photon particle - wave duality
... K2. Given the frequency or wavelength of a photon, write down expressions for the photon’s energy and momentum. K3. State the value of Planck’s constant. K4. Write down Einstein’s equation for the photoelectric effect, explaining all symbols in the equation and giving the physical significance of ea ...
... K2. Given the frequency or wavelength of a photon, write down expressions for the photon’s energy and momentum. K3. State the value of Planck’s constant. K4. Write down Einstein’s equation for the photoelectric effect, explaining all symbols in the equation and giving the physical significance of ea ...
Electron correlation in three-body Coulomb states of barium
... A systematic study of doubly excited Ngng states involves a variation of the principal quantum number of one of the valence electrons while keeping the other constant. In a first experiment n was varied by selecting different intermediate 5dn 9 g states. The result for N59 is shown in Fig. 2. Excita ...
... A systematic study of doubly excited Ngng states involves a variation of the principal quantum number of one of the valence electrons while keeping the other constant. In a first experiment n was varied by selecting different intermediate 5dn 9 g states. The result for N59 is shown in Fig. 2. Excita ...
Physics 218 - Purdue Physics
... • The center of mass does not move although the skaters separate • Center of mass motion is caused only by the external forces acting on the system ...
... • The center of mass does not move although the skaters separate • Center of mass motion is caused only by the external forces acting on the system ...
Monday, Sept. 23, 2013
... Definition: Incident electromagnetic radiation shining on the material transfers energy to the electrons, allowing them to escape the surface of the metal. Ejected electrons are called photoelectrons Other methods of electron emission: • Thermionic emission: Application of heat allows electrons to g ...
... Definition: Incident electromagnetic radiation shining on the material transfers energy to the electrons, allowing them to escape the surface of the metal. Ejected electrons are called photoelectrons Other methods of electron emission: • Thermionic emission: Application of heat allows electrons to g ...
Jim Greer
... (energy-dependent) self-energy, or approximately through use of a complex potential. We discuss the relation between the two approaches and give a prescription for using the self-energy to construct an energy-independent complex potential [4] that generalizes single-electron electrode self-energies ...
... (energy-dependent) self-energy, or approximately through use of a complex potential. We discuss the relation between the two approaches and give a prescription for using the self-energy to construct an energy-independent complex potential [4] that generalizes single-electron electrode self-energies ...
Worksheet to accompany demos on exchange reactions
... electrons, you just count the fictitious CHARGES. If an atom in a molecule has an oxidation number of zero, that just means that it is assigned (considered from a bookkeeping perspective to ―have‖) the same number of electrons as a neutral, isolated atom has. But let's say that O is assigned an oxi ...
... electrons, you just count the fictitious CHARGES. If an atom in a molecule has an oxidation number of zero, that just means that it is assigned (considered from a bookkeeping perspective to ―have‖) the same number of electrons as a neutral, isolated atom has. But let's say that O is assigned an oxi ...
bond
... like the one shown in the preceding illustration (corresponding to resonance of the two Kekulé structures), the -electrons form double donut-shaped clouds, one above and one below the plane of the ring. ...
... like the one shown in the preceding illustration (corresponding to resonance of the two Kekulé structures), the -electrons form double donut-shaped clouds, one above and one below the plane of the ring. ...
SparkNotes: SAT Chemistry: The Structure of Matter
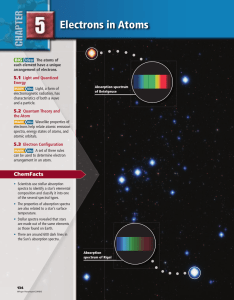
... spontaneous disintegration of an unstable atomic nucleus and the subsequent emission of radiation. But what makes atoms radioactive to begin with, and what makes them undergo radioactive decay? It turns out that there is a stable ratio of protons to neutrons for each element; for the first 20 elemen ...
... spontaneous disintegration of an unstable atomic nucleus and the subsequent emission of radiation. But what makes atoms radioactive to begin with, and what makes them undergo radioactive decay? It turns out that there is a stable ratio of protons to neutrons for each element; for the first 20 elemen ...
lecture1425075996
... 1. The nature of emission of radiation from hot bodies Ex: (black body radiation) 2. Ejection of electrons from metal surface when radiation strikes it (Photo electric effect) 3. Variation of heat capacity of solids as a function of temperature. 4. Line spectra of atoms with special reference to hyd ...
... 1. The nature of emission of radiation from hot bodies Ex: (black body radiation) 2. Ejection of electrons from metal surface when radiation strikes it (Photo electric effect) 3. Variation of heat capacity of solids as a function of temperature. 4. Line spectra of atoms with special reference to hyd ...
click - Uplift North Hills Prep | Uplift Education
... • Emission Spectrum • Set of frequencies of the electromagnetic waves emitted by atoms of a particular element. • A hot, low-density / low pressure gas (gas in the atomic state) produces an emission-line spectrum – energy only at specific λ. • Absorption Spectrum • Pattern of dark lines against a co ...
... • Emission Spectrum • Set of frequencies of the electromagnetic waves emitted by atoms of a particular element. • A hot, low-density / low pressure gas (gas in the atomic state) produces an emission-line spectrum – energy only at specific λ. • Absorption Spectrum • Pattern of dark lines against a co ...
D - Uplift North Hills
... • Emission Spectrum • Set of frequencies of the electromagnetic waves emitted by atoms of a particular element. • A hot, low-density / low pressure gas (gas in the atomic state) produces an emission-line spectrum – energy only at specific λ. • Absorption Spectrum • Pattern of dark lines against a co ...
... • Emission Spectrum • Set of frequencies of the electromagnetic waves emitted by atoms of a particular element. • A hot, low-density / low pressure gas (gas in the atomic state) produces an emission-line spectrum – energy only at specific λ. • Absorption Spectrum • Pattern of dark lines against a co ...
Big Formulas
... Cl O3 ClO O2 ClO O Cl O2 CFC’s (chlorofluorocarbons) are highly stable molecules in the troposphere, however, high-energy UV photons in the stratosphere split chlorine radicals from CFC’s by breaking their C-Cl bond. The freed chlorine radicals are very reactive and can participate in a ...
... Cl O3 ClO O2 ClO O Cl O2 CFC’s (chlorofluorocarbons) are highly stable molecules in the troposphere, however, high-energy UV photons in the stratosphere split chlorine radicals from CFC’s by breaking their C-Cl bond. The freed chlorine radicals are very reactive and can participate in a ...
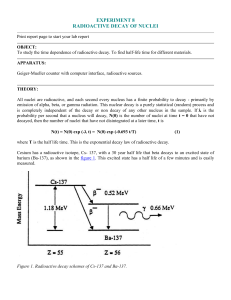
Phys 282 EXP 8
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.