146TO 60B.C. - Heritage History
... War in Africa and Mithridatic Wars in the east. These were Marius, who led the popular party and Sulla, who lead the optimates. Both leaders were popular with the army and each led an army to march on the city of Rome and seize power by force, always using the abuses of the other as an excuse for fu ...
... War in Africa and Mithridatic Wars in the east. These were Marius, who led the popular party and Sulla, who lead the optimates. Both leaders were popular with the army and each led an army to march on the city of Rome and seize power by force, always using the abuses of the other as an excuse for fu ...
ROME WEB
... 6) What were gladiators (Be specific). 7) On average how man fights would a gladiator have a year? 8) What was the “Campus”? Eventually, what was it used for? ...
... 6) What were gladiators (Be specific). 7) On average how man fights would a gladiator have a year? 8) What was the “Campus”? Eventually, what was it used for? ...
The Legacy of Roman Language and Writing (HA) An especially
... The Legacy of Roman Language and Writing (HA) ...
... The Legacy of Roman Language and Writing (HA) ...
Did Paul claim Roman citizenship?
... sloth of the people. The first revolt took place in 494 BC which again centralized only some additional power in the hands of the Senate and the Assembly or congress and attempted to limit their power leaving the people both free and responsible for their own welfare. Tribune C. Terentilius Arsa and ...
... sloth of the people. The first revolt took place in 494 BC which again centralized only some additional power in the hands of the Senate and the Assembly or congress and attempted to limit their power leaving the people both free and responsible for their own welfare. Tribune C. Terentilius Arsa and ...
Lesson 20:The Remarkable Romans
... The Romans built rest stops every 15–20 miles along its long network of roads. In those days, people traveled in four ways. Some walked or rode horses. Others rode in carts pulled by oxen or in horse-drawn chariots. At a typical rest stop, tired horses and oxen could eat hay and drink fresh water fr ...
... The Romans built rest stops every 15–20 miles along its long network of roads. In those days, people traveled in four ways. Some walked or rode horses. Others rode in carts pulled by oxen or in horse-drawn chariots. At a typical rest stop, tired horses and oxen could eat hay and drink fresh water fr ...
Oioclstiae
... east and west sectors. Diocletian kept control of the east and Maximian controlled the west. Eight years later, Diocletian realized that more focus was needed on both civic and military problems. He further divided power by naming two "Junior Emperors l' or Caesari under each "Senior Emperor," or Au ...
... east and west sectors. Diocletian kept control of the east and Maximian controlled the west. Eight years later, Diocletian realized that more focus was needed on both civic and military problems. He further divided power by naming two "Junior Emperors l' or Caesari under each "Senior Emperor," or Au ...
The Founding of Rome
... for all to see. • 451 BC - Twelve Tables – Carved on bronze tablets and placed in the Forum – Foundation for law, all free citizens had the right to be treated equally ...
... for all to see. • 451 BC - Twelve Tables – Carved on bronze tablets and placed in the Forum – Foundation for law, all free citizens had the right to be treated equally ...
Chapter 11.2
... for all to see. • 451 BC - Twelve Tables – Carved on bronze tablets and placed in the Forum – Foundation for law, all free citizens had the right to be treated equally ...
... for all to see. • 451 BC - Twelve Tables – Carved on bronze tablets and placed in the Forum – Foundation for law, all free citizens had the right to be treated equally ...
Lesson 2: From Republic to Empire
... • Caesar was officially made dictator, or absolute ruler, in 47 BC. • Realizing the need for change, Caesar gave land to the poor and increased the Senate to 900 members (filling it with his supporters) • Caesar granted citizenship to people in provinces who had helped him • Reformed the calendar by ...
... • Caesar was officially made dictator, or absolute ruler, in 47 BC. • Realizing the need for change, Caesar gave land to the poor and increased the Senate to 900 members (filling it with his supporters) • Caesar granted citizenship to people in provinces who had helped him • Reformed the calendar by ...
11.2 - The Roman Republic
... for all to see. • 451 BC - Twelve Tables – Carved on bronze tablets and placed in the Forum – Foundation for law, all free citizens had the right to be treated equally ...
... for all to see. • 451 BC - Twelve Tables – Carved on bronze tablets and placed in the Forum – Foundation for law, all free citizens had the right to be treated equally ...
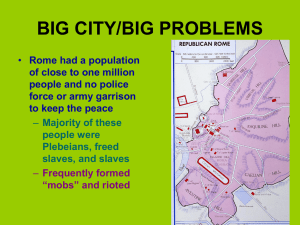
BIG CITY/BIG PROBLEMS - North Andover Public Schools
... – Large population and lack of official police force • Caused the wealthy to form private armies to protect themselves and their interests – Misery and squalor of the majority of the Roman population • Multiplied their grievances against the wealthy and the government • Also fostered their dependenc ...
... – Large population and lack of official police force • Caused the wealthy to form private armies to protect themselves and their interests – Misery and squalor of the majority of the Roman population • Multiplied their grievances against the wealthy and the government • Also fostered their dependenc ...
File - Mr Barck`s Classroom
... Successfully discharged soliders reducing army (still kept 28 legions for auxillery strength) __________________________________ Ruled from 161-180 AD Gifted general Philosopher Empire began to erode under his son Commodus (end of Pax Romana) i. Result: Rome _____________________________ ...
... Successfully discharged soliders reducing army (still kept 28 legions for auxillery strength) __________________________________ Ruled from 161-180 AD Gifted general Philosopher Empire began to erode under his son Commodus (end of Pax Romana) i. Result: Rome _____________________________ ...
