Chapter 5: Thermochemistry
... → DH = negative Temperature decrease in calorimeter: → reaction is endothermic → DH = positive ...
... → DH = negative Temperature decrease in calorimeter: → reaction is endothermic → DH = positive ...
Chemical Engineering Report Series
... to technologies and strategies that enable simpler and more efficient processes compared to conventional processes. Some features of such intensified processes are less recycle streams, reduced need for waste handling, and lower investment and operating costs compared to conventional processes. One ...
... to technologies and strategies that enable simpler and more efficient processes compared to conventional processes. Some features of such intensified processes are less recycle streams, reduced need for waste handling, and lower investment and operating costs compared to conventional processes. One ...
5 organic chemistry: functional groups
... The longest chain contains the OOH group, which means the compound is named as a derivative of octane. Because it is an alcohol, it would be tempting to name it as an octanol. But it contains a CPC double bond, which means it must be an octenol. We now have to indicate that the OOH group is on one e ...
... The longest chain contains the OOH group, which means the compound is named as a derivative of octane. Because it is an alcohol, it would be tempting to name it as an octanol. But it contains a CPC double bond, which means it must be an octenol. We now have to indicate that the OOH group is on one e ...
silbchp4
... A, In forming the ionic compound MgO, each Mg atom transfers two electrons to each O atom. (Note that atoms become smaller when they lose electrons and larger when they gain electrons.) The resulting Mg 2+ and O2- ions aggregate with many others to form an ionic solid. B, In the reactants H2 and Cl2 ...
... A, In forming the ionic compound MgO, each Mg atom transfers two electrons to each O atom. (Note that atoms become smaller when they lose electrons and larger when they gain electrons.) The resulting Mg 2+ and O2- ions aggregate with many others to form an ionic solid. B, In the reactants H2 and Cl2 ...
Dr. Spencer`s PPT
... Nonelectrolytes are not dissociated into ions in solution Extent of dissolution does not dictate strong or weak electrolyte solution (i.e., HC2H3O2 is very soluble but is a weak electrolyte while Ba(OH)2 is only slightly soluble is a strong electrolyte) ...
... Nonelectrolytes are not dissociated into ions in solution Extent of dissolution does not dictate strong or weak electrolyte solution (i.e., HC2H3O2 is very soluble but is a weak electrolyte while Ba(OH)2 is only slightly soluble is a strong electrolyte) ...
Chemical Dynamics at Surfaces
... – as well as the modern experimental methods used to probe the limits of this understanding. ...
... – as well as the modern experimental methods used to probe the limits of this understanding. ...
Chapter 4
... This equation says that all sodium chloride that enters the solution ends up as Na1 and Cl2 ions; there are no undissociated NaCl units in solution. Table 4.1 lists examples of strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. Ionic compounds, such as sodium chloride, potassium iodide (KI ...
... This equation says that all sodium chloride that enters the solution ends up as Na1 and Cl2 ions; there are no undissociated NaCl units in solution. Table 4.1 lists examples of strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. Ionic compounds, such as sodium chloride, potassium iodide (KI ...
Mechanisms and energetics of surface reactions at the copper
... Even if the initial oxygen coverage would be very low (as can be achieved experimentally by mechanical polishing and chemical reduction (Clendening and Campbell 1989)), the oxide layer could grow also in anoxic water due to the cleavage of water molecules. By cleaving the water molecules in S1, ini ...
... Even if the initial oxygen coverage would be very low (as can be achieved experimentally by mechanical polishing and chemical reduction (Clendening and Campbell 1989)), the oxide layer could grow also in anoxic water due to the cleavage of water molecules. By cleaving the water molecules in S1, ini ...
Problem 28. TUNNELING IN CHEMISTRY
... where Hvap = 30720 J/mol is the enthalpy of vaporization of benzene. Estimate the boiling point (T*) of the finely dispersed liquid benzene at the standard atmospheric pressure if the sample consists of droplets with the radius r = 50 nm. The surface tension of benzene is 0.029 J/m2 and its density ...
... where Hvap = 30720 J/mol is the enthalpy of vaporization of benzene. Estimate the boiling point (T*) of the finely dispersed liquid benzene at the standard atmospheric pressure if the sample consists of droplets with the radius r = 50 nm. The surface tension of benzene is 0.029 J/m2 and its density ...
Chem 101 Lab Manual AKAR_revised (2)
... stormwater runoff. At the plant, the wastewater is cleaned and returned to the environment to be used over and over again. Wastewater flows by gravity with occasional help from pumps until it reaches the treatment plant. What happens in a wastewater treatment plant is essentially the same as what oc ...
... stormwater runoff. At the plant, the wastewater is cleaned and returned to the environment to be used over and over again. Wastewater flows by gravity with occasional help from pumps until it reaches the treatment plant. What happens in a wastewater treatment plant is essentially the same as what oc ...
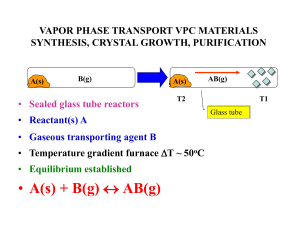
vapor phase transport vpc materials synthesis, crystal growth
... EXOTHERMIC-ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS • Endothermic • WO2(s) + I2(g) (T1 800oC) (T2 1000oC) WO2I2(g) • Exothermic • W(s) + 2H2O(g) + 3I2(g) (T2 1000oC) (T1 800oC) WO2I2 (g) + 4HI(g) • The antithetical nature of these two reactions allows W/WO2 mixtures which often form together to be separated at dif ...
