Slide 1 - cox-radiology.org
... •The Pleural cavity derivatives are derived from splitting of the lateral mesoderm into splanchnic and somatic layers. •The paired cavities are separated by 3 partition into 3 subdivision: Pericardial, Pleural, and Peritoneal cavity •The three partition are: The Unpaired septum transversum, the Pair ...
... •The Pleural cavity derivatives are derived from splitting of the lateral mesoderm into splanchnic and somatic layers. •The paired cavities are separated by 3 partition into 3 subdivision: Pericardial, Pleural, and Peritoneal cavity •The three partition are: The Unpaired septum transversum, the Pair ...
- University of Glasgow
... documented. Three dimensional models of the superior and inferior lumbar articular facets were created by Microscribe. This allowed calculation of the facet orientation and surface area by Rhinoceros software. The surface area was increased towards the inferior vertebral levels, while the orientatio ...
... documented. Three dimensional models of the superior and inferior lumbar articular facets were created by Microscribe. This allowed calculation of the facet orientation and surface area by Rhinoceros software. The surface area was increased towards the inferior vertebral levels, while the orientatio ...
* The function of extensor digitorum :
... •It is originated from medial cord of brachial plexus. •In the upper part of the upper arm it is anterior. •In the midshaft : it pierces the medial intermuscular septum. •In the lower part: it is in the posterior compartment. •It then passes posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus. •It doe ...
... •It is originated from medial cord of brachial plexus. •In the upper part of the upper arm it is anterior. •In the midshaft : it pierces the medial intermuscular septum. •In the lower part: it is in the posterior compartment. •It then passes posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus. •It doe ...
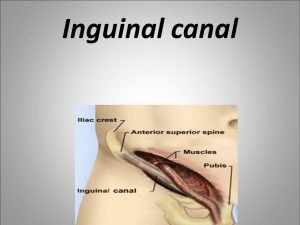
Inguinal canal
... • As the plexus ascends, it becomes reduced in size so that at about the level of deep inguinal ring, a single testicular vein is formed • Drains into left renal vein on left side and inferior vena cava on right side ...
... • As the plexus ascends, it becomes reduced in size so that at about the level of deep inguinal ring, a single testicular vein is formed • Drains into left renal vein on left side and inferior vena cava on right side ...
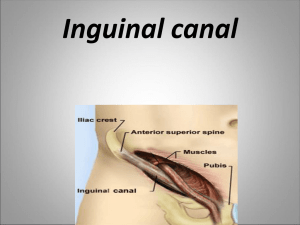
Inguinal canal
... • As the plexus ascends, it becomes reduced in size so that at about the level of deep inguinal ring, a single testicular vein is formed • Drains into left renal vein on left side and inferior vena cava on right side ...
... • As the plexus ascends, it becomes reduced in size so that at about the level of deep inguinal ring, a single testicular vein is formed • Drains into left renal vein on left side and inferior vena cava on right side ...
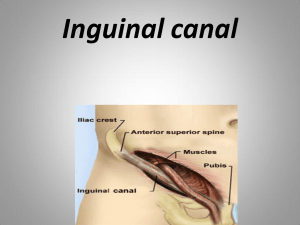
Inguinal canal
... • As the plexus ascends, it becomes reduced in size so that at about the level of deep inguinal ring, a single testicular vein is formed • Drains into left renal vein on left side and inferior vena cava on right side ...
... • As the plexus ascends, it becomes reduced in size so that at about the level of deep inguinal ring, a single testicular vein is formed • Drains into left renal vein on left side and inferior vena cava on right side ...
Abdominal Sonography 1 Pancreas Part 1 2017
... the pancreatic tail), a technique is used in which the patient in left lateral decubitus position, drinks water to fill the stomach. While scanning the pancreas, the patient is then turned to the supine or right lateral decubitus position. Water in the stomach and duodenum is used as an acoustic w ...
... the pancreatic tail), a technique is used in which the patient in left lateral decubitus position, drinks water to fill the stomach. While scanning the pancreas, the patient is then turned to the supine or right lateral decubitus position. Water in the stomach and duodenum is used as an acoustic w ...
