Microscope Basics
... The objective lenses are the most important components of microscopes and thus will be discussed in greater detail here. Their basic function is to gather the light passing through the specimen and then to project the image up into the body of the microscope. Then, the eyepiece lens system further m ...
... The objective lenses are the most important components of microscopes and thus will be discussed in greater detail here. Their basic function is to gather the light passing through the specimen and then to project the image up into the body of the microscope. Then, the eyepiece lens system further m ...
Nonlinear Optics Third Edition
... The book in its present form contains far too much material to be covered within a conventional one-semester course. For this reason, I am often asked for advice on how to structure a course based on the content of my textbook. Some of my thoughts along these lines are as follows: (1) I have endeavo ...
... The book in its present form contains far too much material to be covered within a conventional one-semester course. For this reason, I am often asked for advice on how to structure a course based on the content of my textbook. Some of my thoughts along these lines are as follows: (1) I have endeavo ...
Analysis of optical interferometric displacement detection in nanoelectromechanical systems
... which passes through the center of the nanomechanical beam. This is a valid approximation if l Ⰷ 2W0. For first generation NEMS, where l is several micrometers and 2W0 ⬇ 1 m, this approximation holds well.19 This approximation is expected be less accurate for large optical spot sizes or extremely s ...
... which passes through the center of the nanomechanical beam. This is a valid approximation if l Ⰷ 2W0. For first generation NEMS, where l is several micrometers and 2W0 ⬇ 1 m, this approximation holds well.19 This approximation is expected be less accurate for large optical spot sizes or extremely s ...
Chapter 18 - Handbook of Optics
... was developed by Wynne (1965, 1974) for the region of the spectrum extending from 365 to 1014 nm. It is used to extend the field of a parabolic mirror. Versions for a Ritchey-Chretien primary also exist. The corrector is able to correct spherical aberration, coma, astigmatism, and field curvature wh ...
... was developed by Wynne (1965, 1974) for the region of the spectrum extending from 365 to 1014 nm. It is used to extend the field of a parabolic mirror. Versions for a Ritchey-Chretien primary also exist. The corrector is able to correct spherical aberration, coma, astigmatism, and field curvature wh ...
RAY OPTICS
... Light is an electromagnetic wave phenomenon described by the same theoretical principles that govern all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric-field wave and a magnetic-field wave. Nevertheless, it is p ...
... Light is an electromagnetic wave phenomenon described by the same theoretical principles that govern all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric-field wave and a magnetic-field wave. Nevertheless, it is p ...
Chapter 2 Optical Layout
... This chapter covers the physical layout of a system and its elements by defining the reference frames and showing the user how to enter the correct parameters. SHADOW defines an optical system to be made up of a set of independent optical elements. The output of one element becomes the input of the ...
... This chapter covers the physical layout of a system and its elements by defining the reference frames and showing the user how to enter the correct parameters. SHADOW defines an optical system to be made up of a set of independent optical elements. The output of one element becomes the input of the ...
Optical device having equal length waveguide paths
... in the medium and m is an integer order number, then the phase front of the light in coupler 12 forms a circular Wave converging on the coupler axis at P0. At a different Wave ...
... in the medium and m is an integer order number, then the phase front of the light in coupler 12 forms a circular Wave converging on the coupler axis at P0. At a different Wave ...
ORB: An On-chip Optical Ring Bus Communication Architecture for Multi-Processor Systems-on-Chip
... capacitors [11]. Micro-ring resonator based p-i-n diode type modulators [12] [27] are compact in size (10-30 μm) and have low power consumption, but possess low modulation speeds (several MHz). On the other hand, MOS capacitor structures such as the Mach-Zehnder interferometer based silicon modulato ...
... capacitors [11]. Micro-ring resonator based p-i-n diode type modulators [12] [27] are compact in size (10-30 μm) and have low power consumption, but possess low modulation speeds (several MHz). On the other hand, MOS capacitor structures such as the Mach-Zehnder interferometer based silicon modulato ...
Chapter 5: Optical aberrations in the mouse eye
... normal viewing conditions, i.e. without anaesthesia nor with cyclopegia. The animals were restrained by holding their tails while they were sitting on an elevated platform mounted in front of the system, which allowed centration and focusing of the animal’s pupil. Figure 5.1 The pupil image channel ...
