Muscle Activity Objectives SKELETAL MUSCLE ACTIVITY Definitions
... successfully slide, sarcomere shortens & movement occurs – Bending knee or elbow ...
... successfully slide, sarcomere shortens & movement occurs – Bending knee or elbow ...
Respiratory System: Practice Questions #1
... block the transmission of impulses that regulate breathing lower blood pressure in the mucous membranes of the bronchioles ...
... block the transmission of impulses that regulate breathing lower blood pressure in the mucous membranes of the bronchioles ...
Special Membranes
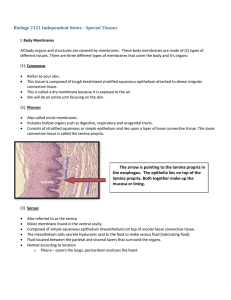
... Biology 2121 Independent Notes – Special Tissues I. Body Membranes All body organs and structures are covered by membranes. These body membranes are made of (2) types of different tissues. There are three different types of membranes that cover the body and it’s organs: (1). Cutaneous ...
... Biology 2121 Independent Notes – Special Tissues I. Body Membranes All body organs and structures are covered by membranes. These body membranes are made of (2) types of different tissues. There are three different types of membranes that cover the body and it’s organs: (1). Cutaneous ...
Cells
... o stores calcium and other minerals until the body needs them o protects internal organs skull protects brain ribs protect heart and lungs o produces blood cells – made by bone marrow which is found at the center of the bone Joints hold your bones together and allow them to move o ball and socke ...
... o stores calcium and other minerals until the body needs them o protects internal organs skull protects brain ribs protect heart and lungs o produces blood cells – made by bone marrow which is found at the center of the bone Joints hold your bones together and allow them to move o ball and socke ...
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
... 2. Compact bone-gives the body _________ 3. _Spongy_______ bone-open spaces that make bones lightweight (marrow) 4. _Cartilage_________-smooth thick flexible tissue that covers end of bone II. MUSCULAR SYSTEM A. Major Function-Provides __Movement_________ B. Two types muscles- ___Voluntary___are mus ...
... 2. Compact bone-gives the body _________ 3. _Spongy_______ bone-open spaces that make bones lightweight (marrow) 4. _Cartilage_________-smooth thick flexible tissue that covers end of bone II. MUSCULAR SYSTEM A. Major Function-Provides __Movement_________ B. Two types muscles- ___Voluntary___are mus ...
Class #9 Chest Muscles and Bones
... Manubrium: Clavicular notch Jugular notch Body: sternal angle- where 2nd rib attaches to the body, it’s where the heart is. Xiphoid Process: be cautious of this during CPR, landmark for hand placement ...
... Manubrium: Clavicular notch Jugular notch Body: sternal angle- where 2nd rib attaches to the body, it’s where the heart is. Xiphoid Process: be cautious of this during CPR, landmark for hand placement ...
Slide ()
... Anatomy and function of extraocular muscles. A: Extraocular muscles in the right orbit (lateral view). B: An illustration of the right eye viewed from above in the primary position (center figure) showing the angle of attachment of the superior and inferior rectus muscles and the superior and inferi ...
... Anatomy and function of extraocular muscles. A: Extraocular muscles in the right orbit (lateral view). B: An illustration of the right eye viewed from above in the primary position (center figure) showing the angle of attachment of the superior and inferior rectus muscles and the superior and inferi ...
Nervous System - Renton School District
... The Size of the Human Brain • The average adult human brain weighs in at 1300 to 1400 grams, or around 3 pounds. • In terms of length, the average brain is around 15 centimeters long (5 inches). • For comparison… A newborn human baby's brain weighs approximately 350 to 400 grams, or three-quarters ...
... The Size of the Human Brain • The average adult human brain weighs in at 1300 to 1400 grams, or around 3 pounds. • In terms of length, the average brain is around 15 centimeters long (5 inches). • For comparison… A newborn human baby's brain weighs approximately 350 to 400 grams, or three-quarters ...
Lumbar Hypermobility - therapyinmotion.net
... Hypermobility is increased movement compared to what is expected. Differences in how the segments are moving may occur at one joint, one segment, in just one direction of movement, or as a more generalized phenomenon throughout the body. Hypermobility can be congenital or can occur due to trauma exp ...
... Hypermobility is increased movement compared to what is expected. Differences in how the segments are moving may occur at one joint, one segment, in just one direction of movement, or as a more generalized phenomenon throughout the body. Hypermobility can be congenital or can occur due to trauma exp ...
Unit 6 Human Body & Organ Systems
... i. Responds to higher levels of carbon dioxide by sending nerve signals to rib muscles and diaphragm ii.Nerve signals cause these muscles to contract and you inhale ...
... i. Responds to higher levels of carbon dioxide by sending nerve signals to rib muscles and diaphragm ii.Nerve signals cause these muscles to contract and you inhale ...
Jon Storm-Mathisen - Universitetet i Oslo
... You must know a fair number of names to able to communicate.. ..but don’t get lost in details The real challenge is to establish ones own internal three-dimensional pictures Therefore: spend ample time with prosected specimens, models and microscopic slides ...
... You must know a fair number of names to able to communicate.. ..but don’t get lost in details The real challenge is to establish ones own internal three-dimensional pictures Therefore: spend ample time with prosected specimens, models and microscopic slides ...
POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL
... Invests the surface of muscles. Attached to the vertebral bodies, fibrous arches and transverse process and iliopubiceminence. Retains pus. Cold abscess. It is not part of lumbar fascia. Its lateral edges blends with anterior layers of that fascia (over quadratus lumborum muscle). Psoa ...