The Calculus of Conquests: The Decline and Fall of the Returns to
... Costs and Benefits for Soldiers and the Supply of Soldiers The remuneration of Roman troops included a regular stipend plus a share of the expected booty. Citizen-soldiers had to be compensated for the opportunity cost of military campaigns, including the mortality risk of battle and the value of th ...
... Costs and Benefits for Soldiers and the Supply of Soldiers The remuneration of Roman troops included a regular stipend plus a share of the expected booty. Citizen-soldiers had to be compensated for the opportunity cost of military campaigns, including the mortality risk of battle and the value of th ...
Minoan Society: Between 2000 – 1700 BCE Minoans built a brilliant
... Persians allowed local law to be left intact. The Persian emperor appointed Satraps or local governors to oversee the provinces called Satrapies. But even though the satraps were Persians, most of their local bureaucrats and administrators were local peoples and the Persian emperors devised methods ...
... Persians allowed local law to be left intact. The Persian emperor appointed Satraps or local governors to oversee the provinces called Satrapies. But even though the satraps were Persians, most of their local bureaucrats and administrators were local peoples and the Persian emperors devised methods ...
File
... 1. What materials were used to construct the Aquaducts 2. How did they work to bring water to Rome 3. How was the water distributed once it reached Rome 4. What was the significance of the Aqua Appia 5. From what sources did the aquaducts bring water to Rome 6. How many Aquaducts came into the City ...
... 1. What materials were used to construct the Aquaducts 2. How did they work to bring water to Rome 3. How was the water distributed once it reached Rome 4. What was the significance of the Aqua Appia 5. From what sources did the aquaducts bring water to Rome 6. How many Aquaducts came into the City ...
In 330 CE, the Emperor Constantine moved his capital city from
... Byzantium, which he renamed Constantinople, in the eastern part of his empire. Although the Western Roman Empire was overrun by Germanic tribes and its capital was sacked in 476, the eastern portion that came to be called the Byzantine Empire after the old city continued and thrived for nearly 1,000 ...
... Byzantium, which he renamed Constantinople, in the eastern part of his empire. Although the Western Roman Empire was overrun by Germanic tribes and its capital was sacked in 476, the eastern portion that came to be called the Byzantine Empire after the old city continued and thrived for nearly 1,000 ...
11/20 Aim: How was the government of Rome similar
... This patron-client relationship led to many interesting situations in ancient Rome. Sometimes candidates for various government magistracies would travel around Rome with several hundred or even a few thousand of their clients. Lastly were the Slaves, who had no freedom or rights whatsoever unless i ...
... This patron-client relationship led to many interesting situations in ancient Rome. Sometimes candidates for various government magistracies would travel around Rome with several hundred or even a few thousand of their clients. Lastly were the Slaves, who had no freedom or rights whatsoever unless i ...
The Geography of Rome
... Around 3,000 years ago, a tribe of people known as the Latins settled on the hilltops above the Tiber river. This cluster of small villages eventually grew to become the city of Rome - one of the most splendid cities in the ancient world and capitol of the mighty Roman Empire ...
... Around 3,000 years ago, a tribe of people known as the Latins settled on the hilltops above the Tiber river. This cluster of small villages eventually grew to become the city of Rome - one of the most splendid cities in the ancient world and capitol of the mighty Roman Empire ...
Ancient Rome Notes
... • The Republic was made up of 3 parts: 1. Consuls- 2 leaders chosen from the senate, served 1 year terms. (They were the leaders of the government) Consuls had the power to veto (which means “I forbid it”) ...
... • The Republic was made up of 3 parts: 1. Consuls- 2 leaders chosen from the senate, served 1 year terms. (They were the leaders of the government) Consuls had the power to veto (which means “I forbid it”) ...
Roman economy

The history of the Roman economy covers the period of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. Recent research has led to a positive reevaluation of the size and sophistication of the Roman economy.Moses Finley was the chief proponent of the primitivist view that the Roman economy was ""underdeveloped and underachieving,"" characterized by subsistence agriculture; urban centres that consumed more than they produced in terms of trade and industry; low-status artisans; slowly developing technology; and a ""lack of economic rationality."" Current views are more complex. Territorial conquests permitted a large-scale reorganization of land use that resulted in agricultural surplus and specialization, particularly in north Africa. Some cities were known for particular industries or commercial activities, and the scale of building in urban areas indicates a significant construction industry. Papyri preserve complex accounting methods that suggest elements of economic rationalism, and the Empire was highly monetized. Although the means of communication and transport were limited in antiquity, transportation in the 1st and 2nd centuries expanded greatly, and trade routes connected regional economies. The supply contracts for the army, which pervaded every part of the Empire, drew on local suppliers near the base (castrum), throughout the province, and across provincial borders. The Empire is perhaps best thought of as a network of regional economies, based on a form of ""political capitalism"" in which the state monitored and regulated commerce to assure its own revenues. Economic growth, though not comparable to modern economies, was greater than that of most other societies prior to industrialization.Socially, economic dynamism opened up one of the avenues of social mobility in the Roman Empire. Social advancement was thus not dependent solely on birth, patronage, good luck, or even extraordinary ability. Although aristocratic values permeated traditional elite society, a strong tendency toward plutocracy is indicated by the wealth requirements for census rank. Prestige could be obtained through investing one's wealth in ways that advertised it appropriately: grand country estates or townhouses, durable luxury items such as jewels and silverware, public entertainments, funerary monuments for family members or coworkers, and religious dedications such as altars. Guilds (collegia) and corporations (corpora) provided support for individuals to succeed through networking, sharing sound business practices, and a willingness to work.