optical coherence tomography
... used in LCI and OCT gives access to only high spatial frequencies, i.e., discontinuities, in the scattering potential. With a wavelength range from l1 to l2 we obtain Fourier components in the scattering potential within the spatial frequency range [K1 , K2]=[4p/l1 ,4p/l2]. With a superluminescent d ...
... used in LCI and OCT gives access to only high spatial frequencies, i.e., discontinuities, in the scattering potential. With a wavelength range from l1 to l2 we obtain Fourier components in the scattering potential within the spatial frequency range [K1 , K2]=[4p/l1 ,4p/l2]. With a superluminescent d ...
Unit 1.6 Optical Switching - DIT School of Electronics and
... The operation of acousto-optic switches is based on the acousto-optic effect, i.e., the interaction between sound and light. The principle of operation of a polarization-insensitive acousto-optic switch is as follows. First, the input signal is split into its two polarized components (TE and TM) by ...
... The operation of acousto-optic switches is based on the acousto-optic effect, i.e., the interaction between sound and light. The principle of operation of a polarization-insensitive acousto-optic switch is as follows. First, the input signal is split into its two polarized components (TE and TM) by ...
Transfer of Light Helicity to Nanostructures
... of plasmonic or metallic structures, including photonic crystals as well as plasmonic waveguides, prepared by conventional integrated photonic circuit techniques based on lithography and chemical etching. There are few reports on the use of structured light itself to form chiral structures on the na ...
... of plasmonic or metallic structures, including photonic crystals as well as plasmonic waveguides, prepared by conventional integrated photonic circuit techniques based on lithography and chemical etching. There are few reports on the use of structured light itself to form chiral structures on the na ...
Digital High-Speed Optical Systems Interconnections for
... procedure described in Reference 10. The width of the rransponed region was about 0.2 pm with a nominal ac~ tive-region width of 1.5 J.1ffi, and the laser wafer was thinned to a thickness of 75 ,urn. The ohmic contactS to the n-type: and p--type regions were Au-Sn and Au-Zn, respectively. The contac ...
... procedure described in Reference 10. The width of the rransponed region was about 0.2 pm with a nominal ac~ tive-region width of 1.5 J.1ffi, and the laser wafer was thinned to a thickness of 75 ,urn. The ohmic contactS to the n-type: and p--type regions were Au-Sn and Au-Zn, respectively. The contac ...
Optical Springs at the 40m
... Central part (Michelson, PRC, SRC) signals are extracted from beat between f1 and f2, not including arm cavity information. Optical Springs at the 40m ...
... Central part (Michelson, PRC, SRC) signals are extracted from beat between f1 and f2, not including arm cavity information. Optical Springs at the 40m ...
Technologies - E
... These are warmed (through heat or electrical discharge) and the contact point is stretched in a way for narrower nucleus to form, and to there be better coupling These are the more widely diffused and present excess losses in the order of 0.2dB ...
... These are warmed (through heat or electrical discharge) and the contact point is stretched in a way for narrower nucleus to form, and to there be better coupling These are the more widely diffused and present excess losses in the order of 0.2dB ...
Silicon Photonics Optical Transceiver for High-speed, High
... The next-generation servers and supercomputers with high performance and low power consumption require not only CPUs with an enhanced processing capability, but also signal transmission technology that connects CPUs with other CPUs or memories at high density and low power. It is becoming difficult ...
... The next-generation servers and supercomputers with high performance and low power consumption require not only CPUs with an enhanced processing capability, but also signal transmission technology that connects CPUs with other CPUs or memories at high density and low power. It is becoming difficult ...
In text you refer to OAP mirrors as 2nd etc, In fig, they are labeled
... One aberration of particular note is that occurring immediately after the closure of the slit in which the beam would appear horizontally oriented despite the vertical orientation of the slit. Noting that this aberration coupled the horizontal and vertical propagation of the beam, I gradually change ...
... One aberration of particular note is that occurring immediately after the closure of the slit in which the beam would appear horizontally oriented despite the vertical orientation of the slit. Noting that this aberration coupled the horizontal and vertical propagation of the beam, I gradually change ...
Signal-to-Signal-to-Noise-Ratio of Full-Field Fourier
... In 3F-OCT we use a holographic interferometer instead of the Michelson interferometer typically used for “flying spot” OCT configurations. Here for simplicity we describe 3F-OCT in the transmission mode (extendable to reflection mode). Our optical source is launched into a fiber-optic coupler which ...
... In 3F-OCT we use a holographic interferometer instead of the Michelson interferometer typically used for “flying spot” OCT configurations. Here for simplicity we describe 3F-OCT in the transmission mode (extendable to reflection mode). Our optical source is launched into a fiber-optic coupler which ...
