COGNITION & LEARNING
... Image: a mental visualization of an object or experience Symbol: something that stands for or represents a specific object or event Abstraction: an idea unrelated to a specific object or event Concept: a mental category for classifying people, things, or ...
... Image: a mental visualization of an object or experience Symbol: something that stands for or represents a specific object or event Abstraction: an idea unrelated to a specific object or event Concept: a mental category for classifying people, things, or ...
Key Knowledge 2
... Shorter words = can rehearse more in a shorter period. Many longer words = some info lost from the limited verbal working memory system. ...
... Shorter words = can rehearse more in a shorter period. Many longer words = some info lost from the limited verbal working memory system. ...
Park et al. (2001) Neuropsychologia
... – Utilization and imitative behavior – Lhermitte (1983; 1986) showed that px with frontal lobe damage tended to rely excessively on perceptual input and show imitative and utilization behavior – E.g., px pick up pencil on doctor’s table, and perform actions that were socially odd – e.g., came in doc ...
... – Utilization and imitative behavior – Lhermitte (1983; 1986) showed that px with frontal lobe damage tended to rely excessively on perceptual input and show imitative and utilization behavior – E.g., px pick up pencil on doctor’s table, and perform actions that were socially odd – e.g., came in doc ...
Exam 2 Review
... Your friend says, “I wait to study all the material the night before the test, so it is fresh in my mind.” You tell her from what you have learned: ...
... Your friend says, “I wait to study all the material the night before the test, so it is fresh in my mind.” You tell her from what you have learned: ...
Long term memory
... Can scientifically study mental processes Humans actively construct knowledge that results in behavior Knowledge is learned ...
... Can scientifically study mental processes Humans actively construct knowledge that results in behavior Knowledge is learned ...
Lap 3 - Mrs. Heidmann
... 4. Describe the social learning theory. Have you ever learned something from someone else? What was it? How did you learn it? 5. In your opinion, what theory is best: classical, operant, or social learning? I know that there is overlap between the theories and that is okay. Please choose one. 6. Mem ...
... 4. Describe the social learning theory. Have you ever learned something from someone else? What was it? How did you learn it? 5. In your opinion, what theory is best: classical, operant, or social learning? I know that there is overlap between the theories and that is okay. Please choose one. 6. Mem ...
Chapter 12 psych
... recognize information that was stored or is still stored in long-term memory • Repression – according to Freud, repression is a mental process that automatically hides emotionally threatening or anxiety-producing information in the unconscious, from which repressed memories cannot be recalled volunt ...
... recognize information that was stored or is still stored in long-term memory • Repression – according to Freud, repression is a mental process that automatically hides emotionally threatening or anxiety-producing information in the unconscious, from which repressed memories cannot be recalled volunt ...
Key Studies Memory
... number lists. The lists were presented over headphones so that it seemed that one list came from the left and one list came from the right and a third from behind. After hearing the lists, Ps were given a cue to recall one of the three lists. The length of time from the presentation to the cue varie ...
... number lists. The lists were presented over headphones so that it seemed that one list came from the left and one list came from the right and a third from behind. After hearing the lists, Ps were given a cue to recall one of the three lists. The length of time from the presentation to the cue varie ...
Memory - RWS Psychology
... number lists. The lists were presented over headphones so that it seemed that one list came from the left and one list came from the right and a third from behind. After hearing the lists, Ps were given a cue to recall one of the three lists. The length of time from the presentation to the cue varie ...
... number lists. The lists were presented over headphones so that it seemed that one list came from the left and one list came from the right and a third from behind. After hearing the lists, Ps were given a cue to recall one of the three lists. The length of time from the presentation to the cue varie ...
Name: Date: 1. An event that decreases the behavior that precedes
... C) the serial position effect. D) motivated forgetting. E) state-dependent memory. 48. When memory researcher Elizabeth Loftus was an adolescent, her uncle incorrectly insisted that as a child she had found her own mother's drowned body. Loftus herself later falsely recollected finding the body. Thi ...
