Unit_4_Notes_
... o Second order reaction: m = 2 means that concentration will have a 1:2 effect on the rate (if the concentration is doubled, then the rate will be quadrupled) o Overall reaction order is the sum of each reactants’ reaction order o For example, consider this rate law Rate = k[A]1[B]2 We would say tha ...
... o Second order reaction: m = 2 means that concentration will have a 1:2 effect on the rate (if the concentration is doubled, then the rate will be quadrupled) o Overall reaction order is the sum of each reactants’ reaction order o For example, consider this rate law Rate = k[A]1[B]2 We would say tha ...
Chapter 1 Student Notes
... All matter is composed of about 118 different kinds of atoms. These atoms can be physically mixed or chemically joined together to make up all kinds of matter. Atom the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Since matter exists in so many different forms, having ...
... All matter is composed of about 118 different kinds of atoms. These atoms can be physically mixed or chemically joined together to make up all kinds of matter. Atom the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Since matter exists in so many different forms, having ...
13.2 Chemical Formulas
... atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen to build the molecule. For sodium nitrate, NaNO3, the chemical formula tells us there are three elements in the compound: sodium (Na), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O). To make a molecule of this compound, you need one atom of sodium, one atom of nitrogen, and th ...
... atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen to build the molecule. For sodium nitrate, NaNO3, the chemical formula tells us there are three elements in the compound: sodium (Na), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O). To make a molecule of this compound, you need one atom of sodium, one atom of nitrogen, and th ...
Chemical Equation Reactions
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
Cumulative Review, entire quarter
... Can I put the two reactants together to make a valid compound? (synthesis) Can I break the compound down into two or more valid compounds? (decomp) Look for gas-forming reactions or removal of water here. Is one reactant an element which can replace an element in the other compound? (SR) If you swit ...
... Can I put the two reactants together to make a valid compound? (synthesis) Can I break the compound down into two or more valid compounds? (decomp) Look for gas-forming reactions or removal of water here. Is one reactant an element which can replace an element in the other compound? (SR) If you swit ...
Topic 9 – Percent Composition, Empirical and Molecular Formulas I
... The mass spectrometer can identify the percent of each element present in a compound. D. Calculating percent by mass. 1. Determine the molar mass of the compound. 2. Divide the mass of the individual element in the compound by the molar mass. % by mass = (mass of element / molar mass) * 100 3. Repea ...
... The mass spectrometer can identify the percent of each element present in a compound. D. Calculating percent by mass. 1. Determine the molar mass of the compound. 2. Divide the mass of the individual element in the compound by the molar mass. % by mass = (mass of element / molar mass) * 100 3. Repea ...
Summary of 5.4
... lone pair is delocalised around the ring so hydrogen bonding is less possible. with hydrogen ions Methylamine vapour reacts with conc HCl(aq) to form white crystalline solid (smoke), methylammonium chloride, CH3 NH2 (g) + HCl(g) --------> CH3 NH3+ Cl - (s) The solubility of aromatic primary amines i ...
... lone pair is delocalised around the ring so hydrogen bonding is less possible. with hydrogen ions Methylamine vapour reacts with conc HCl(aq) to form white crystalline solid (smoke), methylammonium chloride, CH3 NH2 (g) + HCl(g) --------> CH3 NH3+ Cl - (s) The solubility of aromatic primary amines i ...
H3AsO4 + 3 I- + 2 H3O+ H3AsO3 + I3- + H2O
... measured in moles. The number of particles in a mole is 6.02 x 10 23 (Avogadro's number), which is the number of atoms in a sample of the element that has a mass equal to its atomic mass measured in grams. Molar mass (MM) is the sum of atomic masses in the chemical formula. For example, the mass of ...
... measured in moles. The number of particles in a mole is 6.02 x 10 23 (Avogadro's number), which is the number of atoms in a sample of the element that has a mass equal to its atomic mass measured in grams. Molar mass (MM) is the sum of atomic masses in the chemical formula. For example, the mass of ...
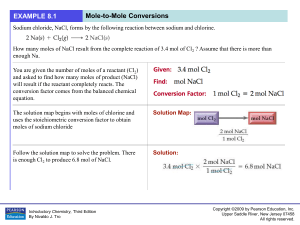
Stoichiometry: Predicting Amounts in Reactions
... Stoichiometry is the process of determining how much product is made or how much reactant is needed during a chemical reaction. As we know, in chemical reactions atoms are conserved. We show thi ...
... Stoichiometry is the process of determining how much product is made or how much reactant is needed during a chemical reaction. As we know, in chemical reactions atoms are conserved. We show thi ...
Ex - Bosna Sema
... What volume of H2 is required to react with 3.00 L of N2, and what volume of NH3 is produced at 200°C? 8. A byproduct of the reaction that inflates automotive airbags is very reactive sodium, which can ignite in air. Sodium produced during the inflation process reacts with another compound added to ...
... What volume of H2 is required to react with 3.00 L of N2, and what volume of NH3 is produced at 200°C? 8. A byproduct of the reaction that inflates automotive airbags is very reactive sodium, which can ignite in air. Sodium produced during the inflation process reacts with another compound added to ...
Ch 17 Equilibrium Notes
... of the individual reactions. (b) Calculate the Kc for the overall reaction Qc(forward)= 1/Qc (reverse) Kc(forward)= 1/Kc (reverse) n ( jA + kB lC + mD) ...
... of the individual reactions. (b) Calculate the Kc for the overall reaction Qc(forward)= 1/Qc (reverse) Kc(forward)= 1/Kc (reverse) n ( jA + kB lC + mD) ...
Document
... Example Calculation of the amount of graphite to produce a mole of hydrogen at constant temperature. The reaction of heated coal with superheated steam absorbs heat. This heat is usually provided by burning some of the coal. Calculate ΔrH º(500 K) for both reactions? a. C(graphite) + H2O(g) = CO(g) ...
... Example Calculation of the amount of graphite to produce a mole of hydrogen at constant temperature. The reaction of heated coal with superheated steam absorbs heat. This heat is usually provided by burning some of the coal. Calculate ΔrH º(500 K) for both reactions? a. C(graphite) + H2O(g) = CO(g) ...
Unit3_Stoichiometry_vs2
... where the left hand shows the reactants (what you start with) and the right side shows the products (what you end up with!) • Since matter is neither created nor destroyed, the total number of atoms of each element needs to be the same on both sides of a chemical equation! • To change the number of ...
... where the left hand shows the reactants (what you start with) and the right side shows the products (what you end up with!) • Since matter is neither created nor destroyed, the total number of atoms of each element needs to be the same on both sides of a chemical equation! • To change the number of ...
JF Physical Chemistry 2010-2011. JF CH 1101: Introduction to
... Answer either : part (a) and part (b) or part (c) and part (d). a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed b ...
... Answer either : part (a) and part (b) or part (c) and part (d). a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed b ...
Chemkin-Pro
... transfer and detailed chemistry. While CFD can simulate the reacting flow in realistic geometries, Energico uses the well-documented concept of it requires the use of severely reduced, global chemistry models that are too simple to accurately evaluating the relative time-scales for chemical simulate ...
... transfer and detailed chemistry. While CFD can simulate the reacting flow in realistic geometries, Energico uses the well-documented concept of it requires the use of severely reduced, global chemistry models that are too simple to accurately evaluating the relative time-scales for chemical simulate ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.