... normal viewing conditions, i.e. without anaesthesia nor with cyclopegia. The animals were restrained by holding their tails while they were sitting on an elevated platform mounted in front of the system, which allowed centration and focusing of the animal’s pupil. Figure 5.1 The pupil image channel ...
24 Geometrical Optics
... focal point —– A point at which rays of light or other radiation converge or from which they appear to diverge, as after refraction or reflection in an optical system. focal plane —– The plane containing the focal point, on which parallel rays focus. positive lens —– Converging lens. negative lens —– ...
... focal point —– A point at which rays of light or other radiation converge or from which they appear to diverge, as after refraction or reflection in an optical system. focal plane —– The plane containing the focal point, on which parallel rays focus. positive lens —– Converging lens. negative lens —– ...
Selective Trapping or Rotation of Isotropic Dielectric Microparticles
... immerging applications of optical trapping.2 In particular, rotation and spin of particles by light have drawn great attention since they may offer more functionality to practical microsystems.3−8 In conventional optical tweezers, the trapping force drops quickly as the radius of particles decreases ...
... immerging applications of optical trapping.2 In particular, rotation and spin of particles by light have drawn great attention since they may offer more functionality to practical microsystems.3−8 In conventional optical tweezers, the trapping force drops quickly as the radius of particles decreases ...
High-refractive-index composite materials for
... the THz spectrum. A solution found to partly overcome this problem is to design either hollow-core or highly porous waveguides, or subwavelength solid-core waveguides, in all of which a substantial portion of the optical power is guided in dry air. In line with this scheme, several types of microstr ...
... the THz spectrum. A solution found to partly overcome this problem is to design either hollow-core or highly porous waveguides, or subwavelength solid-core waveguides, in all of which a substantial portion of the optical power is guided in dry air. In line with this scheme, several types of microstr ...
Multimode or Single-Mode Optical Fiber
... Cloud computing and web services continue to drive increased bandwidth demand, pushing data communications rates from 1 and 10G to 40 and 100G and beyond in enterprise and data center networks. These higher speeds might lead system designers to believe that single-mode optical fiber enjoys an increa ...
... Cloud computing and web services continue to drive increased bandwidth demand, pushing data communications rates from 1 and 10G to 40 and 100G and beyond in enterprise and data center networks. These higher speeds might lead system designers to believe that single-mode optical fiber enjoys an increa ...
Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
... generation of ultra-broad bandwidth light sources that are compact, relatively inexpensive, and require low maintenance. The combination of these new light sources with SDOCT technology has led to in vivo retinal imaging with simultaneous ultra-high axial resolutions and ultrahigh speeds. Spectral d ...
... generation of ultra-broad bandwidth light sources that are compact, relatively inexpensive, and require low maintenance. The combination of these new light sources with SDOCT technology has led to in vivo retinal imaging with simultaneous ultra-high axial resolutions and ultrahigh speeds. Spectral d ...
Resolving the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict in Head Mounted
... changes with per-frame swapping between two different images, thus displaying the images at different depth simultaneously and simulating the light field. The prototype’s depth range spans contiguously from 6.25 cm to infinity. The claimed advantage of the VRD designs is that they can potentially be ...
... changes with per-frame swapping between two different images, thus displaying the images at different depth simultaneously and simulating the light field. The prototype’s depth range spans contiguously from 6.25 cm to infinity. The claimed advantage of the VRD designs is that they can potentially be ...
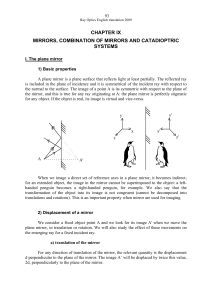
mirrors, combination of mirrors and catadioptric systems
... In previous chapters, we chose as positive along x the direction of propagation of light, from left to right. In the case of mirrors the difficulty comes from the change in the direction of propagation of light, and it is thus important to define precisely the sign convention, both for the positions ...
... In previous chapters, we chose as positive along x the direction of propagation of light, from left to right. In the case of mirrors the difficulty comes from the change in the direction of propagation of light, and it is thus important to define precisely the sign convention, both for the positions ...
Design and construction of a refracting telescope
... microscope is used to view objects close at hand, also the focal length of the objective lens in a telescope is usually longer than that of the eyepiece while the reverse is the case in a microscope (i.e. the focal length of the eyepiece is longer than that of the objective). 1.1. Theory of Telescop ...
