SOL Review Part 3 Nomenclature reactions
... ► If the anion is an element, change its ending to -ide; if the anion is a polyatomic ion, simply write the name of the polyatomic ion. ► If the cation can have more than one possible charge, write the charge as a Roman numeral in parentheses. ...
... ► If the anion is an element, change its ending to -ide; if the anion is a polyatomic ion, simply write the name of the polyatomic ion. ► If the cation can have more than one possible charge, write the charge as a Roman numeral in parentheses. ...
Answers - jpsaos
... gravitational work to be done. (See the balls and bowls in Fig. 8.11.) However, there is another type of equilibrium in which the displacement of the center of mass involves no gravitational work. This is called neutral equilibrium, and the displaced center of gravity essentially moves in a straight ...
... gravitational work to be done. (See the balls and bowls in Fig. 8.11.) However, there is another type of equilibrium in which the displacement of the center of mass involves no gravitational work. This is called neutral equilibrium, and the displaced center of gravity essentially moves in a straight ...
Electron Spin or “Classically Non-Describable Two - Philsci
... motion, though it was unclear from the very beginning how literal one was actually supposed to take this picture, since it was immediately recognised (already by Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck) that it would very likely lead to serious problems with Special Relativity if the model were to reproduce the elec ...
... motion, though it was unclear from the very beginning how literal one was actually supposed to take this picture, since it was immediately recognised (already by Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck) that it would very likely lead to serious problems with Special Relativity if the model were to reproduce the elec ...
STATISTICS
... the others decay? c) What is the probability that exactly three atoms (any three) decay during the 3 hours? d) What is the probability that exactly 6 atoms will decay in 3 hours? e) What is the chance that no atoms will decay in 3 hours? f) What is the general formula for the probability that exactl ...
... the others decay? c) What is the probability that exactly three atoms (any three) decay during the 3 hours? d) What is the probability that exactly 6 atoms will decay in 3 hours? e) What is the chance that no atoms will decay in 3 hours? f) What is the general formula for the probability that exactl ...
Algebraic Symmetries in Quantum Chemistry
... Every vector in the irrep is assigned a unique pattern of weights stemming from the algebra A and any if its subalgebras ...
... Every vector in the irrep is assigned a unique pattern of weights stemming from the algebra A and any if its subalgebras ...
quantum number - Reseda High School
... description of atoms. Both theories are based on the existence of simple building blocks, atoms in one case, and quanta in the other. The work of Plank and Einstein thus suggested a connection between the quantized nature of energy and the properties of individual atoms. In fact, Einstein's Nobel Pr ...
... description of atoms. Both theories are based on the existence of simple building blocks, atoms in one case, and quanta in the other. The work of Plank and Einstein thus suggested a connection between the quantized nature of energy and the properties of individual atoms. In fact, Einstein's Nobel Pr ...
Physical Science - Towns County Schools
... Level 4 requires the complex reasoning of Level 3 with the addition of planning, investigating, applying significant conceptual understanding, and/or developing that will most likely require an extended period of time. You may be required to connect and relate ideas and concepts within the content a ...
... Level 4 requires the complex reasoning of Level 3 with the addition of planning, investigating, applying significant conceptual understanding, and/or developing that will most likely require an extended period of time. You may be required to connect and relate ideas and concepts within the content a ...
Chemical Reactions
... To write a word equation, write the names of the reactants to the left of the arrow separated by plus signs. Write the names of the products to the right of the arrow, also separated by plus ...
... To write a word equation, write the names of the reactants to the left of the arrow separated by plus signs. Write the names of the products to the right of the arrow, also separated by plus ...
Amines
... • The very small amines like aminomethane (methylamine) and 1aminoethane (ethylamine) smell very similar to ammonia. • As the amines get bigger, they tend to smell more "fishy", or they smell of decay. ...
... • The very small amines like aminomethane (methylamine) and 1aminoethane (ethylamine) smell very similar to ammonia. • As the amines get bigger, they tend to smell more "fishy", or they smell of decay. ...
How to characterize the dynamics of cold atoms in non
... the dynamics of a system in its classical and quantum limits. Both are closely related, as the latter is defined only as a function of the former. In particular, quantum chaos is defined as the quantum regime of a system whose classical dynamics is chaotic. A good understanding of the classical dynami ...
... the dynamics of a system in its classical and quantum limits. Both are closely related, as the latter is defined only as a function of the former. In particular, quantum chaos is defined as the quantum regime of a system whose classical dynamics is chaotic. A good understanding of the classical dynami ...
Chemical Equations I
... • Determine the empirical formula • Calculate empirical formula mass • Determine ratio of empirical formula mass to molecular mass – molecular mass is experimentally ...
... • Determine the empirical formula • Calculate empirical formula mass • Determine ratio of empirical formula mass to molecular mass – molecular mass is experimentally ...
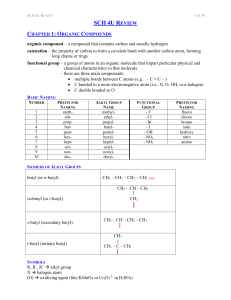
12 U Chem Review
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
sch4ureview
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
(Received February 12, 1988 by M. Cardona)
... Fig. 1, is --~ 2s and ls - * 2p0, all observed lines may be assigned without any constraint taking into account the electric dipole selection rules. Transitions are allowed to final states with m = 4-1 and = = ( - 1 ) m+~ = - 1 , i.e. x even. In Fig. 2 a transition energy level scheme is plotted sho ...
... Fig. 1, is --~ 2s and ls - * 2p0, all observed lines may be assigned without any constraint taking into account the electric dipole selection rules. Transitions are allowed to final states with m = 4-1 and = = ( - 1 ) m+~ = - 1 , i.e. x even. In Fig. 2 a transition energy level scheme is plotted sho ...
Scalar Field Theories with Screening Mechanisms
... If new scalar fields are included in theories then new forces can be found. A screening mechanism dynamically suppresses theses forces without the need for fine tuning. This relies on the presence of non-linearities in the equations of motion. Most physics done is linear, so studying screening mecha ...
... If new scalar fields are included in theories then new forces can be found. A screening mechanism dynamically suppresses theses forces without the need for fine tuning. This relies on the presence of non-linearities in the equations of motion. Most physics done is linear, so studying screening mecha ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.