Development of the mandible ...
Normal peripheral nerves around the knee on 3D high resolution
... symptoms and signs and the determination of surgery and injection plan. Also anatomical information of small peripheral nerves around knee can be used for the detection of those nerves on knee ultrasonography, which frequently is used for intervention of nerve block. ...
... symptoms and signs and the determination of surgery and injection plan. Also anatomical information of small peripheral nerves around knee can be used for the detection of those nerves on knee ultrasonography, which frequently is used for intervention of nerve block. ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.