Pluggable Optical Interfaces and Their Compatibility with Xilinx FPGAs
... the optical/electrical translation in the receive direction, clocked, and then re-transmitted into the other domain. These circuits contain robust equalization structures to ensure that the data being clocked and retransmitted in either direction is correct. By re-timing the data at the electrical/o ...
... the optical/electrical translation in the receive direction, clocked, and then re-transmitted into the other domain. These circuits contain robust equalization structures to ensure that the data being clocked and retransmitted in either direction is correct. By re-timing the data at the electrical/o ...
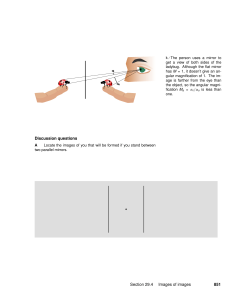
Discussion questions Section 29.4 Images of images 851
... so that the mirror intercepts only a very narrow cone of rays from the lamp. This cone is so narrow that its rays are nearly parallel, and θo is nearly zero. The real image can be observed on a piece of paper. By moving the paper nearer and farther, we can bring the image into focus, at which point ...
... so that the mirror intercepts only a very narrow cone of rays from the lamp. This cone is so narrow that its rays are nearly parallel, and θo is nearly zero. The real image can be observed on a piece of paper. By moving the paper nearer and farther, we can bring the image into focus, at which point ...
PDF
... increase the data capacity of optical communication systems [3,4], as well as in optical micromanipulations where the OAM of the photons can be directly transferred to that of an optically trapped particle causing it to rotate [5,6]. OAM beams also generate Doppler frequency shifts when interacting ...
... increase the data capacity of optical communication systems [3,4], as well as in optical micromanipulations where the OAM of the photons can be directly transferred to that of an optically trapped particle causing it to rotate [5,6]. OAM beams also generate Doppler frequency shifts when interacting ...
Mirrors
... Consider three rays emerging from the top of the arrow. (If you are viewing this document in Microsoft Word, use the zoom level in the upper right hand corner to make the page and the drawing larger, if you wish.) The first (the lowest) ray travels towards the mirror parallel to the principal axis. ...
... Consider three rays emerging from the top of the arrow. (If you are viewing this document in Microsoft Word, use the zoom level in the upper right hand corner to make the page and the drawing larger, if you wish.) The first (the lowest) ray travels towards the mirror parallel to the principal axis. ...
Application scenarios for optical OFDM
... field of high-speed digital signal processing have recently enabled the use of OFDM for fiber-optic applications and optical OFDM quickly became an active research topic [1, 2]. Advantages of optical OFDM are that it is easily scalable to higher modulation formats [3], has a well defined spectral sh ...
... field of high-speed digital signal processing have recently enabled the use of OFDM for fiber-optic applications and optical OFDM quickly became an active research topic [1, 2]. Advantages of optical OFDM are that it is easily scalable to higher modulation formats [3], has a well defined spectral sh ...
Issues with Telescopes
... The Mount Palomar telescope would not be able to resolve these objects It would not be able to “see” the moon ! ...
... The Mount Palomar telescope would not be able to resolve these objects It would not be able to “see” the moon ! ...
Reflector sight

A reflector sight or reflex sight is an optical device that allows the user to look through a partially reflecting glass element and see an illuminated projection of an aiming point or some other image superimposed on the field of view. These sights work on the simple optical principle that anything at the focus of a lens or curved mirror (such as an illuminated reticle) will look like it is sitting in front of the viewer at infinity. Reflector sights employ some sort of ""reflector"" to allow the viewer to see the infinity image and the field of view at the same time, either by bouncing the image created by lens off a slanted glass plate, or by using a mostly clear curved glass reflector that images the reticle while the viewer looks through the reflector. Since the reticle is at infinity it stays in alignment with the device the sight is attached to regardless of the viewer's eye position, removing most of the parallax and other sighting errors found in simple sighting devices.Since their invention in 1900, reflector sights have come to be used as gun sights on all kinds of weapons. They were used on fighter aircraft, in a limited capacity in World War I, widely used in World War II, and still used as the base component in many types of modern head-up displays. They have been used in other types of (usually large) weapons as well, such as anti-aircraft gun sights, anti tank gun sights, and any other role where the operator had to engage fast moving targets over a wide field of view, and the sight itself could be supplied with sufficient electrical power to function. There was some limited use of the sight on small arms after World War II but it came into widespread use after the late 70s with the invention of the red dot sight, with a red light-emitting diode (LED) as its reticle, making a dependable sight with durability and extremely long illumination run time.Reflector sights are also used in civilian applications such as sights on surveying equipment, optical telescope pointing aids, and camera viewfinders.