Lecture 5 Motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field
... denotes the Larmor frequency. 2m (Without spin contribution) uniform magnetic field ! splitting of (2* + 1)-fold degeneracy with multiplets separated by !ωL . where ωL = ...
... denotes the Larmor frequency. 2m (Without spin contribution) uniform magnetic field ! splitting of (2* + 1)-fold degeneracy with multiplets separated by !ωL . where ωL = ...
Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions
... There are millions of compounds that will produce endless chemical reactions, therefore not all chemical reactions can be carried out in the laboratory A system is used to classify chemical reactions, which allows chemist to recognize patterns and predict the products of reactions One of these ...
... There are millions of compounds that will produce endless chemical reactions, therefore not all chemical reactions can be carried out in the laboratory A system is used to classify chemical reactions, which allows chemist to recognize patterns and predict the products of reactions One of these ...
PDF - at www.arxiv.org.
... The creation of a quantum computer is an outstanding fundamental and practical problem. The quantum computer could be used for the execution of very complicated tasks which are not solvable with the classical computers. The first prototype of a solid state quantum computer was created in 2009 with s ...
... The creation of a quantum computer is an outstanding fundamental and practical problem. The quantum computer could be used for the execution of very complicated tasks which are not solvable with the classical computers. The first prototype of a solid state quantum computer was created in 2009 with s ...
Problems - TTU Physics
... A block of mass m moves along the x-axis. At time t = 0, it is at x = 0 and its velocity is v0. At t = 0, a time dependent force given by F = F0e-kt begins to act, where F0 and k are constants. Find (in any order) a. The velocity as a function of time (v(t)). b. The position as a function of time (x ...
... A block of mass m moves along the x-axis. At time t = 0, it is at x = 0 and its velocity is v0. At t = 0, a time dependent force given by F = F0e-kt begins to act, where F0 and k are constants. Find (in any order) a. The velocity as a function of time (v(t)). b. The position as a function of time (x ...
Document
... mechanical calculations of electronic structure. We avoid using it when the core electrons could be polarized, as in the case of magnetic systems. 9c) Tell me everything that you know about basis sets for representing the electronic wavefuction in a quantum mechanical simulation. The full electronic ...
... mechanical calculations of electronic structure. We avoid using it when the core electrons could be polarized, as in the case of magnetic systems. 9c) Tell me everything that you know about basis sets for representing the electronic wavefuction in a quantum mechanical simulation. The full electronic ...
Print this article - Bangladesh Journals Online
... assignable for protons Hd and Ha respectively. The two doublets of doublet at δ 6.5 (JHa-Hb = JHb-Hc = J = 8.0 Hz) and 6.9 (JHb-Hc= JHc-Hd = J = 8.0 Hz) accounts for the Ha and Hd respectively, while the relatively downfield signal at δ 8.5 has been assigned for the imine (=N-H) proton of 2-mercapto ...
... assignable for protons Hd and Ha respectively. The two doublets of doublet at δ 6.5 (JHa-Hb = JHb-Hc = J = 8.0 Hz) and 6.9 (JHb-Hc= JHc-Hd = J = 8.0 Hz) accounts for the Ha and Hd respectively, while the relatively downfield signal at δ 8.5 has been assigned for the imine (=N-H) proton of 2-mercapto ...
VI. Conservation of Energy and Momentum C. Momentum 12. The
... _________________________ is the product of a force and the time interval during which it acts. Unlike most of our calculations, impulse is NOT defined by just one variable. Impulse is nothing more than a ____________________ in momentum. ...
... _________________________ is the product of a force and the time interval during which it acts. Unlike most of our calculations, impulse is NOT defined by just one variable. Impulse is nothing more than a ____________________ in momentum. ...
High Resolution Laboratory UV Spectroscopy for Cassini UVIS at Titan
... Produce First Emission ab initio Quantum Model of Electron Excited Induced UV Fluorescence of N2 of 9 electronic states (b 1Πu, b' 1Σu+, c4' 1Σu+ c3 1Πu, o3 Πu, c4 1Πu, c5 1Πu, c5 '1Σu+ c6'Σu+ X 1Σg+ from 1215 eV for UVIS model. All UV Emission states are perturbed (>20% admixture) and weakly-to-s ...
... Produce First Emission ab initio Quantum Model of Electron Excited Induced UV Fluorescence of N2 of 9 electronic states (b 1Πu, b' 1Σu+, c4' 1Σu+ c3 1Πu, o3 Πu, c4 1Πu, c5 1Πu, c5 '1Σu+ c6'Σu+ X 1Σg+ from 1215 eV for UVIS model. All UV Emission states are perturbed (>20% admixture) and weakly-to-s ...
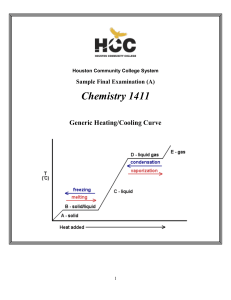
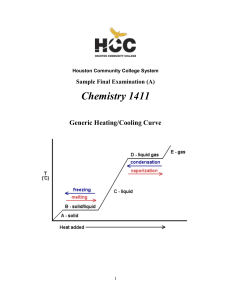
CHEM-1411 Final Practice Exam
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
1411FINALSAMPLE+KEY - Houston Community College
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
Physics 2414, Spring 2005 Group Exercise 7, Mar 31, 2005
... (a) What is the expression for the change in kinetic energy in going from point ‘1’ to point ‘2’ ? (The superscript ‘12’ denotes the end points ‘1’ and ‘2’.) ...
... (a) What is the expression for the change in kinetic energy in going from point ‘1’ to point ‘2’ ? (The superscript ‘12’ denotes the end points ‘1’ and ‘2’.) ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... • Oxidation / Reduction reactions are often called Redox reactions. – Oxidation – loss of electrons (e-) – Reduction – gain of electrons (e-) ...
... • Oxidation / Reduction reactions are often called Redox reactions. – Oxidation – loss of electrons (e-) – Reduction – gain of electrons (e-) ...
Notes
... The form of carbon reacts with the oxygen of the air been blown into the furnace and gives carbon dioxide which then reacts with more coke to give carbon monoxide. It is the carbon monoxide which is named the reducing agent of the process. A reducing agent is a substance which brings about reduction ...
... The form of carbon reacts with the oxygen of the air been blown into the furnace and gives carbon dioxide which then reacts with more coke to give carbon monoxide. It is the carbon monoxide which is named the reducing agent of the process. A reducing agent is a substance which brings about reduction ...
Quantum Monte Carlo Methods Chapter 14
... The numerically time-consuming part in the variational Monte Carlo calculation is the evaluation of the kinetic energy term. The potential energy, as long as it has a spatial dependence only, adds a simple term to the local energy operator. In our discussion below, we base our numerical Monte Carlo ...
... The numerically time-consuming part in the variational Monte Carlo calculation is the evaluation of the kinetic energy term. The potential energy, as long as it has a spatial dependence only, adds a simple term to the local energy operator. In our discussion below, we base our numerical Monte Carlo ...
PPT
... The Nobel Prize in Physics 2001 "for the achievement of Bose-Einstein condensation in dilute gases of alkali atoms, and for early fundamental studies of the properties of the condensates" ...
... The Nobel Prize in Physics 2001 "for the achievement of Bose-Einstein condensation in dilute gases of alkali atoms, and for early fundamental studies of the properties of the condensates" ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.