Respiratory System - Yeditepe University Pharma Anatomy
... Each nasal cavity consists of three general regions: nasal vestibule, respiratory and olfactory regions. Each nasal cavity has a floor, roof, medial wall, and lateral wall. The air respired in travels from the nasal cavities into the nasopharnyx (nasal part of the pharynx) then into the laryngeal ca ...
... Each nasal cavity consists of three general regions: nasal vestibule, respiratory and olfactory regions. Each nasal cavity has a floor, roof, medial wall, and lateral wall. The air respired in travels from the nasal cavities into the nasopharnyx (nasal part of the pharynx) then into the laryngeal ca ...
Biol 241 Fall 10 Syllabus
... Four practical quizzes will be administered in the lab that will test your knowledge of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected Powerpoint slides, models, and fresh tissues. You will have time in lab to l ...
... Four practical quizzes will be administered in the lab that will test your knowledge of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected Powerpoint slides, models, and fresh tissues. You will have time in lab to l ...
Mink Dissection
... How is the relative size of this muscle different in humans? • Sartorius • Thin in a human (this muscle does not cover the entire ventral surface of the leg as in mink, but wraps laterally from the hip and moves medially towards the knee) ...
... How is the relative size of this muscle different in humans? • Sartorius • Thin in a human (this muscle does not cover the entire ventral surface of the leg as in mink, but wraps laterally from the hip and moves medially towards the knee) ...
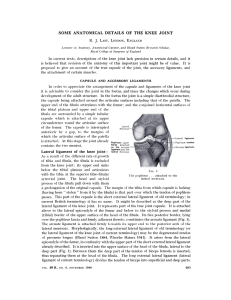
The Knee
... frontal deviation of the position of the knee. Commonly referred to as “knock-knee” due to the distal segments being positioned more laterally than normal Genu varum refers to a frontal deviation of the position of the knee. Commonly referred to as “bow-leg” is the opposite. ...
... frontal deviation of the position of the knee. Commonly referred to as “knock-knee” due to the distal segments being positioned more laterally than normal Genu varum refers to a frontal deviation of the position of the knee. Commonly referred to as “bow-leg” is the opposite. ...
Document
... • Failure of the Conduction System of the Heart • The sinuatrial node is the spontaneous source of the cardiac impulse. The atrioventricular node is responsible for picking up the cardiac impulse from the atria. The atrioventricular bundle is the only route by which the cardiac impulse can spread fr ...
... • Failure of the Conduction System of the Heart • The sinuatrial node is the spontaneous source of the cardiac impulse. The atrioventricular node is responsible for picking up the cardiac impulse from the atria. The atrioventricular bundle is the only route by which the cardiac impulse can spread fr ...
PECTORALIS MAJOR FLAP
... For additional length, the skin paddle may be extended as a random-pattern flap beyond the inferior edge of the muscle. Excessive thickness of the fatty tissue is associated with a higher risk of skin necrosis. Figure 2 The first incision is made from the lateral edge of the skin paddle toward the a ...
... For additional length, the skin paddle may be extended as a random-pattern flap beyond the inferior edge of the muscle. Excessive thickness of the fatty tissue is associated with a higher risk of skin necrosis. Figure 2 The first incision is made from the lateral edge of the skin paddle toward the a ...
Chapter 10 head/neck
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Muscles of the Abdominal Wall
... Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Standard Textbook of Medical Acupressure
... and to create a network for instructors proactively supporting the activities of visually impaired people. In the meeting, it became clear that a textbook regarding medical massage that can be used to train instructors at seminars was necessary. This textbook will provide source material for seminar ...
... and to create a network for instructors proactively supporting the activities of visually impaired people. In the meeting, it became clear that a textbook regarding medical massage that can be used to train instructors at seminars was necessary. This textbook will provide source material for seminar ...
Schwannoma - Rackcdn.com
... Common structures of origin ● V1 and branches ○ Anterior/posterior ethmoidal nerves--enter lateral to crista galli, provide sensation to the superior parts of the septum and lateral nasal wall, ethmoid air cells, and sphenoid sinus ● V2 and branches ○ Posterior superior nasal nerve--passes through ...
... Common structures of origin ● V1 and branches ○ Anterior/posterior ethmoidal nerves--enter lateral to crista galli, provide sensation to the superior parts of the septum and lateral nasal wall, ethmoid air cells, and sphenoid sinus ● V2 and branches ○ Posterior superior nasal nerve--passes through ...
Chapter 3
... II. SPINAL NERVES • Distribution – plexuses • network of interlacing, adjacent axons • do not directly connect to structures they innervate • 5 plexuses – cervical: skin/muscles of head/neck/upper chest – brachial: shoulders/upper limbs – lumbar: lower limbs/abdominal wall – sacral: buttocks/perine ...
... II. SPINAL NERVES • Distribution – plexuses • network of interlacing, adjacent axons • do not directly connect to structures they innervate • 5 plexuses – cervical: skin/muscles of head/neck/upper chest – brachial: shoulders/upper limbs – lumbar: lower limbs/abdominal wall – sacral: buttocks/perine ...
ABDOMINAL CAVITY
... The abdominal cavity is a large cavity so it is subdivided descriptively into 9 regions. • This division is made by 2 horizontal planes and two vertical planes. • The vertical planes are: • They are one on each side. • Each extends from the mid-clavicular point down to the mid-inguinal point. • The ...
... The abdominal cavity is a large cavity so it is subdivided descriptively into 9 regions. • This division is made by 2 horizontal planes and two vertical planes. • The vertical planes are: • They are one on each side. • Each extends from the mid-clavicular point down to the mid-inguinal point. • The ...
