Spin-charge separation in ultra
... and interesting systems. In spite of their apparent conceptual simplicity, both the ground state and the excitations exhibit strong correlation effects and posses a number of exotic properties, ranging from spin-charge separation to fractional statistics (see [6, 7, 8] and ref. therein). Progress in ...
... and interesting systems. In spite of their apparent conceptual simplicity, both the ground state and the excitations exhibit strong correlation effects and posses a number of exotic properties, ranging from spin-charge separation to fractional statistics (see [6, 7, 8] and ref. therein). Progress in ...
Optically detecting the quantization of collective atomic motion
... We find quantitative agreement to this theory as we vary both the cooperativity and the probe duration. In this work, we have demonstrated the quantization of the collective motion of thousands of atoms, observing Stokes asymmetry and zero-point motion. The Stokes asymmetry provides a self-calibrati ...
... We find quantitative agreement to this theory as we vary both the cooperativity and the probe duration. In this work, we have demonstrated the quantization of the collective motion of thousands of atoms, observing Stokes asymmetry and zero-point motion. The Stokes asymmetry provides a self-calibrati ...
REVIEW: (Chapter 8) LINEAR MOMENTUM and COLLISIONS The
... The previous example involved essentially just one particle, the car. The wall was fixed there as a device for exerting a constant force during the collision. A more complex example can be studied when two particles collide. We first make the approximation that the two particles are subjected to no ...
... The previous example involved essentially just one particle, the car. The wall was fixed there as a device for exerting a constant force during the collision. A more complex example can be studied when two particles collide. We first make the approximation that the two particles are subjected to no ...
Low pressure (rare gas + water vapor)
... of the strength of the electric field in the positive column of an (Ar + H2O)-discharge, electrodes fall voltage and the dependencies of some electric, spectroscopic and energetic characteristics on the discharge parameters. In addition to the new information about the discharge these data could als ...
... of the strength of the electric field in the positive column of an (Ar + H2O)-discharge, electrodes fall voltage and the dependencies of some electric, spectroscopic and energetic characteristics on the discharge parameters. In addition to the new information about the discharge these data could als ...
Modern
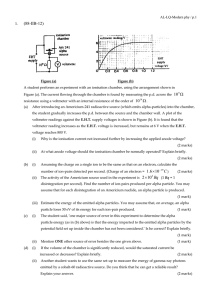
... Describe the energy change of an electron when, after emitting from the hot cathode C, it accelerates towards the grid G and undergoes an inelastic collision with a xenon atom, and finally reaches anode A. (3 marks) ...
... Describe the energy change of an electron when, after emitting from the hot cathode C, it accelerates towards the grid G and undergoes an inelastic collision with a xenon atom, and finally reaches anode A. (3 marks) ...
2011
... What mass of methanol, CH3OH(l), must be added to water to make 150 mL of a 2.0 M CH3OH(aq) solution? A) 2.4 g C) 4.3 g B) 3.5 g D) 9.6 g ...
... What mass of methanol, CH3OH(l), must be added to water to make 150 mL of a 2.0 M CH3OH(aq) solution? A) 2.4 g C) 4.3 g B) 3.5 g D) 9.6 g ...
Regents Chemistry
... o be able to predict the amount of solute that will crystallize (precipitate) from solution when it is chilled o use Table G to predict if a solution is saturated, unsaturated or supersaturated Determine whether a given compound will be soluble or insoluble in water using the guidelines in Table F. ...
... o be able to predict the amount of solute that will crystallize (precipitate) from solution when it is chilled o use Table G to predict if a solution is saturated, unsaturated or supersaturated Determine whether a given compound will be soluble or insoluble in water using the guidelines in Table F. ...
3. What is the empirical formula of a compound that is
... Fats yield much higher energy per unit mass than carbohydrates. Fats are mostly made of long chains of carbon and hydrogen. If the process of oxidation takes a carbon and hydrogen-containing molecule to carbon dioxide and water while producing energy, is it not reasonable that we might get the great ...
... Fats yield much higher energy per unit mass than carbohydrates. Fats are mostly made of long chains of carbon and hydrogen. If the process of oxidation takes a carbon and hydrogen-containing molecule to carbon dioxide and water while producing energy, is it not reasonable that we might get the great ...
- Philsci
... Hamiltonian, dependent on the differences between the particle positions, it turns out that this individual freedom disappears. The symmetry transformations can now only have the form qi´ = aqi + b(t), with the same a and b for all particles. In our scheme this is the translation of the fact in the ...
... Hamiltonian, dependent on the differences between the particle positions, it turns out that this individual freedom disappears. The symmetry transformations can now only have the form qi´ = aqi + b(t), with the same a and b for all particles. In our scheme this is the translation of the fact in the ...