... Invests the surface of muscles. Attached to the vertebral bodies, fibrous arches and transverse process and iliopubiceminence. Retains pus. Cold abscess. It is not part of lumbar fascia. Its lateral edges blends with anterior layers of that fascia (over quadratus lumborum muscle). Psoa ...
Practice Quiz
... 11. The concentric rings observed in a typical cross-section through bone are called ____________________. 12. ___________________ muscle is involuntary and lacks striations. 13. ____________________ processes of the neuron always transmit impulses towards the cell body. 14. Dense connective tissue ...
... 11. The concentric rings observed in a typical cross-section through bone are called ____________________. 12. ___________________ muscle is involuntary and lacks striations. 13. ____________________ processes of the neuron always transmit impulses towards the cell body. 14. Dense connective tissue ...
Appendicular Skeleton
... • Rotation-moving a bone around its longitudinal axis • Circumduction-flexsion, extention, abduction, and adduction of a limb that moves distal end of limb in a circle • Pronation-movement of palm of hand to the posterior facing position • Supination-movement of the palm of the hand to the anterior ...
... • Rotation-moving a bone around its longitudinal axis • Circumduction-flexsion, extention, abduction, and adduction of a limb that moves distal end of limb in a circle • Pronation-movement of palm of hand to the posterior facing position • Supination-movement of the palm of the hand to the anterior ...
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles
... involved in elevating the shoulders that tends to join the upper trapezius muscle and take over when performing exercises involving shoulder horizontal adduction, forearm extension, and shoulder adduction is the levator scapulae muscle. The levator scapulae muscle is “a triangular muscle that origin ...
... involved in elevating the shoulders that tends to join the upper trapezius muscle and take over when performing exercises involving shoulder horizontal adduction, forearm extension, and shoulder adduction is the levator scapulae muscle. The levator scapulae muscle is “a triangular muscle that origin ...
Appendicular Skeleton made up of the and their ______
... The upper limb consists of the o arm (brachium)= __________________ o forearm (antebrachium)= ___________ & ______________ o hand (manus)= _____________, _____________ & _________________ _________ bones form _____________ upper limb Interosseous Membrane _____________________ membrane= “betwe ...
... The upper limb consists of the o arm (brachium)= __________________ o forearm (antebrachium)= ___________ & ______________ o hand (manus)= _____________, _____________ & _________________ _________ bones form _____________ upper limb Interosseous Membrane _____________________ membrane= “betwe ...
Unit 1: Organization of the Body
... hierarchy of structural organization, and homeostasis – will unify and form the basis for ...
... hierarchy of structural organization, and homeostasis – will unify and form the basis for ...
Anatomy Ch 1
... cavity – divided into two parts • Abdominal cavity – contains the liver, stomach, kidneys, and other organs • Pelvic cavity – contains the bladder, some reproductive organs, and rectum ...
... cavity – divided into two parts • Abdominal cavity – contains the liver, stomach, kidneys, and other organs • Pelvic cavity – contains the bladder, some reproductive organs, and rectum ...
anterior compartment of arm & cubital fossa
... when the forearm is supinated. Functionally, this action is performed when lifting an object, such as a bag of groceries or when performing a biceps curl. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps unscrews the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (fl ...
... when the forearm is supinated. Functionally, this action is performed when lifting an object, such as a bag of groceries or when performing a biceps curl. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps unscrews the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (fl ...
File
... 1- Flexors of the neck Sternocleidomastoid muscle Scalene muscles: (Anterior, middle and posterior) 2- Extensor of the neck Trapezius muscle Splenius capitis 3- The infrahyoid muscles (strap muscles) Are a group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck. The four infrahyoid ...
... 1- Flexors of the neck Sternocleidomastoid muscle Scalene muscles: (Anterior, middle and posterior) 2- Extensor of the neck Trapezius muscle Splenius capitis 3- The infrahyoid muscles (strap muscles) Are a group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck. The four infrahyoid ...
Name - MrDenning
... Questions to be answered… most of them can be answered by reading the material above. Some of the questions can be answered while watching the DVD in class. 1. What is the role of the lungs? 2. Why are tears important? 3. How many bones comprise the human body? 4. How many muscles does the human bod ...
... Questions to be answered… most of them can be answered by reading the material above. Some of the questions can be answered while watching the DVD in class. 1. What is the role of the lungs? 2. Why are tears important? 3. How many bones comprise the human body? 4. How many muscles does the human bod ...
Unit 30: Chapter 4 (Back): (p. 482
... ARTICULAR SURFACES - intervertebral disc - for (zyg)apophyseal or "facet" joints - for ribs (thoracic vertebra) Compare and contrast the following groups of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae: Upper Thoracic, Middle Thoracic, Lower Thoracic, Upper Lumbar & Lower Lumbar Define the boundaries of an interve ...
... ARTICULAR SURFACES - intervertebral disc - for (zyg)apophyseal or "facet" joints - for ribs (thoracic vertebra) Compare and contrast the following groups of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae: Upper Thoracic, Middle Thoracic, Lower Thoracic, Upper Lumbar & Lower Lumbar Define the boundaries of an interve ...
Medical Terminology for the Vocational Professional
... Now that you are more familiar with medical terminology you should be able to decipher the description of any testing referred to in medical ...
... Now that you are more familiar with medical terminology you should be able to decipher the description of any testing referred to in medical ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.