... EXOTHERMIC-ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS • Endothermic • WO2(s) + I2(g) (T1 800oC) (T2 1000oC) WO2I2(g) • Exothermic • W(s) + 2H2O(g) + 3I2(g) (T2 1000oC) (T1 800oC) WO2I2 (g) + 4HI(g) • The antithetical nature of these two reactions allows W/WO2 mixtures which often form together to be separated at dif ...
Nickel catalyst auto-reduction during steam reforming of bio
... oxidised catalyst is initially automatically reduced by reforming fuel in a period termed autoreduction , and then sustains the steam reforming reaction. In particular, whether HAc, as a bio-oil model compound, has the ability to perform the reduction step will be investigated. To the authors' knowl ...
... oxidised catalyst is initially automatically reduced by reforming fuel in a period termed autoreduction , and then sustains the steam reforming reaction. In particular, whether HAc, as a bio-oil model compound, has the ability to perform the reduction step will be investigated. To the authors' knowl ...
Chemistry 133 Problem Set Introduction
... was the twenty-dollar gold piece known as the double eagle. By an act of Congress in 1849, each double eagle weighed 516 grains and was 0.900 fine (33.436 g and 90.0 % gold (the remainder was copper). In 1934, the United States increased the price of gold from $20.67 per Troy ounce to $35.00 per Tro ...
... was the twenty-dollar gold piece known as the double eagle. By an act of Congress in 1849, each double eagle weighed 516 grains and was 0.900 fine (33.436 g and 90.0 % gold (the remainder was copper). In 1934, the United States increased the price of gold from $20.67 per Troy ounce to $35.00 per Tro ...
Solutions
... A simple calorimeter consists of an insulated container (for example, a pair of styrene coffee cups as in Figure 6.12) with a thermometer. The heat of the reaction is obtained by conducting the reaction in the calorimeter. The temperature of the mixture is measured before and after the reaction. The ...
... A simple calorimeter consists of an insulated container (for example, a pair of styrene coffee cups as in Figure 6.12) with a thermometer. The heat of the reaction is obtained by conducting the reaction in the calorimeter. The temperature of the mixture is measured before and after the reaction. The ...
INFLUENCE OF BENZENE ON THE PROCESS OF n
... benzene saturation and isomerization of n-paraffins and cycloparaffins is carried out in one process step; a special process configuration and catalyst are required. In parallel with the isomerization reactions, hydrogenation reaction of benzene to cyclohexane and its isomerization to methyl-cyclope ...
... benzene saturation and isomerization of n-paraffins and cycloparaffins is carried out in one process step; a special process configuration and catalyst are required. In parallel with the isomerization reactions, hydrogenation reaction of benzene to cyclohexane and its isomerization to methyl-cyclope ...
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
... 8. Copper metal has a specific heat of 0.385 J/g·°C. Calculate the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 22.8 g of Cu from 20.0°C to 875°C. A) 1.97 10–5 J B) 1.0 10–2 J C) 329 J D) 7.51 kJ E) 10.5 kJ 9. Calculate the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of 12.0 g of wa ...
... 8. Copper metal has a specific heat of 0.385 J/g·°C. Calculate the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 22.8 g of Cu from 20.0°C to 875°C. A) 1.97 10–5 J B) 1.0 10–2 J C) 329 J D) 7.51 kJ E) 10.5 kJ 9. Calculate the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of 12.0 g of wa ...
Chapter 15: Chemical Equilibrium
... There are occasions when the use of an equilibrium arrow is not appropriate. For example, when hydrogen and oxygen react to form water vapor (Figure 15.X), product formation is very strongly favored and no noticeable amounts of reactants are formed by the reverse reaction. The chemical equation repr ...
... There are occasions when the use of an equilibrium arrow is not appropriate. For example, when hydrogen and oxygen react to form water vapor (Figure 15.X), product formation is very strongly favored and no noticeable amounts of reactants are formed by the reverse reaction. The chemical equation repr ...
Redox reactions - SALEM-Immanuel Lutheran College
... E.g. H Cl , since Cl is more electronegative, the presumed electrical charges and thus O.N. of Cl and H are 1 and 1 respectively. ...
... E.g. H Cl , since Cl is more electronegative, the presumed electrical charges and thus O.N. of Cl and H are 1 and 1 respectively. ...
Solutions to Exercises
... A simple calorimeter consists of an insulated container (for example, a pair of styrene coffee cups as in Figure 6.12) with a thermometer. The heat of the reaction is obtained by conducting the reaction in the calorimeter. The temperature of the mixture is measured before and after the reaction. The ...
... A simple calorimeter consists of an insulated container (for example, a pair of styrene coffee cups as in Figure 6.12) with a thermometer. The heat of the reaction is obtained by conducting the reaction in the calorimeter. The temperature of the mixture is measured before and after the reaction. The ...
Chapter 15
... There are occasions when the use of an equilibrium arrow is not appropriate. For example, when hydrogen and oxygen react to form water vapor (Figure 15.X), product formation is very strongly favored and no noticeable amounts of reactants are formed by the reverse reaction. The chemical equation repr ...
... There are occasions when the use of an equilibrium arrow is not appropriate. For example, when hydrogen and oxygen react to form water vapor (Figure 15.X), product formation is very strongly favored and no noticeable amounts of reactants are formed by the reverse reaction. The chemical equation repr ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.