... microscope is used to view objects close at hand, also the focal length of the objective lens in a telescope is usually longer than that of the eyepiece while the reverse is the case in a microscope (i.e. the focal length of the eyepiece is longer than that of the objective). 1.1. Theory of Telescop ...
PreDesigner Manual
... Optics users often want to make a preliminary assessment of a task, before any actual design is undertaken. We may know a few key values, and will need to find out the others, so we can understand in broad brush terms - how the required system will behave, its field of view, magnification etc. The p ...
... Optics users often want to make a preliminary assessment of a task, before any actual design is undertaken. We may know a few key values, and will need to find out the others, so we can understand in broad brush terms - how the required system will behave, its field of view, magnification etc. The p ...
Wave aberration of human eyes and new descriptors
... an aperture. In the eye, diffraction is an interaction between light passing through the optics of the eye and the edge of the iris. Even in the absence of aberrations, an infinitesimal point cannot be formed on the retina, and this is because of diffraction. In general, because all optical systems, ...
... an aperture. In the eye, diffraction is an interaction between light passing through the optics of the eye and the edge of the iris. Even in the absence of aberrations, an infinitesimal point cannot be formed on the retina, and this is because of diffraction. In general, because all optical systems, ...
History of Fiber Optics
... Those first-generation systems could transmit light several kilometers without repeaters, but were limited by loss of about 2 dB/km in the fiber. A second generation soon appeared, using new InGaAsP lasers which emitted at 1.3 micrometer, where fiber attenuation was as low as 0.5 dB/km, and pulse d ...
... Those first-generation systems could transmit light several kilometers without repeaters, but were limited by loss of about 2 dB/km in the fiber. A second generation soon appeared, using new InGaAsP lasers which emitted at 1.3 micrometer, where fiber attenuation was as low as 0.5 dB/km, and pulse d ...
Gain-Flattening Filters Using Dielectric Multilayer Thin Film
... ness monitor, in a position different from that of the substrate for thin film deposition, and to use a new monitoring substrate for each layer, but the need to keep accurate track of the film thickness distribution meant that this method was not suited to high-precision optical thickness control. I ...
... ness monitor, in a position different from that of the substrate for thin film deposition, and to use a new monitoring substrate for each layer, but the need to keep accurate track of the film thickness distribution meant that this method was not suited to high-precision optical thickness control. I ...
3-D Ultrahigh Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography with
... When the wave front aberrations of the eye are measured precisely and in real time, it is possible to correct them by using a wave front correcting device that compensates the eye’s aberrations. This is a direct application of Adaptive Optics (AO) on the eye imaging. In the ideal case, the AO system ...
... When the wave front aberrations of the eye are measured precisely and in real time, it is possible to correct them by using a wave front correcting device that compensates the eye’s aberrations. This is a direct application of Adaptive Optics (AO) on the eye imaging. In the ideal case, the AO system ...
Reflector sight

A reflector sight or reflex sight is an optical device that allows the user to look through a partially reflecting glass element and see an illuminated projection of an aiming point or some other image superimposed on the field of view. These sights work on the simple optical principle that anything at the focus of a lens or curved mirror (such as an illuminated reticle) will look like it is sitting in front of the viewer at infinity. Reflector sights employ some sort of ""reflector"" to allow the viewer to see the infinity image and the field of view at the same time, either by bouncing the image created by lens off a slanted glass plate, or by using a mostly clear curved glass reflector that images the reticle while the viewer looks through the reflector. Since the reticle is at infinity it stays in alignment with the device the sight is attached to regardless of the viewer's eye position, removing most of the parallax and other sighting errors found in simple sighting devices.Since their invention in 1900, reflector sights have come to be used as gun sights on all kinds of weapons. They were used on fighter aircraft, in a limited capacity in World War I, widely used in World War II, and still used as the base component in many types of modern head-up displays. They have been used in other types of (usually large) weapons as well, such as anti-aircraft gun sights, anti tank gun sights, and any other role where the operator had to engage fast moving targets over a wide field of view, and the sight itself could be supplied with sufficient electrical power to function. There was some limited use of the sight on small arms after World War II but it came into widespread use after the late 70s with the invention of the red dot sight, with a red light-emitting diode (LED) as its reticle, making a dependable sight with durability and extremely long illumination run time.Reflector sights are also used in civilian applications such as sights on surveying equipment, optical telescope pointing aids, and camera viewfinders.