![Titration #1 Determination of [NaOH]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006790962_1-275eb40711c8f3ecc850bd432b1a775b-300x300.png)
Momentum
... Mass is measured in kilograms (kg). Velocity is measured in metres per second (m/s). Momentum is measured in kilogram metres per second (kg m/s). ...
... Mass is measured in kilograms (kg). Velocity is measured in metres per second (m/s). Momentum is measured in kilogram metres per second (kg m/s). ...
E:\My Documents\sch4u\SCH4U review McKay answers.wpd
... 1) Describe the contributions of the following scientists to our current understanding of atomic structure and the quantum theory: a) Bohr: energy levels b) DeBroglie: wave properties of matter c) Heisenberg: uncertainty principle d) Schrodinger: wave equation for orbitals e) Pauli: magnetic spin pr ...
... 1) Describe the contributions of the following scientists to our current understanding of atomic structure and the quantum theory: a) Bohr: energy levels b) DeBroglie: wave properties of matter c) Heisenberg: uncertainty principle d) Schrodinger: wave equation for orbitals e) Pauli: magnetic spin pr ...
Unravelling the Dark Matter - Dark Energy Paradigm
... We review here the minimal model for a dynamical 3-space. As well as the various confirmed gravitational predictions, there is also an extensive set of direct detection experiments, discussed in [9], with the most recent being from the analysis of NASA/JPL doppler shift data from spacecraft earth-fl ...
... We review here the minimal model for a dynamical 3-space. As well as the various confirmed gravitational predictions, there is also an extensive set of direct detection experiments, discussed in [9], with the most recent being from the analysis of NASA/JPL doppler shift data from spacecraft earth-fl ...
Precision, accuracy and significant figures
... © Pearson Education Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) 2008. This page from the Chemistry Dimensions 2, Teacher’s Resource may be reproduced for classroom use. ...
... © Pearson Education Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) 2008. This page from the Chemistry Dimensions 2, Teacher’s Resource may be reproduced for classroom use. ...
Modeling the Solubility of Nitrogen Dioxide in Water Using
... associate with water molecules, but do not associate among themselves. However, NO2 molecules are capable of forming dimers N2O4 through eq 1, which is in fact dominant at low temperatures particularly in liquid phase.24 In the SAFT framework, the dimerization is modeled as an association bonding th ...
... associate with water molecules, but do not associate among themselves. However, NO2 molecules are capable of forming dimers N2O4 through eq 1, which is in fact dominant at low temperatures particularly in liquid phase.24 In the SAFT framework, the dimerization is modeled as an association bonding th ...
Many-body van der Waals interactions in molecules and condensed
... In order to enable rational predictions and design of molecular and condensed-matter materials, including the interfaces between them, a reliable first-principles method is required that can describe vdW interactions both accurately and efficiently. However, forming an accurate description of vdW in ...
... In order to enable rational predictions and design of molecular and condensed-matter materials, including the interfaces between them, a reliable first-principles method is required that can describe vdW interactions both accurately and efficiently. However, forming an accurate description of vdW in ...
6 Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
... energy of the system goes on decreasing till it registers a minimum. At this point the overlapping halts, since the positive cores (nuclei) of the two atoms are apart by a certain equilibrium distance, the stabilizing effect of overlapping is completely balanced by the repulsion between the positive ...
... energy of the system goes on decreasing till it registers a minimum. At this point the overlapping halts, since the positive cores (nuclei) of the two atoms are apart by a certain equilibrium distance, the stabilizing effect of overlapping is completely balanced by the repulsion between the positive ...
Preprint
... 2.1.2 Light scattering from atomic beams and atoms at rest The interaction of a neutral atomic beam with an optical standing wave was studied by several groups in the early 1980’s. Quantitative studies which focused on the effect of conservative optical potentials were performed by Pritchard and col ...
