Lecture 8 – Head and Jaw osteology
... (which open into pores on the head). • These ducts allow mineral crystals or grains of sand to enter the three sacs in the inner ear. These grains act as otoliths to help detect gravity. ...
... (which open into pores on the head). • These ducts allow mineral crystals or grains of sand to enter the three sacs in the inner ear. These grains act as otoliths to help detect gravity. ...
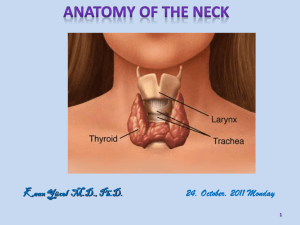
Anterior Cervical Region - Yeditepe University Dentistry Anatomy
... The deep cervical fascia consists of three fascial layers (sheaths): investing, pretracheal, and prevertebral layers support the viscera (e.g., the thyroid gland), muscles, vessels, and deep lymph nodes. The deep cervical fascia also condenses around the common carotid arteries, internal jugular vei ...
... The deep cervical fascia consists of three fascial layers (sheaths): investing, pretracheal, and prevertebral layers support the viscera (e.g., the thyroid gland), muscles, vessels, and deep lymph nodes. The deep cervical fascia also condenses around the common carotid arteries, internal jugular vei ...
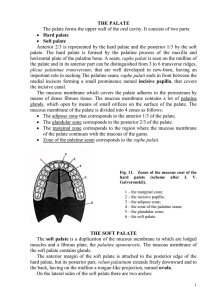
the palate
... palate. The hard palate is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of the palatine bone. A seam, raphe palati is seen on the midline of the palate and in its anterior part can be distinguished from 3 to 6 transverse ridges, plicae palatinae transversum, that are well devel ...
... palate. The hard palate is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of the palatine bone. A seam, raphe palati is seen on the midline of the palate and in its anterior part can be distinguished from 3 to 6 transverse ridges, plicae palatinae transversum, that are well devel ...
04Brachial_plexus_&_Radial_nerve2012-09
... TO (2ND Part): • The cords are given names according their relations with axillary artery. • Medial cord: medial • Lateral cord: lateral • Posterior cord: behind ...
... TO (2ND Part): • The cords are given names according their relations with axillary artery. • Medial cord: medial • Lateral cord: lateral • Posterior cord: behind ...
- DUNE - University of New England
... development of the anterior pararenal space (Lei at al., 1990), although clinical correlations related to this approach may be compromised (Kimura and Araki, 1996). Yet, the presence of the liver on right limits the anterior pararenal space, which also contains the head of the pancreas and the relat ...
... development of the anterior pararenal space (Lei at al., 1990), although clinical correlations related to this approach may be compromised (Kimura and Araki, 1996). Yet, the presence of the liver on right limits the anterior pararenal space, which also contains the head of the pancreas and the relat ...
Musculoskeletal System - Catherine Huff`s Site
... – Possible swelling dorsal to hip joint – Luxated limb shorter if legs extended in VD position ...
... – Possible swelling dorsal to hip joint – Luxated limb shorter if legs extended in VD position ...
Surgical Technique - Dr. med. Markus C. Michel
... muscles using a section of the approach described by Smith Petersen.1 No tendons or muscles are cut or detached. The joint capsule is split and left in place. The hip joint is not dislocated; we perform the osteotomy of the femoral neck in situ. To date we have performed several hundred MicroHip™ op ...
... muscles using a section of the approach described by Smith Petersen.1 No tendons or muscles are cut or detached. The joint capsule is split and left in place. The hip joint is not dislocated; we perform the osteotomy of the femoral neck in situ. To date we have performed several hundred MicroHip™ op ...
Client Seated - The Littered Box
... sternal head that you have located). Place palpating fingers just lateral to the lateral border of the clavicular head of the SCM and just superior to the clavicle, and feel for the contraction of the scalenes as the client takes in short, quick breaths through the nose. Once felt, palpate as much o ...
... sternal head that you have located). Place palpating fingers just lateral to the lateral border of the clavicular head of the SCM and just superior to the clavicle, and feel for the contraction of the scalenes as the client takes in short, quick breaths through the nose. Once felt, palpate as much o ...