... C) the serial position effect. D) motivated forgetting. E) state-dependent memory. 48. When memory researcher Elizabeth Loftus was an adolescent, her uncle incorrectly insisted that as a child she had found her own mother's drowned body. Loftus herself later falsely recollected finding the body. Thi ...
Learning and Memory - Tri-County Regional School Board
... Multiple Memory Systems Hypothesis Memory can be divided into categories that reflect the type of information being remembered. Each system primarily employs a distinct brain region Declarative Hippocampus Procedural Basal Ganglia Emotional Amygdala ‘Working With’ Memory Prefron ...
... Multiple Memory Systems Hypothesis Memory can be divided into categories that reflect the type of information being remembered. Each system primarily employs a distinct brain region Declarative Hippocampus Procedural Basal Ganglia Emotional Amygdala ‘Working With’ Memory Prefron ...
PSY100 Term Test 2: 2007-2008 1) The two identity statuses that
... 32) Darrel was dancing with his new girlfriend at an Elvis tribute. When the band started playing “Can’t Help Falling in Love with You” his girlfriend gave him a long passionate kiss, which Darrel found very enjoyable. Now Darrel finds that every time he hears “Can’t Help Falling in Love with You” o ...
... 32) Darrel was dancing with his new girlfriend at an Elvis tribute. When the band started playing “Can’t Help Falling in Love with You” his girlfriend gave him a long passionate kiss, which Darrel found very enjoyable. Now Darrel finds that every time he hears “Can’t Help Falling in Love with You” o ...
Multiple Memory Systems in the Brain
... Memorization, like many functions of our body, is so much a part of our daily life that we take it for granted. The brain has robust and reliable memory processing systems that work automatically without much conscious effort. However, the memory function of the brain differs from other bodily funct ...
... Memorization, like many functions of our body, is so much a part of our daily life that we take it for granted. The brain has robust and reliable memory processing systems that work automatically without much conscious effort. However, the memory function of the brain differs from other bodily funct ...
Learning and Memory
... ¢ A: Because I said that an attendant might mop your brow and might move your glasses over a little bit, and you would make the wrong movement. ...
... ¢ A: Because I said that an attendant might mop your brow and might move your glasses over a little bit, and you would make the wrong movement. ...
Working Memory and Older Adults
... single, global instrument (Craik et aI., in press). For example, one type of working memory instrument was described in the Dobbs and Rule (1989) study discussed earlier. The emphasis of thiS lag task on the active manipulation of information with minimal storage demands suggests that it is a measur ...
... single, global instrument (Craik et aI., in press). For example, one type of working memory instrument was described in the Dobbs and Rule (1989) study discussed earlier. The emphasis of thiS lag task on the active manipulation of information with minimal storage demands suggests that it is a measur ...
The Neurobiology of Learning and Memory
... You Are Your Memory Your memory stores: • Your personal experiences • Emotions • Preferences/dislikes • Motor skills ...
... You Are Your Memory Your memory stores: • Your personal experiences • Emotions • Preferences/dislikes • Motor skills ...
7 Memory [Kompatibilitätsmodus]
... your ability to answer does NOT depend on tying the item to your past – i.e., Do not have to recall the time last week when you ate a banana to say that bananas are yellow ...
... your ability to answer does NOT depend on tying the item to your past – i.e., Do not have to recall the time last week when you ate a banana to say that bananas are yellow ...
Learning, Memory, and Amnesia
... Learning, Memory, and Amnesia • Research in the role of the hippocampus in episodic memory shows damage impairs abilities on two types of tasks: • Delayed matching-to-sample tasks – a subject sees an object and must later choose the object that matches. • Delayed non-matching-to-sample tasks– subje ...
... Learning, Memory, and Amnesia • Research in the role of the hippocampus in episodic memory shows damage impairs abilities on two types of tasks: • Delayed matching-to-sample tasks – a subject sees an object and must later choose the object that matches. • Delayed non-matching-to-sample tasks– subje ...
