Chapter 3 Reading Questions
... 24. A balancing coefficient is a a. numerical multiplier of all the atoms in the formula that follows it. b. numerical change in the formula subscripts c. numerical change in the charge of an ion d. all of the above are correct 25. Which of the following is NOT true about balancing equations? a. A ...
... 24. A balancing coefficient is a a. numerical multiplier of all the atoms in the formula that follows it. b. numerical change in the formula subscripts c. numerical change in the charge of an ion d. all of the above are correct 25. Which of the following is NOT true about balancing equations? a. A ...
Chemistry Honors Unit 2 Study Guide Atomic Theory Mr. Brown Use
... Law of Definite Proportions/Composition = Chemical compounds always contain the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the amount or source of the sample. EX. NaCl always contain 39.34% by mass of Na and 60.66% by mass of Cl. Law of Multiple Proportions = If two or more ...
... Law of Definite Proportions/Composition = Chemical compounds always contain the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the amount or source of the sample. EX. NaCl always contain 39.34% by mass of Na and 60.66% by mass of Cl. Law of Multiple Proportions = If two or more ...
MATTER-Ch. 3-homogeneous vs. heterogeneous, elements
... The nucleus of an atom has all of the following characteristics EXCEPT that it a. is positively charged. c. contains nearly all of the atom's mass. b. is very dense. d. contains nearly all of the atom's volume. ____ 25. Which part of an atom has a mass approximately equal to 1/2000 of the mass of a ...
... The nucleus of an atom has all of the following characteristics EXCEPT that it a. is positively charged. c. contains nearly all of the atom's mass. b. is very dense. d. contains nearly all of the atom's volume. ____ 25. Which part of an atom has a mass approximately equal to 1/2000 of the mass of a ...
PUC Schools - cloudfront.net
... Standard 7: Chemical Thermodynamics 27. (7.c) When water changes phase from liquid to gas, the process is a) Exothermic b) Endothermic c) Neutral d) Kinetic 28. (7.c) The temperature of iced water melting is _____ oC. The temperature of boiling water is _____ oC. a) 100, 200 b) 0, 100 c) 100, 0 d) ...
... Standard 7: Chemical Thermodynamics 27. (7.c) When water changes phase from liquid to gas, the process is a) Exothermic b) Endothermic c) Neutral d) Kinetic 28. (7.c) The temperature of iced water melting is _____ oC. The temperature of boiling water is _____ oC. a) 100, 200 b) 0, 100 c) 100, 0 d) ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-Reduction
... When you run reactions in liquid solutions, it is convenient to dispense the amounts of reactants by measuring out volumes of reactant solutions When we dissolve a substance in a liquid, we call the substance the solute and the liquid the solvent. solvent. The general term concentration refers to th ...
... When you run reactions in liquid solutions, it is convenient to dispense the amounts of reactants by measuring out volumes of reactant solutions When we dissolve a substance in a liquid, we call the substance the solute and the liquid the solvent. solvent. The general term concentration refers to th ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... 4. Check your work by counting atoms of each element , they should be the same on both sides of the equation. 5. If you cannot balance an equation, you have probably written a formula incorrectly, Check and try again. Hints for balancing and writing chemical equations: * Remember the seven elements ...
... 4. Check your work by counting atoms of each element , they should be the same on both sides of the equation. 5. If you cannot balance an equation, you have probably written a formula incorrectly, Check and try again. Hints for balancing and writing chemical equations: * Remember the seven elements ...
CHEMISTRY SEMESTER ONE LAB 1 Lab 1: Stoichiometry and
... 7. Decant the wash water from the copper and add 10 more mL of distilled water, swirl and decant again. Put the liquid from these two washes in the labeled waste container provided in your kit. 8. Now wash the copper with several mL of acetone (Be careful! Acetone is very flammable). Swirl and allow ...
... 7. Decant the wash water from the copper and add 10 more mL of distilled water, swirl and decant again. Put the liquid from these two washes in the labeled waste container provided in your kit. 8. Now wash the copper with several mL of acetone (Be careful! Acetone is very flammable). Swirl and allow ...
Microsoft Word format
... processes as physical or chemical changes, and learn that mass is conserved in chemical reactions. The observations include separation of iron and sulfur with a magnet, separation of sand and salt by dissolution/evaporation, combustion and acid dissolution of magnesium metal, the reaction of solid i ...
... processes as physical or chemical changes, and learn that mass is conserved in chemical reactions. The observations include separation of iron and sulfur with a magnet, separation of sand and salt by dissolution/evaporation, combustion and acid dissolution of magnesium metal, the reaction of solid i ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... 11. When H2SO4 and Ba(OH)2 are reacted in a double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2 ...
... 11. When H2SO4 and Ba(OH)2 are reacted in a double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2 ...
Tuesday, June 03, 2008 1. Given the incomplete equation
... Base your answer to the question on the information below. Ozone gas, O 3, can be used to kill adult insects in storage bins for grain without damaging the grain. The ozone is produced from oxygen gas, O2, in portable ozone generators located near the storage bins. The concentrations of ozone used a ...