Chapter 9: Joints - HCC Learning Web
... Movement that returns body parts to normal position from abduction ...
... Movement that returns body parts to normal position from abduction ...
SKULL – Part 1
... PELVIC BONE – ORIENTATION Each pelvic bone is made up of 3 bones: Ilium – large wing-like portion Ischium – part you sit on Pubis – front projection, forms pubic symphysis with other pelvic bone KEY LANDMARKS – use these to orient the bone into anatomical position Obturator Foramen – large ...
... PELVIC BONE – ORIENTATION Each pelvic bone is made up of 3 bones: Ilium – large wing-like portion Ischium – part you sit on Pubis – front projection, forms pubic symphysis with other pelvic bone KEY LANDMARKS – use these to orient the bone into anatomical position Obturator Foramen – large ...
Muscles - PA
... Insertion Lateral third of clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula Action Elevates, retracts and rotates scapula; superior fibers elevate, middle fibers retract, and inferior fibers depress scapula; superior and inferior fibers act together in superior rotation of ...
... Insertion Lateral third of clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula Action Elevates, retracts and rotates scapula; superior fibers elevate, middle fibers retract, and inferior fibers depress scapula; superior and inferior fibers act together in superior rotation of ...
B. Vertebral Column
... sacrum) immediately below it (diagram of anterior shear, see below). Like disc herniation, most anterior shear happens at L4-L5 and L5-S1. There is minimal anterior shear force while sitting, but sitting does train the low lumbar spine to go easily into flexion. And here is the connection: it takes ...
... sacrum) immediately below it (diagram of anterior shear, see below). Like disc herniation, most anterior shear happens at L4-L5 and L5-S1. There is minimal anterior shear force while sitting, but sitting does train the low lumbar spine to go easily into flexion. And here is the connection: it takes ...
Thoracic Sympathetic Trunk
... from fibers originally in the left vagus nerve •Posterior vagal trunk on the posterior surface of the esophagus, mainly from fibers originally in the right vagus nerve. •The vagal trunks continue on the surface of the esophagus as it passes through the diaphragm into the abdomen. ...
... from fibers originally in the left vagus nerve •Posterior vagal trunk on the posterior surface of the esophagus, mainly from fibers originally in the right vagus nerve. •The vagal trunks continue on the surface of the esophagus as it passes through the diaphragm into the abdomen. ...
Facelifts and Laser Resurfacing
... • Perioral Region , Chin, and lower border mandible • Muscles: quadratus labii inferioris, mentalis, and triangularis; all deep to platysma and insert into inferior rim of mandible http://face-andemotion.com/dataface/anatomy/media/Ha ...
... • Perioral Region , Chin, and lower border mandible • Muscles: quadratus labii inferioris, mentalis, and triangularis; all deep to platysma and insert into inferior rim of mandible http://face-andemotion.com/dataface/anatomy/media/Ha ...
Ardipithecus ramidus
... be swung forward, it and the pelvis are unsupported and would slump toward the ground were it not for The Ar. ramidus pelvis has a mosaic of characters for both bipedality and climbing. Left to right: muscles acting on the opposite side of the body (the Human, Au. afarensis (“Lucy”), Ar. ramidus, Pa ...
... be swung forward, it and the pelvis are unsupported and would slump toward the ground were it not for The Ar. ramidus pelvis has a mosaic of characters for both bipedality and climbing. Left to right: muscles acting on the opposite side of the body (the Human, Au. afarensis (“Lucy”), Ar. ramidus, Pa ...
Gluteal region
... • Cutaneous arterial supply- branches from sup. & inf. Gluteal arteries • Cutaneous lymphatic drainage- lateral group of superficial inguinal lymph nodes • Deep fascia- above & in front of gluteus medius is thick but over gluteus maximus it is thin. The deep fascia splits & encloses gluteus maximus ...
... • Cutaneous arterial supply- branches from sup. & inf. Gluteal arteries • Cutaneous lymphatic drainage- lateral group of superficial inguinal lymph nodes • Deep fascia- above & in front of gluteus medius is thick but over gluteus maximus it is thin. The deep fascia splits & encloses gluteus maximus ...
