Slide 1
... the two shoulders, especially on a patient with limited flexibility who cannot sufficiently depress the shoulder away from the IR. Optional Breathing Technique: If patient can cooperate and remain immobilized, a low mA and a 3- or 4-second exposure time can be used, with patient breathing short, eve ...
... the two shoulders, especially on a patient with limited flexibility who cannot sufficiently depress the shoulder away from the IR. Optional Breathing Technique: If patient can cooperate and remain immobilized, a low mA and a 3- or 4-second exposure time can be used, with patient breathing short, eve ...
Non Muscular Anatomy
... • Fibrocartilaginous ring around the acetabulum and transverse ligament • Deepens the hip joint increasing joint stability • Acts as a shock absorber • Decreases the force transmitted to the articular cartilage by increasing the surface area of the acetabulum • Provides a seal for the joint to maint ...
... • Fibrocartilaginous ring around the acetabulum and transverse ligament • Deepens the hip joint increasing joint stability • Acts as a shock absorber • Decreases the force transmitted to the articular cartilage by increasing the surface area of the acetabulum • Provides a seal for the joint to maint ...
The Skeletal System I. Introduction A. There are 206 bones in an
... B. Cranium – houses and protects the brain 1. Frontal bone – forms the forehead and the orbits of eyes; supraorbital margins (a ridge that protects the eyes) and supraorbital foramen (allows the artery and nerve to pass to the forehead) 2. Ethmoid – forms the roof of the nasal cavity; a very light b ...
... B. Cranium – houses and protects the brain 1. Frontal bone – forms the forehead and the orbits of eyes; supraorbital margins (a ridge that protects the eyes) and supraorbital foramen (allows the artery and nerve to pass to the forehead) 2. Ethmoid – forms the roof of the nasal cavity; a very light b ...
female genitalia
... Internal Parts: (see atlas) ureters, trigone area, orifice of ureter, internal urethral orifice, neck, apex, base (fundus), superior side, and 2 inferolateral sides. ...
... Internal Parts: (see atlas) ureters, trigone area, orifice of ureter, internal urethral orifice, neck, apex, base (fundus), superior side, and 2 inferolateral sides. ...
Axillary & Median Nerves
... to elbow joint, where branches innervate most of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm (except for the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle and the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus, which are innervated by the ulnar nerve). ...
... to elbow joint, where branches innervate most of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm (except for the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle and the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus, which are innervated by the ulnar nerve). ...
Femoral Nerve
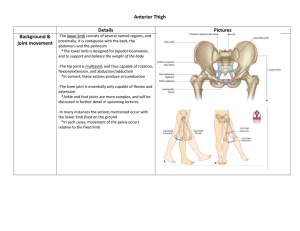
... -The lower limb consists of several named regions, and proximally, it is contiguous with the back, the abdomen, and the perineum *The lower limb is designed for bipedal locomotion, and to support and balance the weight of the body -The hip joint is multiaxial, and thus capable of rotation, flexion/e ...
... -The lower limb consists of several named regions, and proximally, it is contiguous with the back, the abdomen, and the perineum *The lower limb is designed for bipedal locomotion, and to support and balance the weight of the body -The hip joint is multiaxial, and thus capable of rotation, flexion/e ...
Skeletal System Part 3
... lungs, and great blood vessels Supports the shoulder girdles and upper limbs Provides attachment for many neck, back, chest, and shoulder muscles Uses intercostal muscles to lift and depress the thorax during breathing ...
... lungs, and great blood vessels Supports the shoulder girdles and upper limbs Provides attachment for many neck, back, chest, and shoulder muscles Uses intercostal muscles to lift and depress the thorax during breathing ...
Frog dissection - Canyons District Biology Resources
... subclavian (10) The sublavians supply blood to the arms and follow the clavicle bone 7. The common carotid, which will branch into the left (7) and right carotid arteries (8). The carotid arteries supply blood to the head and neck. 7. Observe the coronary vessels (6) on the outside of the heart - th ...
... subclavian (10) The sublavians supply blood to the arms and follow the clavicle bone 7. The common carotid, which will branch into the left (7) and right carotid arteries (8). The carotid arteries supply blood to the head and neck. 7. Observe the coronary vessels (6) on the outside of the heart - th ...
Document
... Descends between first dorsal interosseous muscle and oblique head of adductor pollicis, along medial side (ulnar side) of first metacarpal bone to the base of proximal phalanx Lies beneath tendon of flexor pollicis longus muscle, where it divides into two branches, which run along the sides of ...
... Descends between first dorsal interosseous muscle and oblique head of adductor pollicis, along medial side (ulnar side) of first metacarpal bone to the base of proximal phalanx Lies beneath tendon of flexor pollicis longus muscle, where it divides into two branches, which run along the sides of ...
pdf - Zill Anatomy Web Pages
... Flexor retinaculum on medial side of ankle (Tom, Dick and Harry: Tibialis posterior, Flexor Digitorum longus, Posterior Tibial Artery and Tibial Nerve, Flexor Hallucis ...
... Flexor retinaculum on medial side of ankle (Tom, Dick and Harry: Tibialis posterior, Flexor Digitorum longus, Posterior Tibial Artery and Tibial Nerve, Flexor Hallucis ...
dermatomes_and_myotomes_information
... Top of head Temporal & occipital regions of head Neck and posterior cheek Superior shoulder and clavicle Deltoid patch & lateral arm Lateral forearm, thumb and index finger Posterior lateral forearm & middle finger Medial forearm, ulna border & ring/little fingers Medial side of forearm & upper arm ...
... Top of head Temporal & occipital regions of head Neck and posterior cheek Superior shoulder and clavicle Deltoid patch & lateral arm Lateral forearm, thumb and index finger Posterior lateral forearm & middle finger Medial forearm, ulna border & ring/little fingers Medial side of forearm & upper arm ...
