Summary: Advanced Connections Questions
... Summary: Advanced Connections Questions 1. Many flashlights use two D-cells. Are the D-cells used in series or in parallel with the light bulb? Why? a. Flashlights use series circuits because voltage adds, so series D-cells provides more current, thus more light. 2. Would you recommend wiring string ...
... Summary: Advanced Connections Questions 1. Many flashlights use two D-cells. Are the D-cells used in series or in parallel with the light bulb? Why? a. Flashlights use series circuits because voltage adds, so series D-cells provides more current, thus more light. 2. Would you recommend wiring string ...
Tilt Switch App Circuits
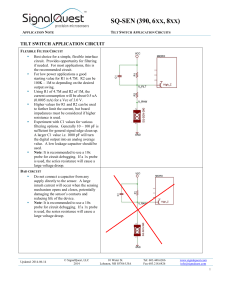
... if needed. For most applications, this is the recommended circuit. For low power applications a good starting value for R1 is 4.7M. R2 can be 100K – 1M to depending on the desired output swing. Using R1 of 4.7M and R2 of 1M, the current consumption will be about 0.5 uA (0.0005 mA) for a Vcc of 3 ...
... if needed. For most applications, this is the recommended circuit. For low power applications a good starting value for R1 is 4.7M. R2 can be 100K – 1M to depending on the desired output swing. Using R1 of 4.7M and R2 of 1M, the current consumption will be about 0.5 uA (0.0005 mA) for a Vcc of 3 ...
Section 13.3: Alternating Current
... circuit breaker can also be reset to close the circuit again. A GFCI is similar to a circuit breaker. A GFCI is more sensitive to very small changes in current and opens the circuit much more quickly than a circuit breaker. An AFCI is similar to a GFCI. It acts quickly to shut off a circuit when an ...
... circuit breaker can also be reset to close the circuit again. A GFCI is similar to a circuit breaker. A GFCI is more sensitive to very small changes in current and opens the circuit much more quickly than a circuit breaker. An AFCI is similar to a GFCI. It acts quickly to shut off a circuit when an ...
Name - edl.io
... Nothing. The series is in parallel, so if they shut off, it doesn’t affect the rest of the circuit. c. Explain why household circuits are set up in parallel. ...
... Nothing. The series is in parallel, so if they shut off, it doesn’t affect the rest of the circuit. c. Explain why household circuits are set up in parallel. ...
Low Voltage Power Circuit Breaker
... purpose of improving system coordination. Review the three curves on this page and the next page. Circuit breaker short-time-delay (STD) mechanisms allow an intentional delay to be installed on low voltage power circuit breakers. Short-time-delays allow the fault current to flow for several cycles, ...
... purpose of improving system coordination. Review the three curves on this page and the next page. Circuit breaker short-time-delay (STD) mechanisms allow an intentional delay to be installed on low voltage power circuit breakers. Short-time-delays allow the fault current to flow for several cycles, ...
Questions about Electric Circuits
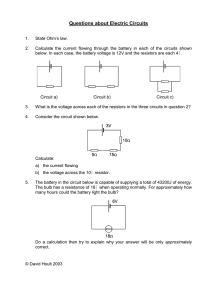
... below. In each case, the battery voltage is 12V and the resistors are each 4Ω. ...
... below. In each case, the battery voltage is 12V and the resistors are each 4Ω. ...
Electric Motors
... Controller reads current value from sensors Detects when current rises above a threshold Signals actuators to break contacts - - In high-power apps, sensors may need to be separated… ...
... Controller reads current value from sensors Detects when current rises above a threshold Signals actuators to break contacts - - In high-power apps, sensors may need to be separated… ...
Unit 7: Electrical Circuits and Systems Review KEY
... If resistance is decreased in a circuit, what happens to the current? What law is this? ...
... If resistance is decreased in a circuit, what happens to the current? What law is this? ...
Student 2
... increases across the parallel branches. The energy carried by the electrons is the same. Current, unlike voltage raised between circuits. The current drawn by a resistor depends on its resistance (Ohms Law states that resistance is inversely proportional to current) Low resistance has high current a ...
... increases across the parallel branches. The energy carried by the electrons is the same. Current, unlike voltage raised between circuits. The current drawn by a resistor depends on its resistance (Ohms Law states that resistance is inversely proportional to current) Low resistance has high current a ...
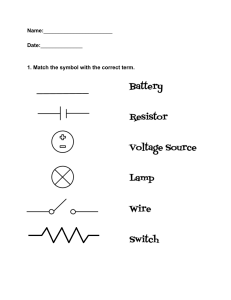
1. Match the symbol with the correct term.
... C. ___________ are positively charged particles. D. Atoms are made out of protons, electrons, and ____________. E. Batteries have two _____________. One is positive and one is negative. F. A ____________ circuit has multiple loops. G. ____________ is the flow of electrical charge in a circuit. ...
... C. ___________ are positively charged particles. D. Atoms are made out of protons, electrons, and ____________. E. Batteries have two _____________. One is positive and one is negative. F. A ____________ circuit has multiple loops. G. ____________ is the flow of electrical charge in a circuit. ...
3 ELECTRICAL SAFETY DEVICES – SAFETY MOMENT
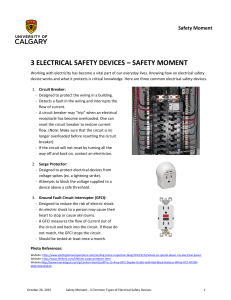
... device works and what it protects is critical knowledge. Here are three common electrical safety devices. 1. Circuit Breaker: - Designed to protect the wiring in a building. - Detects a fault in the wiring and interrupts the flow of current. - A circuit breaker may “trip” when an electrical receptac ...
... device works and what it protects is critical knowledge. Here are three common electrical safety devices. 1. Circuit Breaker: - Designed to protect the wiring in a building. - Detects a fault in the wiring and interrupts the flow of current. - A circuit breaker may “trip” when an electrical receptac ...
( ) cos60 sin60 , 0. it Be t Be tt = +
... The capacitor has a value of 500μF; the initial value of the current is zero, and the initial voltage on the capacitor is 1V. Find the values of R, L, B1, and B2. ...
... The capacitor has a value of 500μF; the initial value of the current is zero, and the initial voltage on the capacitor is 1V. Find the values of R, L, B1, and B2. ...
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and interrupt current flow. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation. Circuit breakers are made in varying sizes, from small devices that protect an individual household appliance up to large switchgear designed to protect high voltage circuits feeding an entire city.