BIO 218 F 2012 CH 12 Martini Lecture Outline
... Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy has practical applications An understanding is critical during medical examinations An understanding is essential for both invasive and noninvasive laboratory procedures An understandi ...
... Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy has practical applications An understanding is critical during medical examinations An understanding is essential for both invasive and noninvasive laboratory procedures An understandi ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 12 Martini Lecture Outline
... Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy has practical applications An understanding is critical during medical examinations An understanding is essential for both invasive and noninvasive laboratory procedures An understandi ...
... Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy has practical applications An understanding is critical during medical examinations An understanding is essential for both invasive and noninvasive laboratory procedures An understandi ...
Region 16: Kidneys and Retroperitoneal Structures Abdominal aorta
... a. hilus opens into renal sinus contains renal vessels, nerve, lymphathics, major and minor calyces, and renal pelvis (enlarged upper end of ureter) b. medulla: characterized by pyramids whose apexes project into minor calyx as a papilla and its base lies at corticomedullary junction c. pyramids ar ...
... a. hilus opens into renal sinus contains renal vessels, nerve, lymphathics, major and minor calyces, and renal pelvis (enlarged upper end of ureter) b. medulla: characterized by pyramids whose apexes project into minor calyx as a papilla and its base lies at corticomedullary junction c. pyramids ar ...
anatomy of female reproductive organs
... corpus. The area of insertion of each fallopian lube is termed the cornu. The fundus is the part above the cornu. Is tapers to a small central constricted area, the isthmus,and below this is the cervix. The cervix projects obliquely into the vagina and can be divided into vaginal and supravaginal po ...
... corpus. The area of insertion of each fallopian lube is termed the cornu. The fundus is the part above the cornu. Is tapers to a small central constricted area, the isthmus,and below this is the cervix. The cervix projects obliquely into the vagina and can be divided into vaginal and supravaginal po ...
Human Body Systems
... – Nerve cells (neurons) pass messages throughout the body along the spinal cord – Dendrites get messages from other neurons and give them to the cell body – Axon moves messages away from that neuron to other nerve cells ...
... – Nerve cells (neurons) pass messages throughout the body along the spinal cord – Dendrites get messages from other neurons and give them to the cell body – Axon moves messages away from that neuron to other nerve cells ...
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease? (COPD)
... There is no one definition of COPD. It is often referred to as a “mixing bowl”,” grab bag” or “catchall” for various lung disorders. Most frequently, it is described as a mixture of two disease states: chronic (obstructive) bronchitis and emphysema. COPD is most often the result of long time cigaret ...
... There is no one definition of COPD. It is often referred to as a “mixing bowl”,” grab bag” or “catchall” for various lung disorders. Most frequently, it is described as a mixture of two disease states: chronic (obstructive) bronchitis and emphysema. COPD is most often the result of long time cigaret ...
Anatomy of the Respiratory System in Children
... The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped organs made up of spongy, pinkish-gray tissue. They take up most of the space in the chest, or the thorax (the part of the body between the base of the neck and diaphragm). The lungs are enveloped in a membrane called the pleura. The lungs are separated from each ...
... The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped organs made up of spongy, pinkish-gray tissue. They take up most of the space in the chest, or the thorax (the part of the body between the base of the neck and diaphragm). The lungs are enveloped in a membrane called the pleura. The lungs are separated from each ...
Wall of pharynx A
... • Muscles of the Pharynx:- Two groups according to the orientation of muscle fibres • 1- constrictor muscles:- outer circular layer • They are found paired in the pharyngeal wall. • They constitute the principal components of the pharyngeal wall. • They are arranged in superior- inferior sequence. • ...
... • Muscles of the Pharynx:- Two groups according to the orientation of muscle fibres • 1- constrictor muscles:- outer circular layer • They are found paired in the pharyngeal wall. • They constitute the principal components of the pharyngeal wall. • They are arranged in superior- inferior sequence. • ...
Unusual origin of Abductor digiti minimi – A Case Report CASE
... areas where nerves pass through unyielding passages as in carpal tunnel and Guyon’s canal. Any external structure compressing median or ulnar nerves in the carpal or Guyon’s canal is responsible for neuropathies of these nerves. Compression of ulnar nerve is more frequent at cervical spine or elbow ...
... areas where nerves pass through unyielding passages as in carpal tunnel and Guyon’s canal. Any external structure compressing median or ulnar nerves in the carpal or Guyon’s canal is responsible for neuropathies of these nerves. Compression of ulnar nerve is more frequent at cervical spine or elbow ...