AP Psychology Unit Exam #4
... 11. Michael Ross and his colleagues observed that people exposed to very convincing arguments about the desirability of frequent toothbrushing tended to: A) quickly forget the arguments if they were in the habit of brushing frequently. B) quickly forget the arguments if they were not in the habit of ...
... 11. Michael Ross and his colleagues observed that people exposed to very convincing arguments about the desirability of frequent toothbrushing tended to: A) quickly forget the arguments if they were in the habit of brushing frequently. B) quickly forget the arguments if they were not in the habit of ...
Press Release for The Seven Sins of Memory published
... • Give yourself highly distinctive cues that have few other associations in longterm memory and are unlikely to remind you of irrelevant information. • Provide yourself with sufficient information. Write down not only the phone number you wish to remember, but whom it belongs to and how you know tha ...
... • Give yourself highly distinctive cues that have few other associations in longterm memory and are unlikely to remind you of irrelevant information. • Provide yourself with sufficient information. Write down not only the phone number you wish to remember, but whom it belongs to and how you know tha ...
Learning and Memory (Chapter 12). Lecturer
... PSYCHOLOGY of Memory Some Memory Terms: Encoding: processing new information into a form that can be stored Storage: maintaining a memory Recall: to bring back to mind, to retrieve Recognition: to perceive something as previously known, it is “familiar” Short Term Memory (STM) vs. Long Term Memory ...
... PSYCHOLOGY of Memory Some Memory Terms: Encoding: processing new information into a form that can be stored Storage: maintaining a memory Recall: to bring back to mind, to retrieve Recognition: to perceive something as previously known, it is “familiar” Short Term Memory (STM) vs. Long Term Memory ...
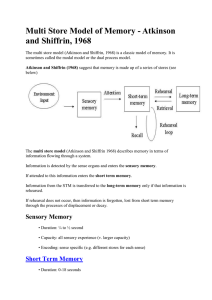
Multi-store Model (PPH 2012)
... considerably increased by combining/organising separate ‘bits’ of information, e.g. letters or digits, into larger chunks. Chunking involves making the info more meaningful, through organising it in line with existing knowledge from your LTM - in this case, of abbreviations for qualifications. ...
... considerably increased by combining/organising separate ‘bits’ of information, e.g. letters or digits, into larger chunks. Chunking involves making the info more meaningful, through organising it in line with existing knowledge from your LTM - in this case, of abbreviations for qualifications. ...
Module 25
... experiment, researchers altered family photos to include an event that never happened. After viewing the fake images, half the participants falsely remembered the experience, even describing it in vivid detail. This is an example of the misinformation effect (a memory that has been corrupted by misl ...
... experiment, researchers altered family photos to include an event that never happened. After viewing the fake images, half the participants falsely remembered the experience, even describing it in vivid detail. This is an example of the misinformation effect (a memory that has been corrupted by misl ...
Models hand out File
... essential. Why are we able to recall information which we did not rehearse (e.g. swimming) yet unable to recall information which we have rehearsed (e.g. reading your notes while revising). Therefore, the role of rehearsal as a means of transferring from STM to LTM is much less important than Atkins ...
... essential. Why are we able to recall information which we did not rehearse (e.g. swimming) yet unable to recall information which we have rehearsed (e.g. reading your notes while revising). Therefore, the role of rehearsal as a means of transferring from STM to LTM is much less important than Atkins ...
Long Term memory
... Working memory = prefrontal function • Prefrontal area = working memory’s central executive. – manages behavioral strategies and decision making; – coordinates activity in brain areas involved in perceptual and response functions in a task; and – directs the neural traffic in working memory. ...
... Working memory = prefrontal function • Prefrontal area = working memory’s central executive. – manages behavioral strategies and decision making; – coordinates activity in brain areas involved in perceptual and response functions in a task; and – directs the neural traffic in working memory. ...














![7 Memory [Kompatibilitätsmodus]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002622603_1-6a6e87d002b88972052b641d80fc2325-300x300.png)