10.9- Eye Notes
... – Contains nerve fibers – Contains central arteries and veins – Lacks receptors ...
... – Contains nerve fibers – Contains central arteries and veins – Lacks receptors ...
ppt
... Pay attention to the fact that the muscles of the thigh are designed To act on the knee joint For example, quadriceps femoris occupies the anterior compartment of the thigh but its Main action is to extend the knee joint The same should be considered for the muscles of the posterior compartment of ...
... Pay attention to the fact that the muscles of the thigh are designed To act on the knee joint For example, quadriceps femoris occupies the anterior compartment of the thigh but its Main action is to extend the knee joint The same should be considered for the muscles of the posterior compartment of ...
Letter to the editor
... various studies difficult, if not impossible. Secondly, the use of JCS as proposed by Grood and Suntay has the advantage of reporting joint motions in clinically relevant terms. This makes the application and interpretation of biomechanical findings easier and more welcoming to clinicians. Although al ...
... various studies difficult, if not impossible. Secondly, the use of JCS as proposed by Grood and Suntay has the advantage of reporting joint motions in clinically relevant terms. This makes the application and interpretation of biomechanical findings easier and more welcoming to clinicians. Although al ...
Soft Tissue Biceps Tenodesis – KY
... anterior purple cannula. Tie the “shuttle single/double knot” and pass a fiberwire through the tissue and biceps tendon and pull out the anterior cannula. Grab the fiberwire that is coming out of the anterior cannula about 10 cm from cannula opening (this fiberwire has already been placed in the ten ...
... anterior purple cannula. Tie the “shuttle single/double knot” and pass a fiberwire through the tissue and biceps tendon and pull out the anterior cannula. Grab the fiberwire that is coming out of the anterior cannula about 10 cm from cannula opening (this fiberwire has already been placed in the ten ...
OMM-and-the-Athlete-WS-UE-2-OCT-13
... Extent of movement is same as assessed in the same joint on the opposite side. No forceful or abnormal movement must ever be used. The manipulative movement is a sharp thrust, with velocity, to result in a 1/8th “ gapping or sliding at the joint being treated. Therapeutic movements occur when all of ...
... Extent of movement is same as assessed in the same joint on the opposite side. No forceful or abnormal movement must ever be used. The manipulative movement is a sharp thrust, with velocity, to result in a 1/8th “ gapping or sliding at the joint being treated. Therapeutic movements occur when all of ...
Respiratory
... Respiratory mucosa - lines nasal cavity Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Goblet cells within epithelium Cilia move contaminated mucus posteriorly to be swallowed ...
... Respiratory mucosa - lines nasal cavity Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Goblet cells within epithelium Cilia move contaminated mucus posteriorly to be swallowed ...
Axillary & Median Nerves
... • The median nerve continues into the hand by passing deep to the flexor retinaculum. • It innervates: • Three thenar muscles associated with the thumb • Lateral 2 lumbrical muscles associated with movement of the index and middle fingers; and • Skin over the palmar surface of the lateral three and ...
... • The median nerve continues into the hand by passing deep to the flexor retinaculum. • It innervates: • Three thenar muscles associated with the thumb • Lateral 2 lumbrical muscles associated with movement of the index and middle fingers; and • Skin over the palmar surface of the lateral three and ...
Thorax-intercostal spaces
... Present on the inner surface of anterior thoracic wall. Origin: Lower 1/3 of posterior surface of sternum, posterior surface of xiphisternum & posterior surfaces of costal cartilages of 4th to 7th ribs. Insertion: Lower border and posterior surfaces costal cartilages of 2nd to 6th ribs. Attachments ...
... Present on the inner surface of anterior thoracic wall. Origin: Lower 1/3 of posterior surface of sternum, posterior surface of xiphisternum & posterior surfaces of costal cartilages of 4th to 7th ribs. Insertion: Lower border and posterior surfaces costal cartilages of 2nd to 6th ribs. Attachments ...
Practice Identifying Bone Markings: Use in conjuction with your bone
... Bone markings: Every bone (or matching pair of bones) in the body looks different from every other bone (or matching pair) because of bone markings. There are three basic types of bone markings: Processes that are sites of muscle and ligament attachment. Processes that help to form joints. Depressi ...
... Bone markings: Every bone (or matching pair of bones) in the body looks different from every other bone (or matching pair) because of bone markings. There are three basic types of bone markings: Processes that are sites of muscle and ligament attachment. Processes that help to form joints. Depressi ...
L1: Organisation of ANS L2: Thoracic walls and breast
... - Subclavian artery Axillary artery lateral thoracic artery lateral mammary branches - Internal thoracic artery medial mammary branches - Lateral mammary branches of posterior intercostal arteries Venous drainage (same as arteries) - Medial mammary vein internal thoracic vein internal jug ...
... - Subclavian artery Axillary artery lateral thoracic artery lateral mammary branches - Internal thoracic artery medial mammary branches - Lateral mammary branches of posterior intercostal arteries Venous drainage (same as arteries) - Medial mammary vein internal thoracic vein internal jug ...
Mass Effect of a Thyroid Goiter That Crimps the Great Vessels
... subclavian veins on the asymmetric first ribs, left lower than right; atrophy of the soft tissues of the left anterior chest wall (not labeled) (Figure 3); costoclavicular compression of the gray proton-dense fibrosis of the second division right of the subclavian artery with binding nerve trunks (n ...
... subclavian veins on the asymmetric first ribs, left lower than right; atrophy of the soft tissues of the left anterior chest wall (not labeled) (Figure 3); costoclavicular compression of the gray proton-dense fibrosis of the second division right of the subclavian artery with binding nerve trunks (n ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.