Chapter 7 Answers
... 11. The palatine bones are L shaped. 12. The palatine bones are located behind the maxillae. 13. The horizontal portions of the palatine bones form the posterior section of the hard palate and the floor of the nasal cavity. 14. The perpendicular portions of the palatine bones help form the lateral w ...
... 11. The palatine bones are L shaped. 12. The palatine bones are located behind the maxillae. 13. The horizontal portions of the palatine bones form the posterior section of the hard palate and the floor of the nasal cavity. 14. The perpendicular portions of the palatine bones help form the lateral w ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... tracheal rings. It is surrounded by a sheath derived from the ...
... tracheal rings. It is surrounded by a sheath derived from the ...
AORTA AND PERIPHERAL ARTERIES ANATOMY
... it divides into the radial and ulnar arteries Course; At first the brachial artery lies medial to the humerus; as it runs down the arm it gradually gets in front of the bone, and at the bend of the elbow it lies midway between its two epicondyles ...
... it divides into the radial and ulnar arteries Course; At first the brachial artery lies medial to the humerus; as it runs down the arm it gradually gets in front of the bone, and at the bend of the elbow it lies midway between its two epicondyles ...
Four cases of variations in the forearm extensor musculature in a
... ended by getting inserted into the base of the third metacarpal bone and adjoining carpal bones [Figure 2]. In the same limb, the APL muscle showed three tendons of insertion. The two additional tendons were seen on the lateral and medial sides of the main tendon. The one on the lateral side was rel ...
... ended by getting inserted into the base of the third metacarpal bone and adjoining carpal bones [Figure 2]. In the same limb, the APL muscle showed three tendons of insertion. The two additional tendons were seen on the lateral and medial sides of the main tendon. The one on the lateral side was rel ...
1-Nose, Nasal Cavity, Paranasal Sinuses,2017-02
... 3- Laryngeal inlet. o The muscles are arranged in circular and longitudinal layers. Explanation: The pharynx is made up of muscles that cover/make up the posterior and lateral walls. But they do not cover the anterior wall that’s why it is deficient. Instead the anterior wall is open and connects wi ...
... 3- Laryngeal inlet. o The muscles are arranged in circular and longitudinal layers. Explanation: The pharynx is made up of muscles that cover/make up the posterior and lateral walls. But they do not cover the anterior wall that’s why it is deficient. Instead the anterior wall is open and connects wi ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... tracheal rings. It is surrounded by a sheath derived from the ...
... tracheal rings. It is surrounded by a sheath derived from the ...
Chapter 12
... three articulations, the *, *, and proximal *joints. Distal end of the forearm articulates with carpal bones to form the radiocarpal and distal radioulnar joints. ...
... three articulations, the *, *, and proximal *joints. Distal end of the forearm articulates with carpal bones to form the radiocarpal and distal radioulnar joints. ...
Interactive Hip
... in-depth view of the hip and acetabulum. View clear, detailed and accurate 3D modeling of the key anatomy of the hip and acetabulum. Choose from hundreds of highly detailed and labeled views of the hip, pelvis, thigh, lumbar plexus, sacral and coccygeal plexuses, surface features and bone regions. T ...
... in-depth view of the hip and acetabulum. View clear, detailed and accurate 3D modeling of the key anatomy of the hip and acetabulum. Choose from hundreds of highly detailed and labeled views of the hip, pelvis, thigh, lumbar plexus, sacral and coccygeal plexuses, surface features and bone regions. T ...
Anatomy Exam 3 Outline Lecture 16 – Pelvis and Perineum
... iv. Internal iliac trunks 1. Superior border of greater sciatic foramen, the internal iliac artery divides into two trunks a. Anterior trunk supplies viscera b. Posterior trunk supplies posterior pelvic wall, gluteal region v. Collateral circulation 1. Sometimes internal iliac a becomes stenotic ...
... iv. Internal iliac trunks 1. Superior border of greater sciatic foramen, the internal iliac artery divides into two trunks a. Anterior trunk supplies viscera b. Posterior trunk supplies posterior pelvic wall, gluteal region v. Collateral circulation 1. Sometimes internal iliac a becomes stenotic ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.