... Base your answer to the question on the information below. Ozone gas, O 3, can be used to kill adult insects in storage bins for grain without damaging the grain. The ozone is produced from oxygen gas, O2, in portable ozone generators located near the storage bins. The concentrations of ozone used a ...
Metals
... A compound is a distinct substance that contains two or more elements combined in a definite proportion by weight. ...
... A compound is a distinct substance that contains two or more elements combined in a definite proportion by weight. ...
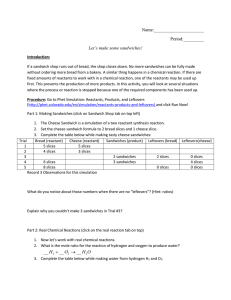
Name: Period:______ Let`s make some sandwiches! Introduction: If
... b. How many moles of H2 are left in excess after the reaction (if any)? c. How many moles of O2 are left in excess after the reaction (if any)? d. Which reactant is the Limiting Reactant? 10. In reality, reactants don’t have to react in perfect whole numbers of moles. In a two-reactant synthesis rea ...
... b. How many moles of H2 are left in excess after the reaction (if any)? c. How many moles of O2 are left in excess after the reaction (if any)? d. Which reactant is the Limiting Reactant? 10. In reality, reactants don’t have to react in perfect whole numbers of moles. In a two-reactant synthesis rea ...
Chemical Reactions
... (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
... (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
111.70 + 48 = 159.70 g/mol
... CALCULATE THE MOLAR MASS OF CARBON DIOXIDE, CO2 The atomic mass of C = 12.01 The atomic mass of O = 16.00 The molar mass of CO2 = 12.01 g/mol + 2(16.00 g/mol) = 12.01+ 32 = 44.01 g/mol http://www.slideshare.net/robertgist/mole-calculations-aeg3 - GOOD REF. ...
... CALCULATE THE MOLAR MASS OF CARBON DIOXIDE, CO2 The atomic mass of C = 12.01 The atomic mass of O = 16.00 The molar mass of CO2 = 12.01 g/mol + 2(16.00 g/mol) = 12.01+ 32 = 44.01 g/mol http://www.slideshare.net/robertgist/mole-calculations-aeg3 - GOOD REF. ...
practice test2(Answers)
... Which of the following does NOT represent a step on the heating curve of water? A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 1 ...
... Which of the following does NOT represent a step on the heating curve of water? A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 1 ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... 6. What is an activity series chart? What type of reaction do you use it for? a) Using the activity chart, why can sodium replace hydrogen? 7. What are 5 indicators of a chemical reaction? 8. List the chemical formulas for the 7 diatomic molecules. 9. Know how to translate chemical equations and bal ...
... 6. What is an activity series chart? What type of reaction do you use it for? a) Using the activity chart, why can sodium replace hydrogen? 7. What are 5 indicators of a chemical reaction? 8. List the chemical formulas for the 7 diatomic molecules. 9. Know how to translate chemical equations and bal ...
3.0 Hess`s Law
... calculated using enthalpies of formation for all the substances in the reaction of interest, without knowing anything else about how the reaction occurs. • Mathematically, the overall equation for enthalpy change will be in the form of the following equation: ...
... calculated using enthalpies of formation for all the substances in the reaction of interest, without knowing anything else about how the reaction occurs. • Mathematically, the overall equation for enthalpy change will be in the form of the following equation: ...
Page 1 of 4 FOSS California Mixtures and Solutions
... Carbohydrate: A group of carbon-based nutrients, such as sugars and starches. Carbon-14 dating: A process used to find the age of carbon-based matter. Carbon dioxide gas: A compound made from carbon and oxygen (CO2) Chemical equation: A model of a chemical reaction showing reactants and products. Ch ...
... Carbohydrate: A group of carbon-based nutrients, such as sugars and starches. Carbon-14 dating: A process used to find the age of carbon-based matter. Carbon dioxide gas: A compound made from carbon and oxygen (CO2) Chemical equation: A model of a chemical reaction showing reactants and products. Ch ...
Empirical Formula
... Percent Yield is the ratio in percent of amount of product you produced in the lab compared to the amount of product that you should of produced if the reaction went to completion and no problems arose in the lab Must always use the LR to determine the amount of product produced Theoretical yi ...
... Percent Yield is the ratio in percent of amount of product you produced in the lab compared to the amount of product that you should of produced if the reaction went to completion and no problems arose in the lab Must always use the LR to determine the amount of product produced Theoretical yi ...
Study Guide for Ch. 1
... Temperature scales and their details. Differentiate between solutions, colloids, and suspensions. Understand the physical properties involved in determining solids, liquids, & gases. Use significant figures in calculations and rounding of numbers. Convert numbers between scientific notation and stan ...
... Temperature scales and their details. Differentiate between solutions, colloids, and suspensions. Understand the physical properties involved in determining solids, liquids, & gases. Use significant figures in calculations and rounding of numbers. Convert numbers between scientific notation and stan ...
File
... Alex’s hypothesis was that the rate will be affected by changing the concentrations of the propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen i ...
... Alex’s hypothesis was that the rate will be affected by changing the concentrations of the propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen i ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.