
NATURAL BOUNDARIES OF DIRICHLET SERIES Gautami
... to the half plane ℜ(s) > 0 . If h(Y ) is a product of cyclotomic polynomials, then and only then can D(s) be continued to the whole complex plane. Dahlquist [3] generalised this result to h being any analytic function with isolated singularities within the unit circle. This line of investigation was ...
... to the half plane ℜ(s) > 0 . If h(Y ) is a product of cyclotomic polynomials, then and only then can D(s) be continued to the whole complex plane. Dahlquist [3] generalised this result to h being any analytic function with isolated singularities within the unit circle. This line of investigation was ...
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
... In one town, Avenue A is parallel to Avenue B. Avenue A is also perpendicular to Main Street. How are Avenue B and Main Street related? Explain. 20. Label the streets in the diagram A for Avenue A, B for Avenue B, and M for ...
... In one town, Avenue A is parallel to Avenue B. Avenue A is also perpendicular to Main Street. How are Avenue B and Main Street related? Explain. 20. Label the streets in the diagram A for Avenue A, B for Avenue B, and M for ...
Version of Gödel`s First Incompleteness Theorem
... – proves that a number with a certain property exists, but disallows all values If neither G nor ¬G has a proof, then the proof system is incomplete AV ...
... – proves that a number with a certain property exists, but disallows all values If neither G nor ¬G has a proof, then the proof system is incomplete AV ...
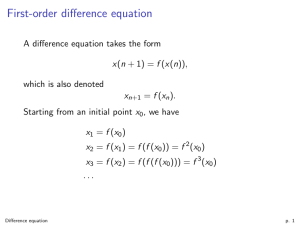
First-order difference equation
... {f n (x0 ) : n ≥ 0} is called the forward orbit of x0 and is denoted O + (x0 ). The backward orbit O − (x0 ) is defined, if f is invertible, by the negative iterates of f . Lastly, the (whole) orbit of x0 is {f k (x0 ) : −∞ < k < ∞}. The forward orbit is also called the positive orbit. The function ...
... {f n (x0 ) : n ≥ 0} is called the forward orbit of x0 and is denoted O + (x0 ). The backward orbit O − (x0 ) is defined, if f is invertible, by the negative iterates of f . Lastly, the (whole) orbit of x0 is {f k (x0 ) : −∞ < k < ∞}. The forward orbit is also called the positive orbit. The function ...
(pdf)
... homotopic to a fixed point. With a little consideration, one can see that any loop will be homotopic to a fixed point unless it goes around the hole in the center of the annulus. However, a loop can go around the hole in many different ways. Recall that a loop is a continuous map from [0, 1] to the ...
... homotopic to a fixed point. With a little consideration, one can see that any loop will be homotopic to a fixed point unless it goes around the hole in the center of the annulus. However, a loop can go around the hole in many different ways. Recall that a loop is a continuous map from [0, 1] to the ...
Teaching Geometry-dj
... 10. The pink sticks need to alternate properly with blues, and purples too, so there is a trick to inserting them. Rotate the above configuration away from you, so that you now hold orange vertically, looking down the future pink direction. Put your thumbs on the ends of the blue and purple sticks n ...
... 10. The pink sticks need to alternate properly with blues, and purples too, so there is a trick to inserting them. Rotate the above configuration away from you, so that you now hold orange vertically, looking down the future pink direction. Put your thumbs on the ends of the blue and purple sticks n ...
Ch. 4
... Let A, B, C, and D are four distinct points such that C and D are on the same side of AB . Then ( BAD ) < ( BAC ) if and only if ray AD is between rays AB and AC . So we use the Plane Separation Axiom and a couple of theorems from that section. Points F and B are on opposite sides of line AC , ...
... Let A, B, C, and D are four distinct points such that C and D are on the same side of AB . Then ( BAD ) < ( BAC ) if and only if ray AD is between rays AB and AC . So we use the Plane Separation Axiom and a couple of theorems from that section. Points F and B are on opposite sides of line AC , ...
Brouwer fixed-point theorem

Brouwer's fixed-point theorem is a fixed-point theorem in topology, named after Luitzen Brouwer. It states that for any continuous function f mapping a compact convex set into itself there is a point x0 such that f(x0) = x0. The simplest forms of Brouwer's theorem are for continuous functions f from a closed interval I in the real numbers to itself or from a closed disk D to itself. A more general form than the latter is for continuous functions from a convex compact subset K of Euclidean space to itself.Among hundreds of fixed-point theorems, Brouwer's is particularly well known, due in part to its use across numerous fields of mathematics.In its original field, this result is one of the key theorems characterizing the topology of Euclidean spaces, along with the Jordan curve theorem, the hairy ball theorem and the Borsuk–Ulam theorem.This gives it a place among the fundamental theorems of topology. The theorem is also used for proving deep results about differential equations and is covered in most introductory courses on differential geometry.It appears in unlikely fields such as game theory. In economics, Brouwer's fixed-point theorem and its extension, the Kakutani fixed-point theorem, play a central role in the proof of existence of general equilibrium in market economies as developed in the 1950s by economics Nobel prize winners Kenneth Arrow and Gérard Debreu.The theorem was first studied in view of work on differential equations by the French mathematicians around Poincaré and Picard.Proving results such as the Poincaré–Bendixson theorem requires the use of topological methods.This work at the end of the 19th century opened into several successive versions of the theorem. The general case was first proved in 1910 by Jacques Hadamard and by Luitzen Egbertus Jan Brouwer.




















![[hal-00574623, v2] Averaging along Uniform Random Integers](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/019969824_1-25527940ea4f317ec31969269e4745aa-300x300.png)