1.1 - cloudfront.net
... 2. Flatworms do not have a respiratory system, so they have pores that allow oxygen to enter through their body. 3. There are no blood vessels in the flatworms. Their gastrovascular cavity helps them to digest food and to send nutrients throughout the body. 4. The flatworms have a ladder-like nervou ...
... 2. Flatworms do not have a respiratory system, so they have pores that allow oxygen to enter through their body. 3. There are no blood vessels in the flatworms. Their gastrovascular cavity helps them to digest food and to send nutrients throughout the body. 4. The flatworms have a ladder-like nervou ...
Trapezius transfer for deltoid paralysis
... prime movers for abduction; they also lift the humeral shaft. Subscapularis, supraspinatus and infraspinatus are a steering group which stabilise the humeral head in the glenoid. The sternal head of pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, teres major and teres minor form a depressor group which also rot ...
... prime movers for abduction; they also lift the humeral shaft. Subscapularis, supraspinatus and infraspinatus are a steering group which stabilise the humeral head in the glenoid. The sternal head of pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, teres major and teres minor form a depressor group which also rot ...
FEMORAL SHEATH
... narrow, fascial tunnel in the thigh It is located deep to middle third of the sartorius muscle Provides an intermuscular passage through which the femoral vessels pass to reach the popliteal fossa, where they become popliteal vessels. It begins about 15 cm inferior to the inguinal ligament, where th ...
... narrow, fascial tunnel in the thigh It is located deep to middle third of the sartorius muscle Provides an intermuscular passage through which the femoral vessels pass to reach the popliteal fossa, where they become popliteal vessels. It begins about 15 cm inferior to the inguinal ligament, where th ...
Palpating Bony Prominences Palpating Muscle Bellies
... The therapist starts palpating the head of the ulna. The triquetrum is the next bony structure distal to the head of the ulna. A depression can be felt at the junction between these two structures, indicating the presence of an articular disk. It is easy for the thumb and the index finger to hold on ...
... The therapist starts palpating the head of the ulna. The triquetrum is the next bony structure distal to the head of the ulna. A depression can be felt at the junction between these two structures, indicating the presence of an articular disk. It is easy for the thumb and the index finger to hold on ...
Overview Editorial Board NeoPlus 2007
... Cranial nerve III, the oculomotor nerve, provides motor fibers to the striated muscles of four of the six extraocular muscles (superior rectus, medial rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique) and superior eyelid (levator palpebrae superioris). CN III does not play a role in the gag reflex. Cra ...
... Cranial nerve III, the oculomotor nerve, provides motor fibers to the striated muscles of four of the six extraocular muscles (superior rectus, medial rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique) and superior eyelid (levator palpebrae superioris). CN III does not play a role in the gag reflex. Cra ...
Weekly Schedule of Blood, Inflammation and Immunity
... Identify the importance of mesoderm in embryological basis of the diseases. Recognize the various components & types of Connective Tissue. Identify the congenital anomalies of cartilages. Correlate the types, structure and function of bones and the mechanism of bone modeling and remodeling with back ...
... Identify the importance of mesoderm in embryological basis of the diseases. Recognize the various components & types of Connective Tissue. Identify the congenital anomalies of cartilages. Correlate the types, structure and function of bones and the mechanism of bone modeling and remodeling with back ...
FEMORAL SHEATH
... narrow, fascial tunnel in the thigh It is located deep to middle third of the sartorius muscle Provides an intermuscular passage through which the femoral vessels pass to reach the popliteal fossa, where they become popliteal ve ssels. It begins about 15 cm inferior to the inguinal ligament, where t ...
... narrow, fascial tunnel in the thigh It is located deep to middle third of the sartorius muscle Provides an intermuscular passage through which the femoral vessels pass to reach the popliteal fossa, where they become popliteal ve ssels. It begins about 15 cm inferior to the inguinal ligament, where t ...
LESSON 5 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION The
... lungs it is called exhalation. The movement of the diaphragm is under the control of the involuntary or autonomic nervous system. However, we can override this, causing our diaphragm to contract or relax at will. ...
... lungs it is called exhalation. The movement of the diaphragm is under the control of the involuntary or autonomic nervous system. However, we can override this, causing our diaphragm to contract or relax at will. ...
A New Test for a Weak Deltoid
... trauma. 3 The patient may complain of atypical pain and paresthesias, especially in the lateral aspect of the upper arm with nondermatomal radiation to the forearm and hand. The muscles within the space will palpate tender. Active shoulder rehabilitation, lateral rotation and extension usually produ ...
... trauma. 3 The patient may complain of atypical pain and paresthesias, especially in the lateral aspect of the upper arm with nondermatomal radiation to the forearm and hand. The muscles within the space will palpate tender. Active shoulder rehabilitation, lateral rotation and extension usually produ ...
Elementary Physical Education Parent Guide
... Jump a rope using at least four different foot patterns repeatedly in a sequence. Demonstrate hand dribbling a ball in a 1 on 1 game-like situation. Identify fourteen bones of the body. Describe the changes that occur in the body as a result of smoking and drinking alcohol. Combine the skills of tra ...
... Jump a rope using at least four different foot patterns repeatedly in a sequence. Demonstrate hand dribbling a ball in a 1 on 1 game-like situation. Identify fourteen bones of the body. Describe the changes that occur in the body as a result of smoking and drinking alcohol. Combine the skills of tra ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.