II. Forces
... Different sounds appear different because they have different pitch or frequency. Click here for video clip II. Forces A. gravitational 1. The force of gravity between any two objects increases as the mass of either object increases. The force of gravity decreases as the distance between the objects ...
... Different sounds appear different because they have different pitch or frequency. Click here for video clip II. Forces A. gravitational 1. The force of gravity between any two objects increases as the mass of either object increases. The force of gravity decreases as the distance between the objects ...
Alkali D Line Data
... f is the partial pressure of water vapor in the air, in Pa (which can be computed from the relative humidity via the Goff-Gratch equation [15]). This formula is appropriate for laboratory conditions and has an estimated (3σ) uncertainty of 3 × 10−8 from 350-650 nm. The lifetimes are weighted average ...
... f is the partial pressure of water vapor in the air, in Pa (which can be computed from the relative humidity via the Goff-Gratch equation [15]). This formula is appropriate for laboratory conditions and has an estimated (3σ) uncertainty of 3 × 10−8 from 350-650 nm. The lifetimes are weighted average ...
Applying Newton`s 2nd Law to
... Two body questions can be vertical or horizontal! Ex 1) Two blocks of identical material are connected by a light rope on a level surface. An applied force of 55 N [right] causes the blocks to ● Since the boxes are attached by a wire, they accelerate. While in motion, the magnitude of the force of ...
... Two body questions can be vertical or horizontal! Ex 1) Two blocks of identical material are connected by a light rope on a level surface. An applied force of 55 N [right] causes the blocks to ● Since the boxes are attached by a wire, they accelerate. While in motion, the magnitude of the force of ...
prs-A3
... The following diagram represents the collection of carbon dioxide and water formed by the decomposition of a hydrocarbon. What was the empirical formula of the original hydrocarbon? • C4H16 • C 2H 8 • CH4 • While the diagram indicates 4 carbons, and you might think there could have been 1 C4H16, 2 ...
... The following diagram represents the collection of carbon dioxide and water formed by the decomposition of a hydrocarbon. What was the empirical formula of the original hydrocarbon? • C4H16 • C 2H 8 • CH4 • While the diagram indicates 4 carbons, and you might think there could have been 1 C4H16, 2 ...
Lesson 1 Reversible reactions and equilibrium
... 1. Three applications instead of just one – good Plants get time to take in each application. 2. More soluble fertiliser – bad It will dissolve in rain and wash into local drains. 3. Avoid applying it before rain is due – good This means it won’t dissolve in the rain and wash into drains. 4. Grow a ...
... 1. Three applications instead of just one – good Plants get time to take in each application. 2. More soluble fertiliser – bad It will dissolve in rain and wash into local drains. 3. Avoid applying it before rain is due – good This means it won’t dissolve in the rain and wash into drains. 4. Grow a ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint
... Atomic Mass Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams. Use atomic mass units. an atomic mass unit (amu) is one twelth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This gives us a basis for comparison. The decimal numbers on the table are atomic masses in amu. ...
... Atomic Mass Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams. Use atomic mass units. an atomic mass unit (amu) is one twelth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This gives us a basis for comparison. The decimal numbers on the table are atomic masses in amu. ...
A magnetic model of matter
... electromagnetism are symmetrical between positive and negative charges, when both types are considered together. If the dual-charged particles, and their antiparticles, realize a certain ratio between electric and magnetic charge, but not its negative value, the rule of CP invariance is broken. This ...
... electromagnetism are symmetrical between positive and negative charges, when both types are considered together. If the dual-charged particles, and their antiparticles, realize a certain ratio between electric and magnetic charge, but not its negative value, the rule of CP invariance is broken. This ...
Chapter 23 Objective Questions The magnitude of the electric force
... are fixed in space and separated by a distance d. A third particle with charge –Q is free to move and lies initially at rest on the perpendicular bisector of the two fixed charges a distance x from the midpoint between those charges (Fig. P23.14). (a) Show that if x is small compared with d, the mot ...
... are fixed in space and separated by a distance d. A third particle with charge –Q is free to move and lies initially at rest on the perpendicular bisector of the two fixed charges a distance x from the midpoint between those charges (Fig. P23.14). (a) Show that if x is small compared with d, the mot ...