Muscular-Anatomy-Handout
... Elliott, J., G. Jull, J. T. Noteboom, R. Darnell, G. Galloway and W. W. Gibbon (2006). "Fatty infiltration in the cervical extensor muscles in persistent whiplash-associated disorders: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis." Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31(22): E847-855. ...
... Elliott, J., G. Jull, J. T. Noteboom, R. Darnell, G. Galloway and W. W. Gibbon (2006). "Fatty infiltration in the cervical extensor muscles in persistent whiplash-associated disorders: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis." Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31(22): E847-855. ...
14-PHARYNX2009-02-12 01:493.3 MB
... Medially by the aryepiglottic fold Laterally by the lamina of thyroid cartilage & the thyrohyoid membrane. • Branches of internal laryngeal (& recurrent laryngeal) nerve lie deep to the mucous membrane of the fossa and are vulnerable to injury during removal of a ...
... Medially by the aryepiglottic fold Laterally by the lamina of thyroid cartilage & the thyrohyoid membrane. • Branches of internal laryngeal (& recurrent laryngeal) nerve lie deep to the mucous membrane of the fossa and are vulnerable to injury during removal of a ...
Nasal Cavity - Cloudfront.net
... 1. What do you call the bones found within the nasal cavity? 2. What specific bone divides the nasal cavity into two sides? 3. The space at the back of the mouth is the________. 4. The spaces within the bones of the skull are called the ______________________ 5. What structure is known as the windpi ...
... 1. What do you call the bones found within the nasal cavity? 2. What specific bone divides the nasal cavity into two sides? 3. The space at the back of the mouth is the________. 4. The spaces within the bones of the skull are called the ______________________ 5. What structure is known as the windpi ...
Femoral nerve
... Long sensory nerve to the medial knee Also includes the four motor branches to the quadriceps femoris heads Rectus femoris enters on the superior deep surface of the muscle Vastus lateralis enters on the lower part of that muscle with the lateral circumflex femoral artery Vastus medialis branch ...
... Long sensory nerve to the medial knee Also includes the four motor branches to the quadriceps femoris heads Rectus femoris enters on the superior deep surface of the muscle Vastus lateralis enters on the lower part of that muscle with the lateral circumflex femoral artery Vastus medialis branch ...
Lecture 16 - Pelvis and Perineum: Introduction to Pelvis
... In common/loose usage, the term pelvis refers to a region—the pelvic region A part of the trunk inferior to the abdomen and superior to the lower limbs An area of transition where the trunk and the lower limbs meet Note that this definition of pelvis carries no real anatomical meaning, as it ...
... In common/loose usage, the term pelvis refers to a region—the pelvic region A part of the trunk inferior to the abdomen and superior to the lower limbs An area of transition where the trunk and the lower limbs meet Note that this definition of pelvis carries no real anatomical meaning, as it ...
Scapula
... a tear of the subclavian artery or brachial plexus injury, must be kept in mind when evaluating and treating ...
... a tear of the subclavian artery or brachial plexus injury, must be kept in mind when evaluating and treating ...
No Slide Title - Delmar Cengage Learning
... • Relax the muscles of animals that are undergoing surgery; used to prevent or treat muscle spasms • Work by disrupting the transmission of nerve impulses from the motor nerves to skeletal muscle fibers • Most are competitive nondepolarizers (compete with ACh for the same receptor sites) • Are also ...
... • Relax the muscles of animals that are undergoing surgery; used to prevent or treat muscle spasms • Work by disrupting the transmission of nerve impulses from the motor nerves to skeletal muscle fibers • Most are competitive nondepolarizers (compete with ACh for the same receptor sites) • Are also ...
Subrata Kumar Banerjea B.H.M.S Solved Papers on Anatomy
... (i) Posterior ramus of 1st cervical nerve or sub-occipital nerve, (ii) Anterior rami of 1st cervical nerve. Artery (iii) 3rd part of of vertebra? artery. Distinguishing Points (i) It has no body and no spine. (ii) It consists of— (A) 2 arches : anterior and posterior. (B) 2 lateral masses. Descripti ...
... (i) Posterior ramus of 1st cervical nerve or sub-occipital nerve, (ii) Anterior rami of 1st cervical nerve. Artery (iii) 3rd part of of vertebra? artery. Distinguishing Points (i) It has no body and no spine. (ii) It consists of— (A) 2 arches : anterior and posterior. (B) 2 lateral masses. Descripti ...
