doc - CLAS Users
... lesser trochanter: Large blunt process on the posterior face of the femoral shaft, just below the neck, for attachment of muscles that flex the thigh. condyle: A smooth, rounded articular surface that is found in pairs (lateral and medial); distal end of femur. ...
... lesser trochanter: Large blunt process on the posterior face of the femoral shaft, just below the neck, for attachment of muscles that flex the thigh. condyle: A smooth, rounded articular surface that is found in pairs (lateral and medial); distal end of femur. ...
FREE Sample Here
... 13. The physical therapist performs auscultation of the lateral portion of right middle lobe. Which of the following stethoscope locations BEST identifies this lung segment? A. Adjacent to the 5th rib lateral right chest wall B. Adjacent to 3rd–5th rib posterior right chest wall C. Adjacent to the 4 ...
... 13. The physical therapist performs auscultation of the lateral portion of right middle lobe. Which of the following stethoscope locations BEST identifies this lung segment? A. Adjacent to the 5th rib lateral right chest wall B. Adjacent to 3rd–5th rib posterior right chest wall C. Adjacent to the 4 ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... 9. The sternum begins as a pair of longitudinal sternal bars of mesenchyme. These migrate medially and fuse as the ribs attach to them. Ossification is by the endochondral method, beginning in month 5 and concluding soon after birth. 10. Skull fractures may be linear (elongated cracks) or depressed ...
... 9. The sternum begins as a pair of longitudinal sternal bars of mesenchyme. These migrate medially and fuse as the ribs attach to them. Ossification is by the endochondral method, beginning in month 5 and concluding soon after birth. 10. Skull fractures may be linear (elongated cracks) or depressed ...
Lower Limb Kinesiology
... The anterior portion of the joint is reinforced by aponeurotic expansions from a number of muscles that cross the joint No Normally Movement Slipping of one pubic Pathology: to other (Osteitis Pubis) ...
... The anterior portion of the joint is reinforced by aponeurotic expansions from a number of muscles that cross the joint No Normally Movement Slipping of one pubic Pathology: to other (Osteitis Pubis) ...
Respiratory System
... • Inhalation is an active process; it requires ATP to fuel the muscles as they contract • Exhalation is a passive process; it occurs when the muscles relax, so there is no ATP used • During exercise or with some lung diseases (COPD), exhalation becomes an active process because accessory muscles mus ...
... • Inhalation is an active process; it requires ATP to fuel the muscles as they contract • Exhalation is a passive process; it occurs when the muscles relax, so there is no ATP used • During exercise or with some lung diseases (COPD), exhalation becomes an active process because accessory muscles mus ...
Bones of upper limb
... The head lies distally at the wrist. The articulations between the ulna & humerus at the elbow joint allows primarily only flexion & extension (small amount of abduction & adduction occurs). ...
... The head lies distally at the wrist. The articulations between the ulna & humerus at the elbow joint allows primarily only flexion & extension (small amount of abduction & adduction occurs). ...
MRI and NLS-diagnostics of ankle joint damages
... During analysis of virtual NLS-picture of ankle joint anterior part we see visualized tendons of anterior tibial muscle (m. tibialis anterior), long extensor muscle of fingers (m. extensor digitîrum longus) and tendon of long extensor muscle of toe (m. extensor hallucis longus). Tendon of anterior t ...
... During analysis of virtual NLS-picture of ankle joint anterior part we see visualized tendons of anterior tibial muscle (m. tibialis anterior), long extensor muscle of fingers (m. extensor digitîrum longus) and tendon of long extensor muscle of toe (m. extensor hallucis longus). Tendon of anterior t ...
Differences of anatomical landmarks among protocols after semantic
... fornices are seen in full profile on both sides [4, 10] ...
... fornices are seen in full profile on both sides [4, 10] ...
Full Text
... levator ani also obtains attachment to the ischial spine immediately ventral to the coccygeus muscle. The most superior part of the coccygeus muscle occupies a space at an angle between the pelvic splanchnic and pudendal nerves. Notably, medial to the coccygeus muscle, a third parasagittal muscle, i ...
... levator ani also obtains attachment to the ischial spine immediately ventral to the coccygeus muscle. The most superior part of the coccygeus muscle occupies a space at an angle between the pelvic splanchnic and pudendal nerves. Notably, medial to the coccygeus muscle, a third parasagittal muscle, i ...
Squint Eye Setup_Left inferior oblique
... remaining three rectus muscles 2 Insert medial rectus into marked hole. 3 Insert in turn. Make sure the oblique is positioned under the Inferior rectus. ...
... remaining three rectus muscles 2 Insert medial rectus into marked hole. 3 Insert in turn. Make sure the oblique is positioned under the Inferior rectus. ...
Posterior triangle of the neck
... 1. To become familiar with the surface anatomy of the posterior triangle of the neck. 2. To study the cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus that emerge from the posterior triangle and the cutaneous vessels of this region. 3. To become familiar with the boundaries of the posterior triangle of the ...
... 1. To become familiar with the surface anatomy of the posterior triangle of the neck. 2. To study the cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus that emerge from the posterior triangle and the cutaneous vessels of this region. 3. To become familiar with the boundaries of the posterior triangle of the ...
Human physiology is the science of the mechanical
... system of the body works in isolation, and the well-being of the person depends upon the well-being of all the interacting body systems. The traditional divisions by system are somewhat arbitrary. Many body parts participate in more than one system, and systems might be organized by function, by emb ...
... system of the body works in isolation, and the well-being of the person depends upon the well-being of all the interacting body systems. The traditional divisions by system are somewhat arbitrary. Many body parts participate in more than one system, and systems might be organized by function, by emb ...