... 2.1.2 Light scattering from atomic beams and atoms at rest The interaction of a neutral atomic beam with an optical standing wave was studied by several groups in the early 1980’s. Quantitative studies which focused on the effect of conservative optical potentials were performed by Pritchard and col ...
Slides - Agenda
... An exact procedure for computing many-particle Bohmian trajectories The correlations are introduced into the time-dependent potentials 4th The interacting potential from (a classical-like) Bohmian trajectories 5th There is a real potential to account for “non-classical” correlations 6th There is a i ...
... An exact procedure for computing many-particle Bohmian trajectories The correlations are introduced into the time-dependent potentials 4th The interacting potential from (a classical-like) Bohmian trajectories 5th There is a real potential to account for “non-classical” correlations 6th There is a i ...
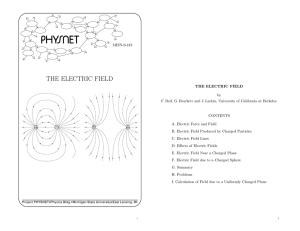
the electric field
... only imagine placing at P a particle having some convenient charge q. (For example, we might choose q to be simply +1 coulomb.) Then we can calculate the electric force F~ on this particle to find the electric field ~ = F~ /q at P . E ~ at a point P , we must actually place To measure the electric f ...
... only imagine placing at P a particle having some convenient charge q. (For example, we might choose q to be simply +1 coulomb.) Then we can calculate the electric force F~ on this particle to find the electric field ~ = F~ /q at P . E ~ at a point P , we must actually place To measure the electric f ...
Redox - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... Separate samples of hydrogen peroxide are added to aqueous potassium iodide and to acidified potassium dichromate(VI). The iodide ions are oxidised and dichromate(VI) ions are reduced. ...
... Separate samples of hydrogen peroxide are added to aqueous potassium iodide and to acidified potassium dichromate(VI). The iodide ions are oxidised and dichromate(VI) ions are reduced. ...
Measurements in Quantum Optics
... with the advent of an inherently non-deterministic theory, quantum mechanics, it was recognized that also the concept of a measurement had to be remodelled. For example, the theory presupposes that not every value of a measurable quantity is a valid experimental result. In this light, Albert Einstei ...
... with the advent of an inherently non-deterministic theory, quantum mechanics, it was recognized that also the concept of a measurement had to be remodelled. For example, the theory presupposes that not every value of a measurable quantity is a valid experimental result. In this light, Albert Einstei ...
Strangeness Production at Low Energies
... Ø No model describes all particle species simultaneously Deep sub-threshold strangeness production: § φ sizeable source for K- production § Feed-down can explain lower effective temperature and rapidity spectrum of KØ No indication for sequential freeze-out of K+/KThe global picture: § Universal c ...
... Ø No model describes all particle species simultaneously Deep sub-threshold strangeness production: § φ sizeable source for K- production § Feed-down can explain lower effective temperature and rapidity spectrum of KØ No indication for sequential freeze-out of K+/KThe global picture: § Universal c ...
Theory and experimental verification of Kapitza-Dirac-Talbot
... and to the manipulation of Bose-Einstein condensates [25, 26]. The working principle of all phase grating examples is the same: A coherent laser beam creates a periodic pattern of the electrical field. This couples to the particle’s polarizability, shifts the energy and thus imprints a phase pattern ...
... and to the manipulation of Bose-Einstein condensates [25, 26]. The working principle of all phase grating examples is the same: A coherent laser beam creates a periodic pattern of the electrical field. This couples to the particle’s polarizability, shifts the energy and thus imprints a phase pattern ...
Chapter 13
... description of gases first presented in Chapter 2. As you know, it is often useful for scientists and science students to use simplified versions of reality (models) to explain scientific phenomena. This section introduces the ideal gas model that helps us to explain the characteristics of most gase ...
... description of gases first presented in Chapter 2. As you know, it is often useful for scientists and science students to use simplified versions of reality (models) to explain scientific phenomena. This section introduces the ideal gas model that helps us to explain the characteristics of most gase ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.