4.4 Heat transfer by radiation 4.4.1 Black body radiation f c λ = c f = 1
... where h = 6.625 ⋅ 10 −34 Js is the Planck’s constant and f frequency of an atom oscillator. Amount of energy emitted by an atom is equal to a decrease in potential energy of its constituents (electrons and nucleus). The expression (4.49) explains the observed line spectra of atoms which are due to t ...
... where h = 6.625 ⋅ 10 −34 Js is the Planck’s constant and f frequency of an atom oscillator. Amount of energy emitted by an atom is equal to a decrease in potential energy of its constituents (electrons and nucleus). The expression (4.49) explains the observed line spectra of atoms which are due to t ...
mole concept a
... contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in exactly 0.012 kilogram or 12 gram of the carbon-12 isotope. This definition gives us a method by which we can find out the amount of a substance (in moles) if we know the number of elementary entities present in it or vice versa. Now the que ...
... contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in exactly 0.012 kilogram or 12 gram of the carbon-12 isotope. This definition gives us a method by which we can find out the amount of a substance (in moles) if we know the number of elementary entities present in it or vice versa. Now the que ...
Electronic structure and reactivity analysis of some TTF
... that molecule tends to react where the value of descriptor is largest when attacked by soft reagent and where the value is smaller when attacked by hard reagent [34]. The use of descriptors for the site selectivity of the molecule for nucleophilic and electrophilic attack has been made. Parameters o ...
... that molecule tends to react where the value of descriptor is largest when attacked by soft reagent and where the value is smaller when attacked by hard reagent [34]. The use of descriptors for the site selectivity of the molecule for nucleophilic and electrophilic attack has been made. Parameters o ...
CHE 105 Spring 2017 Exam 3
... D. Of all the visible colors, the one with the longest wavelength emits photons with the highest energy. ✓E. Visible light comprises only a small fraction of the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
... D. Of all the visible colors, the one with the longest wavelength emits photons with the highest energy. ✓E. Visible light comprises only a small fraction of the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
momentum
... Collisions – Characteristics The term collision represents an event during which two particles come close to each other and interact by means of forces. May involve physical contact, but must be generalized to include cases with interaction without physical contact The interaction forces are assu ...
... Collisions – Characteristics The term collision represents an event during which two particles come close to each other and interact by means of forces. May involve physical contact, but must be generalized to include cases with interaction without physical contact The interaction forces are assu ...
trt 408 physical chemistry
... arranged in patterns with long range, repeating order. Or Its may be amorphous in which case its atoms or molecules do not have any long range order. ...
... arranged in patterns with long range, repeating order. Or Its may be amorphous in which case its atoms or molecules do not have any long range order. ...
the problem book
... Hint: You may use the azimuthal symmetry to write down a general expression for the potential in the form of a series, and then use the boundary conditions to determine the coefficients. ...
... Hint: You may use the azimuthal symmetry to write down a general expression for the potential in the form of a series, and then use the boundary conditions to determine the coefficients. ...
Optics and interferometry with Na 2 molecules
... signal despite the plethora of close lying rovibrational This is not entirely surprising. states in the molecules. The fact that two nearby molecules are very unlikely to have the same quantum numbers for both rovibrational state and total angular momentum projection is not important since the first ...
... signal despite the plethora of close lying rovibrational This is not entirely surprising. states in the molecules. The fact that two nearby molecules are very unlikely to have the same quantum numbers for both rovibrational state and total angular momentum projection is not important since the first ...
ХИМИЯ НА АНГЛИЙСКОМ ЯЗЫКЕ
... 2.1. The ratio of the mass of oxygen to carbon atom is 1.3329. What is the mass of the oxygen atom? 2.2. The ratio of the mass of bromine atom to carbon is 6.650. What is the mass of the bromine atom? 2.3. Calculate the number of moles in each of the following: a) 3.01x1022 N2 molecules; b) 4.82x102 ...
... 2.1. The ratio of the mass of oxygen to carbon atom is 1.3329. What is the mass of the oxygen atom? 2.2. The ratio of the mass of bromine atom to carbon is 6.650. What is the mass of the bromine atom? 2.3. Calculate the number of moles in each of the following: a) 3.01x1022 N2 molecules; b) 4.82x102 ...
Cite this as: G. Vasan, A. Erbe: Physical Chemistry Chemical
... real metals can easily be incorporated, arbitrarily shaped geometries can be calculated, and the effect of interfaces can be studied. The drawbacks are relatively long computation times and rather low overall system size which can be studied. Despite these limitations in system size, important morp ...
... real metals can easily be incorporated, arbitrarily shaped geometries can be calculated, and the effect of interfaces can be studied. The drawbacks are relatively long computation times and rather low overall system size which can be studied. Despite these limitations in system size, important morp ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.