Lower leg Exam Review
... • The purpose of the deltoid ligament is… • To limit eversion of the foot ...
... • The purpose of the deltoid ligament is… • To limit eversion of the foot ...
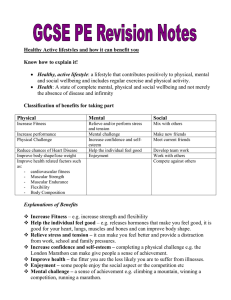
GCSE Revision bookle..
... Weights and reps depend on what you are trying to improve e.g. strength=more weight less reps; muscular endurance= lower weight more reps. Number of sets usually 2/3 e.g. 2 sets of 10 reps. Recovery should be about 1-2 min between sets. And frequency of training must allow for rest days or easier tr ...
... Weights and reps depend on what you are trying to improve e.g. strength=more weight less reps; muscular endurance= lower weight more reps. Number of sets usually 2/3 e.g. 2 sets of 10 reps. Recovery should be about 1-2 min between sets. And frequency of training must allow for rest days or easier tr ...
Word - Runcorn Rowing Club
... Please try to do the following stretches at least twice a week after any UT2 or UT1 sessions. Do the stretches immediately after your cool down. Each stretch should be held for 45 to 60 seconds and should be repeated three to five times at least. This session twice a week will help improve your post ...
... Please try to do the following stretches at least twice a week after any UT2 or UT1 sessions. Do the stretches immediately after your cool down. Each stretch should be held for 45 to 60 seconds and should be repeated three to five times at least. This session twice a week will help improve your post ...
DEEP MUSCLES - INTRODUCTION
... upon the proximal end of the humerus and acts as an adductor of the forelimb. Teres Major - This muscle originates upon imd covers the axillary posterior borders of the scapula. It inserts upon the humerus by means of a tendon in common with the latissimus dorsi. Its action is to rotate and flex the ...
... upon the proximal end of the humerus and acts as an adductor of the forelimb. Teres Major - This muscle originates upon imd covers the axillary posterior borders of the scapula. It inserts upon the humerus by means of a tendon in common with the latissimus dorsi. Its action is to rotate and flex the ...
Introduction to the Female Pelvis
... • Using the index, add and highlight the Rectum • Select the “Highlight” tool from the toolbar • Click on the uterus and vagina to highlight these structures Highlight structures or de-highlight a structure with the highlight tool ...
... • Using the index, add and highlight the Rectum • Select the “Highlight” tool from the toolbar • Click on the uterus and vagina to highlight these structures Highlight structures or de-highlight a structure with the highlight tool ...
Muscle Flaps - Alpha Hand Surgery Centre
... • 2/3 axons terminate as free endings in the connective tissue surrounding extrafusal and intrafusal muscIe fibers. These free ...
... • 2/3 axons terminate as free endings in the connective tissue surrounding extrafusal and intrafusal muscIe fibers. These free ...
Learning objectives
... Abduction- by the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus Lateral rotation- by the gluteus maximus, quadratus femoris, piriformis, obturator internus and externus, gemelli Medial rotation- by the anterior part of the glueteus minimus and medius and tensor fasciae latae muscles ...
... Abduction- by the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus Lateral rotation- by the gluteus maximus, quadratus femoris, piriformis, obturator internus and externus, gemelli Medial rotation- by the anterior part of the glueteus minimus and medius and tensor fasciae latae muscles ...
13. Surface Anatomy
... spinous process of the vertebra prominens (C7), especially during neck flexion. Palpate your nuchal region; the bump you feel at the inferior boundary of this region is the vertebra prominens. As you move your fingers superiorly along the midline of the neck, you can palpate the ligamentum nuchae, a ...
... spinous process of the vertebra prominens (C7), especially during neck flexion. Palpate your nuchal region; the bump you feel at the inferior boundary of this region is the vertebra prominens. As you move your fingers superiorly along the midline of the neck, you can palpate the ligamentum nuchae, a ...
28-duodenum & Pancreas
... the head ( the uncinate process ) extends to the left behind the superior mesenteric vessels. The neck is the constricted portion of the pancreas which connects the head to the body. It lies in front of the beginning of the portal vein and the origin of the superior mesenteric artery from the aorta. ...
... the head ( the uncinate process ) extends to the left behind the superior mesenteric vessels. The neck is the constricted portion of the pancreas which connects the head to the body. It lies in front of the beginning of the portal vein and the origin of the superior mesenteric artery from the aorta. ...
FREE Sample Here - Test bank Store
... Copyright ©2011, 2001, 1994 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. ...
... Copyright ©2011, 2001, 1994 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. ...
4.20.05 Histology and Digestion
... • The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm. • The upper abdominal cavity contains the stomach, liver, spleen, gall bladder, and most of the intestines. • The lower abdominal cavity contains the rectum, urinary bladder, and the rest of the ...
... • The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm. • The upper abdominal cavity contains the stomach, liver, spleen, gall bladder, and most of the intestines. • The lower abdominal cavity contains the rectum, urinary bladder, and the rest of the ...
Exercise 5 Bivalve Anatomy II: Crassostrea virginica, Argopecten
... Bivalves do not have obvious head or tail regions, but anatomical terms used to describe these areas in other animals are applied to them. The umbo or hinge area, where the valves are joined together, is the dorsal part of the animal (Figure 1). The region opposite is the ventral margin. In species ...
... Bivalves do not have obvious head or tail regions, but anatomical terms used to describe these areas in other animals are applied to them. The umbo or hinge area, where the valves are joined together, is the dorsal part of the animal (Figure 1). The region opposite is the ventral margin. In species ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.