OF THE TIBIO-FIBULAR LIGAMENTS
... to the ankle, of all three ligaments by an abduction strain. Often there is a fracture of the posterior surface of the tibia-the so-called posterior malleolar fracture. The mechanism of this fracture is uncertain ; the fragment is either pulled off ...
... to the ankle, of all three ligaments by an abduction strain. Often there is a fracture of the posterior surface of the tibia-the so-called posterior malleolar fracture. The mechanism of this fracture is uncertain ; the fragment is either pulled off ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... root) is the smaller branch of the spinal nerve, which passes posteriorly through the paravertebral musculature and itself splits into a medial and a lateral branch, both of which innervate the Intrinsic back muscles, but only one of which continues to the skin. ...
... root) is the smaller branch of the spinal nerve, which passes posteriorly through the paravertebral musculature and itself splits into a medial and a lateral branch, both of which innervate the Intrinsic back muscles, but only one of which continues to the skin. ...
STUDY THIS FOR THE TEST! PRACTICE! HAS ANSWERS!!! File
... Found in the fetal skeleton & connects the ribs to the sternum. ...
... Found in the fetal skeleton & connects the ribs to the sternum. ...
appendix 5 - Anal IMRT Guidance
... External genitalia: Delineation of the male genitalia should include the penis and scrotum out laterally to the inguinal creases. In woman it should include the clitoris, labia majora and minora, out to the inguinal creases. Superior border in both sexes should lie midway through the symphysis pubis ...
... External genitalia: Delineation of the male genitalia should include the penis and scrotum out laterally to the inguinal creases. In woman it should include the clitoris, labia majora and minora, out to the inguinal creases. Superior border in both sexes should lie midway through the symphysis pubis ...
Bodily Systems and the Spatial-Functional
... that the body lends itself to partitioning into bodily systems and sub-systems (along the lines described below), but we recognize also that it lends itself also to other sorts of partitions, for example into what anatomists call ‘regions,’ such as the foot, the left upper lobe of the lung and other ...
... that the body lends itself to partitioning into bodily systems and sub-systems (along the lines described below), but we recognize also that it lends itself also to other sorts of partitions, for example into what anatomists call ‘regions,’ such as the foot, the left upper lobe of the lung and other ...
The Cranial Nerves
... 12 pairs, (two are attached to the cerebrum and 10 are attached to the brain stem Nine are attached to the ventral surface of the brain stem, while one is attached to the back of the midbrain (Trochlear). They leave the cranial cavity by passing through small foramina in the skull bones Both ‘names’ ...
... 12 pairs, (two are attached to the cerebrum and 10 are attached to the brain stem Nine are attached to the ventral surface of the brain stem, while one is attached to the back of the midbrain (Trochlear). They leave the cranial cavity by passing through small foramina in the skull bones Both ‘names’ ...
Vertebrate$`Relationships
... This anterior elongation of the notochord apparently is a specialization that aids in burrowing. Figure 2-2c shows some details of the internal structure of amphioxus. Amphioxus and vertebrates differ in the use of the pharyngeal slits. Amphioxus has no gill tissue associated with these slits; its b ...
... This anterior elongation of the notochord apparently is a specialization that aids in burrowing. Figure 2-2c shows some details of the internal structure of amphioxus. Amphioxus and vertebrates differ in the use of the pharyngeal slits. Amphioxus has no gill tissue associated with these slits; its b ...
The Arteries动脉
... opening Here it is continuous with the femoral artery Ends at the lower border of the popliteus where it divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries ...
... opening Here it is continuous with the femoral artery Ends at the lower border of the popliteus where it divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries ...
Cervical anatomy - Fisiokinesiterapia
... 2) Posterior Spinal A: (may also arise from intradural VA or off PICA): courses medially, and upon reaching the lower medulla, divides into an ascending and descending branches Ascending branch: through foramen magnum → restiform body, gracile and cuneat tubercles, rootlets of XI, and choroid plexus ...
... 2) Posterior Spinal A: (may also arise from intradural VA or off PICA): courses medially, and upon reaching the lower medulla, divides into an ascending and descending branches Ascending branch: through foramen magnum → restiform body, gracile and cuneat tubercles, rootlets of XI, and choroid plexus ...
Name: B2 6 Mark Questions Date: Time: Total marks available: Total
... (ii) John washes his clothes using a biological washing powder on a 60 °C washing programme. Explain why the clothes were not washed as well as he had hoped. ...