Slide ()
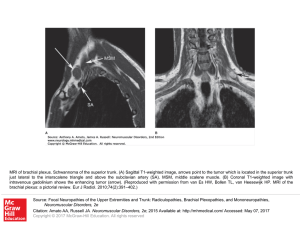
... MRI of brachial plexus. Schwannoma of the superior trunk. (A) Sagittal T1-weighted image, arrows point to the tumor which is located in the superior trunk just lateral to the interscalene triangle and above the subclavian artery (SA). MSM, middle scalene muscle. (B) Coronal T1-weighted image with in ...
... MRI of brachial plexus. Schwannoma of the superior trunk. (A) Sagittal T1-weighted image, arrows point to the tumor which is located in the superior trunk just lateral to the interscalene triangle and above the subclavian artery (SA). MSM, middle scalene muscle. (B) Coronal T1-weighted image with in ...
Pelvis and Perineum Pelvis - region of the trunk that is
... In females, the urterine arteries also send branches to the ureters Venous Drainage - parallels the arteries with similar names Lymph Drainage - into the external nodal network which includes: - lumbar lymph nodes - common iliac lymph nodes - external iliac lymph nodes - internal iliac lymph nodes ...
... In females, the urterine arteries also send branches to the ureters Venous Drainage - parallels the arteries with similar names Lymph Drainage - into the external nodal network which includes: - lumbar lymph nodes - common iliac lymph nodes - external iliac lymph nodes - internal iliac lymph nodes ...
Upper limb - Wikispaces
... 10. Biceps: scapula to radius- flex elbow 11. Triceps: scapula/humerus to ulna- extend elbow 12. Pronator: Medial humerus to radius- medial rotation of forearm (pronation) 13. Flexor carpi radialis: medial humerus to 2nd/3rd metacarpal- flex/abduct hand 14. Flexor Digitorum: medial humerus/ulna to p ...
... 10. Biceps: scapula to radius- flex elbow 11. Triceps: scapula/humerus to ulna- extend elbow 12. Pronator: Medial humerus to radius- medial rotation of forearm (pronation) 13. Flexor carpi radialis: medial humerus to 2nd/3rd metacarpal- flex/abduct hand 14. Flexor Digitorum: medial humerus/ulna to p ...
The Aponeurotic Roots of the Thoracolumbar
... glistening, which represent very much flattened tendons. They consist of closely packed, parallel, collagenous bundles, and by this characteristic may be differentiated from the fibrous membranes of fascia which have their collagenous more irregularly interwoven." ...
... glistening, which represent very much flattened tendons. They consist of closely packed, parallel, collagenous bundles, and by this characteristic may be differentiated from the fibrous membranes of fascia which have their collagenous more irregularly interwoven." ...
Ch._4_PPT.pptx
... Esophagus: After food becomes soft and moist, the tongue pushes it down to the esophagus. Rhythmic contractions of the smooth muscles push the food to the opening of the stomach ...
... Esophagus: After food becomes soft and moist, the tongue pushes it down to the esophagus. Rhythmic contractions of the smooth muscles push the food to the opening of the stomach ...
How Your Bones, Muscles, and Skin Interact with Other Body Systems
... skin do their jobs. Your digestive system provides the nutrients that the cells in your bones, muscles, and skin need in order to grow and repair themselves. • Your respiratory system provides oxygen to keep the cells in your bones, muscles, and skin healthy and growing. • Your circulatory system ca ...
... skin do their jobs. Your digestive system provides the nutrients that the cells in your bones, muscles, and skin need in order to grow and repair themselves. • Your respiratory system provides oxygen to keep the cells in your bones, muscles, and skin healthy and growing. • Your circulatory system ca ...
Unit 9L 4 Movement_bones1821
... 5.Some bones are filled with ______________________, which makes blood cells. ...
... 5.Some bones are filled with ______________________, which makes blood cells. ...
T Tongue :p
... 3) Deep : external carotid artery with its two terminations leaving the gland: superficial temporal artery and deeply, the maxillary artery. as a general rule: arteries are always deep to veins giving more protection to the arteries. WHY? Because arteries have higher blood pressure , if a problem oc ...
... 3) Deep : external carotid artery with its two terminations leaving the gland: superficial temporal artery and deeply, the maxillary artery. as a general rule: arteries are always deep to veins giving more protection to the arteries. WHY? Because arteries have higher blood pressure , if a problem oc ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.