CYL_Practice_harmonic_oscillator_rigid_rotor
... 8.17(b) Assuming that the vibrations of a 14N2molecule are equivalent to those of a harmonic oscillator with a force constant k= 2293.8 N m ", what is the zero-point energy of vibration of this molecule? The effective mass of a homonuclear diatomic molecule is half its total mass, and m(l4N) = 14.00 ...
... 8.17(b) Assuming that the vibrations of a 14N2molecule are equivalent to those of a harmonic oscillator with a force constant k= 2293.8 N m ", what is the zero-point energy of vibration of this molecule? The effective mass of a homonuclear diatomic molecule is half its total mass, and m(l4N) = 14.00 ...
Document
... • Thermal Conductivity of insulating crystals a T3 at low temperatures. a T-1 at high temperatures. • Strong effect of defects and specimen dimensions at low ...
... • Thermal Conductivity of insulating crystals a T3 at low temperatures. a T-1 at high temperatures. • Strong effect of defects and specimen dimensions at low ...
Common Exam - 2011 Department of Physics University of Utah
... Please note that there is a separate booklet for each numbered question (i.e., use booklet #1 for problem #1, etc.). To receive full credit, not only should the correct solutions be given, but a sufficient number of steps should be given so that a faculty grader can follow your reasoning. Define all ...
... Please note that there is a separate booklet for each numbered question (i.e., use booklet #1 for problem #1, etc.). To receive full credit, not only should the correct solutions be given, but a sufficient number of steps should be given so that a faculty grader can follow your reasoning. Define all ...
CHEM 210 Ch06
... • Any ion that has a net positive charge at that pH will migrate toward the negatively charged cathode. • Any ion having a net negative charge will migrate toward the positively charged anode. • If the net charge is zero, the species will not move. • An amino acid’s isoelectric pH, or isoelectric po ...
... • Any ion that has a net positive charge at that pH will migrate toward the negatively charged cathode. • Any ion having a net negative charge will migrate toward the positively charged anode. • If the net charge is zero, the species will not move. • An amino acid’s isoelectric pH, or isoelectric po ...
views of dark energy
... and gauge particles, unified with each other and with gravity – led to a maze of conceivable choices. ...
... and gauge particles, unified with each other and with gravity – led to a maze of conceivable choices. ...
Spin-Orbit Suppression of Cold Inelastic Collisions of Aluminum and Helium Please share
... validate its theoretical description. Theoretical quantum calculations based on ab initio interatomic potentials have had some recent success in predicting inelastic collision rates [7,14,15]. In many atomic systems, however, the collision rates are either too fast or too slow to be directly measure ...
... validate its theoretical description. Theoretical quantum calculations based on ab initio interatomic potentials have had some recent success in predicting inelastic collision rates [7,14,15]. In many atomic systems, however, the collision rates are either too fast or too slow to be directly measure ...
Nonclassical States of Cold Atomic Ensembles and of Light Fields
... long-range r-4 potential leads to semiclassical behavior for a wide range of collision energies, but where quantum phenomena dominate collisions at very low energies. Cold ion-atom collisions have been proposed as a means to demonstrate quantum gates [30], to cool atoms [31] or molecules [27,32,33] ...
... long-range r-4 potential leads to semiclassical behavior for a wide range of collision energies, but where quantum phenomena dominate collisions at very low energies. Cold ion-atom collisions have been proposed as a means to demonstrate quantum gates [30], to cool atoms [31] or molecules [27,32,33] ...
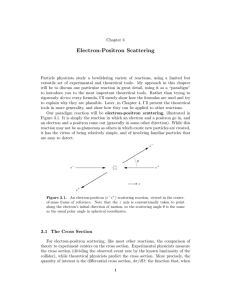
Electron-Positron Scattering
... that DF (x − y) satisfies the Klein-Gordon equation everywhere except at y = x. At y = x, we would have to add an infinite (delta function) potential term to the Klein-Gordon equation, to represent the disturbance that creates the particle. This infinite potential term results in an infinite wavefunctio ...
... that DF (x − y) satisfies the Klein-Gordon equation everywhere except at y = x. At y = x, we would have to add an infinite (delta function) potential term to the Klein-Gordon equation, to represent the disturbance that creates the particle. This infinite potential term results in an infinite wavefunctio ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.