... (ii) John washes his clothes using a biological washing powder on a 60 °C washing programme. Explain why the clothes were not washed as well as he had hoped. ...
FEMORAL TRIANGLE BOUNDARIES OF THE TRIANGLE FLOOR
... • Medial wall : pectineus and adductor longus • Lateral wall : iliopsoas and sartorius • Femoral artery and vein lie anterior to the fascia covering iliopsoas and pectineus muscles • Femoral nerve lies posterior to the fascia ...
... • Medial wall : pectineus and adductor longus • Lateral wall : iliopsoas and sartorius • Femoral artery and vein lie anterior to the fascia covering iliopsoas and pectineus muscles • Femoral nerve lies posterior to the fascia ...
2 m – 35. Spinal nerves. Cervical plexus
... C3-C4: Levator scapulae, trapezius and scalenus medius The middle and anterior scalenus muscles also receive innervation directly from the cervical plexus. The cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus supply the skin of the neck, upper thorax, scalp and ear. These nerves all enter the skin at the m ...
... C3-C4: Levator scapulae, trapezius and scalenus medius The middle and anterior scalenus muscles also receive innervation directly from the cervical plexus. The cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus supply the skin of the neck, upper thorax, scalp and ear. These nerves all enter the skin at the m ...
Elbow and Forearm
... b. Its palmar cutaneous branch arises proximal to the carpal tunnel <= c. It divides into lateral and medial branches distal to the carpal tunnel – it does, but also the recurrent d. It is the sole nerve supply to the flexors of the forearm e. ? 8. Elbow capsule attachments include: a. Medial and la ...
... b. Its palmar cutaneous branch arises proximal to the carpal tunnel <= c. It divides into lateral and medial branches distal to the carpal tunnel – it does, but also the recurrent d. It is the sole nerve supply to the flexors of the forearm e. ? 8. Elbow capsule attachments include: a. Medial and la ...
Head and Neck
... The frontal bone formed the forehead the two halves fail to fuse leaving a midline metopic suture, and forms the upper margins of the orbits and formed the supraorbital ridge. The supraorbital notch or foramen can be recognized medially. There are two zygomatic process of frontal bone and suture lat ...
... The frontal bone formed the forehead the two halves fail to fuse leaving a midline metopic suture, and forms the upper margins of the orbits and formed the supraorbital ridge. The supraorbital notch or foramen can be recognized medially. There are two zygomatic process of frontal bone and suture lat ...
Anatomy and Embryology of the Colon, Rectum, and Anus
... Epithelium of the Anal Canal The lining of the anal canal consists of an upper mucosal (endoderm) and a lower cutaneous (ectoderm) segment (Figure 1-1). The dentate (pectinate) line is the “saw-toothed” junction between these two distinct origins of venous and lymphatic drainage, nerve supply, and e ...
... Epithelium of the Anal Canal The lining of the anal canal consists of an upper mucosal (endoderm) and a lower cutaneous (ectoderm) segment (Figure 1-1). The dentate (pectinate) line is the “saw-toothed” junction between these two distinct origins of venous and lymphatic drainage, nerve supply, and e ...
Chapter 7
... Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the ...
... Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the ...
Orthotics Best Practice Group Spinal Manual
... The vertebral arch extends posteriorly from the body of the vertebra. With the body of the vertebra, it surrounds the spinal cord. It is formed by the pedicles, two short rounded processes that extend posteriorly from the lateral margin of the dorsal surface of the body and unite with the laminae, t ...
... The vertebral arch extends posteriorly from the body of the vertebra. With the body of the vertebra, it surrounds the spinal cord. It is formed by the pedicles, two short rounded processes that extend posteriorly from the lateral margin of the dorsal surface of the body and unite with the laminae, t ...
Emergency Department Radiography
... – Canale view (Maximal PF and Inv 15°)= talar neck – Harris-Beath view = body of calcaneous, middle and posterior facets of the subtalar joint – Broden’s view = generally CT used instead ...
... – Canale view (Maximal PF and Inv 15°)= talar neck – Harris-Beath view = body of calcaneous, middle and posterior facets of the subtalar joint – Broden’s view = generally CT used instead ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.