Biochem PowerPoint Presentation
... - Substrate molecule fits in shape of active site - Active sites are specific for substrates ...
... - Substrate molecule fits in shape of active site - Active sites are specific for substrates ...
Chapter 3-5 Organic Chemistry
... extreme heat, and/or other environmental factors are altered, the protein may unravel and lose its shape Biologically inactive Structure + function (A change in structure alters function) ...
... extreme heat, and/or other environmental factors are altered, the protein may unravel and lose its shape Biologically inactive Structure + function (A change in structure alters function) ...
Mechanisms of Enzyme Regulation • Substrate concentration
... cleaved at a specific site in their polypeptide chain by specific proteases. a. Many digestive enzymes that hydrolyze proteins (e.g., trypsin, pepsin) are synthesized as zymogens in the stomach and pancreas. b. Blood clotting is mediated by a series of proteolytic zymogen activities of several serum ...
... cleaved at a specific site in their polypeptide chain by specific proteases. a. Many digestive enzymes that hydrolyze proteins (e.g., trypsin, pepsin) are synthesized as zymogens in the stomach and pancreas. b. Blood clotting is mediated by a series of proteolytic zymogen activities of several serum ...
DNA Similarities
... Suppose there is a species of mice, and a small population becomes isolated. Reproductive isolation occurs, and there are now two species of mice. I know you are not a molecular biologist. Just speculate. 1: How could the sequences of their filler DNA change? ...
... Suppose there is a species of mice, and a small population becomes isolated. Reproductive isolation occurs, and there are now two species of mice. I know you are not a molecular biologist. Just speculate. 1: How could the sequences of their filler DNA change? ...
Name: Avalon Draven Daily Date: 11-09
... salt solution to the tube. The salt causes the protein and other debris to clump together. Then, place the tube in the centrifuge. Inside the centrifuge, it spins the tube at high speeds, so that the heavy chunks of protein and debris sink to the bottom of the tub, while the DNA floats about. The ch ...
... salt solution to the tube. The salt causes the protein and other debris to clump together. Then, place the tube in the centrifuge. Inside the centrifuge, it spins the tube at high speeds, so that the heavy chunks of protein and debris sink to the bottom of the tub, while the DNA floats about. The ch ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY
... be cut out of the source organism The DNA has to be isolated DNA can then be introduced into host DNA ...
... be cut out of the source organism The DNA has to be isolated DNA can then be introduced into host DNA ...
Bio- Chapter 2 section 4 kearns 2014
... Catalyst = a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction Catalysts work by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction ...
... Catalyst = a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction Catalysts work by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction ...
Chapter 15 Review Questions
... 8. RNA contains ribose and DNA contains deoxyribose (one less oxygen on the sugar); DNA stays in the nucleus, RNA travels back and forth between the nucleus and the cytoplasm; DNA is double-stranded, RNA is single-stranded; DNA is helical, RNA is straight or folded in some other shape 9. They are bo ...
... 8. RNA contains ribose and DNA contains deoxyribose (one less oxygen on the sugar); DNA stays in the nucleus, RNA travels back and forth between the nucleus and the cytoplasm; DNA is double-stranded, RNA is single-stranded; DNA is helical, RNA is straight or folded in some other shape 9. They are bo ...
key
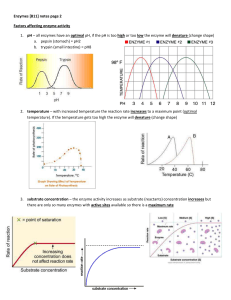
... 2. temperature – with increased temperature the reaction rate increases to a maximum point (optimal temperature). If the temperature gets too high the enzyme will denature (change shape) ...
... 2. temperature – with increased temperature the reaction rate increases to a maximum point (optimal temperature). If the temperature gets too high the enzyme will denature (change shape) ...
Chem TB Flashcards Unit 5
... an example of: 87) What statements concerning the difference between DNA and RNA is correct? 88) The expressed function or biological effect of a gene product is termed a: 89) What statements concerning mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is incorrect? 90) A noncoding RNA is one that: 91) Regarding transcript ...
... an example of: 87) What statements concerning the difference between DNA and RNA is correct? 88) The expressed function or biological effect of a gene product is termed a: 89) What statements concerning mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is incorrect? 90) A noncoding RNA is one that: 91) Regarding transcript ...
REVIEW SHEET FOR GENETIC ENGINEERING AND TRANSGENICS
... REVIEW SHEET FOR GENETIC ENGINEERING AND TRANSGENICS TERMS: Recognition (restriction) sites: a 4 or 8 base pair sequence that is a palindrome. It’s where restriction enzymes recognize and cut at specific places along the DNA molecule. Restriction maps: A restriction map shows the location of cleavag ...
... REVIEW SHEET FOR GENETIC ENGINEERING AND TRANSGENICS TERMS: Recognition (restriction) sites: a 4 or 8 base pair sequence that is a palindrome. It’s where restriction enzymes recognize and cut at specific places along the DNA molecule. Restriction maps: A restriction map shows the location of cleavag ...
Enzymes and How They Work
... 2) Catalysts- chemicals which speed up a reaction without being consumed B. Properties of enzymes: 1) Speed up reactions 2) Can be used over and over, only needed in small amount 3) Decrease amount of energy needed to start a reaction (activation energy) 4) Specific to a substrate based on its shape ...
... 2) Catalysts- chemicals which speed up a reaction without being consumed B. Properties of enzymes: 1) Speed up reactions 2) Can be used over and over, only needed in small amount 3) Decrease amount of energy needed to start a reaction (activation energy) 4) Specific to a substrate based on its shape ...
DNA Replication Paper Lab
... alive, there must be a way to make sure every new cell gets these instructions. A new cell is made by already existing cells, therefore, there is a mechanism to copy these “life instructions” into new cells. DNA has the instructions for life coded by the order in which the nucleotides occur in a chr ...
... alive, there must be a way to make sure every new cell gets these instructions. A new cell is made by already existing cells, therefore, there is a mechanism to copy these “life instructions” into new cells. DNA has the instructions for life coded by the order in which the nucleotides occur in a chr ...
Biosynthesis of Essential Amino Acids
... 1. It has been shown in many instances that enzymes catalyzing chemically similar reactions (e.g. malate and lactate dehydrogenases) have amazingly similar tertiary structures which suggests they evolved from a common ancestral protein. Likewise, chemical similarity in sequences of reactions in diff ...
... 1. It has been shown in many instances that enzymes catalyzing chemically similar reactions (e.g. malate and lactate dehydrogenases) have amazingly similar tertiary structures which suggests they evolved from a common ancestral protein. Likewise, chemical similarity in sequences of reactions in diff ...