Plant Nuclear Genome Size Variation
... Chromosome numbers vary n = 2 to n = ~680 Euploid variation – polyploidy ~35% of vascular plants are neopolyploids All are paleopolyploids Aneuploid variation – gain or less of one or ...
... Chromosome numbers vary n = 2 to n = ~680 Euploid variation – polyploidy ~35% of vascular plants are neopolyploids All are paleopolyploids Aneuploid variation – gain or less of one or ...
Plant Nuclear Genome Size Variation
... Chromosome numbers vary n = 2 to n = ~680 Euploid variation – polyploidy ~35% of vascular plants are neopolyploids Most are likely paleopolyploids Aneuploid variation – gain or less of one or ...
... Chromosome numbers vary n = 2 to n = ~680 Euploid variation – polyploidy ~35% of vascular plants are neopolyploids Most are likely paleopolyploids Aneuploid variation – gain or less of one or ...
Brooker Chapter 17
... Remarkably, in the last 50 years, the P element has expanded throughout D. melanogaster populations worldwide The only strains without the P element are lab stocks collected prior to 1950 ...
... Remarkably, in the last 50 years, the P element has expanded throughout D. melanogaster populations worldwide The only strains without the P element are lab stocks collected prior to 1950 ...
Plant Nuclear Genome Size Variation
... Chromosome numbers vary n = 2 to n = ~680 Euploid variation – polyploidy ~35% of vascular plants are neopolyploids Most are likely paleopolyploids Aneuploid variation – gain or less of one or ...
... Chromosome numbers vary n = 2 to n = ~680 Euploid variation – polyploidy ~35% of vascular plants are neopolyploids Most are likely paleopolyploids Aneuploid variation – gain or less of one or ...
Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
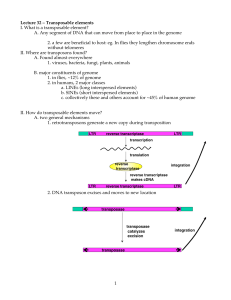
... ANSWER: Retroelements. A single element can be transcribed into multiple copies of RNA, which can be converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase, and inserted into multiple sites in the genome. Figure 21.8 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What is the advantage of a gene family? ANSWER: The overall advanta ...
... ANSWER: Retroelements. A single element can be transcribed into multiple copies of RNA, which can be converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase, and inserted into multiple sites in the genome. Figure 21.8 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What is the advantage of a gene family? ANSWER: The overall advanta ...
Document
... Using DNA that encodes a functional, therapeutic NCL gene to replace the mutated or missing NCL gene Injection of the viral vector containing the corrective NCL gene into the brain of affected ...
... Using DNA that encodes a functional, therapeutic NCL gene to replace the mutated or missing NCL gene Injection of the viral vector containing the corrective NCL gene into the brain of affected ...
TE content correlates positively with genome size
... •transposition begins with transcription •LTRs (long terminal repeats) are the critical cis-acting sequences (note: these are direct repeats) •element encodes reverse transcriptase and integrase enzymes, plus additional proteins required for replication •RNA copied into double-stranded cDNA in cytop ...
... •transposition begins with transcription •LTRs (long terminal repeats) are the critical cis-acting sequences (note: these are direct repeats) •element encodes reverse transcriptase and integrase enzymes, plus additional proteins required for replication •RNA copied into double-stranded cDNA in cytop ...
LINEs
... Class II TEs IS elements and transposons bounded by inverted terminal repeats (ITR) e.g. ATGCNNNNNNNNNNNCGTA ...
... Class II TEs IS elements and transposons bounded by inverted terminal repeats (ITR) e.g. ATGCNNNNNNNNNNNCGTA ...
Transposons - iPlant Pods
... (1) At the beginning of kernel development, the Ds transposon inserts into the colored (C) gene, resulting in colorless tissue. (2) Ds transposition early in kernel development restores the C gene, giving rise to a large colored sector. (3) Transposition later in kernel development results in smalle ...
... (1) At the beginning of kernel development, the Ds transposon inserts into the colored (C) gene, resulting in colorless tissue. (2) Ds transposition early in kernel development restores the C gene, giving rise to a large colored sector. (3) Transposition later in kernel development results in smalle ...
Fig1 from Nature Rev Mol. Cell Biol (Nov2003) 4(11):865
... Prokaryotic IS elements (e.g. IS10, Ac/Ds, mariner) encode only transposase sequences ...
... Prokaryotic IS elements (e.g. IS10, Ac/Ds, mariner) encode only transposase sequences ...
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (long interspersed elements) b. SINEs (short interspersed elements) c. collectively these and others account for ~45% of human ge ...
... A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (long interspersed elements) b. SINEs (short interspersed elements) c. collectively these and others account for ~45% of human ge ...
Transposons - iPlant Pods
... (1) At the beginning of kernel development, the Ds transposon inserts into the colored (C) gene, resulting in colorless tissue. (2) Ds transposition early in kernel development restores the C gene, giving rise to a large colored sector. (3) Transposition later in kernel development results in smalle ...
... (1) At the beginning of kernel development, the Ds transposon inserts into the colored (C) gene, resulting in colorless tissue. (2) Ds transposition early in kernel development restores the C gene, giving rise to a large colored sector. (3) Transposition later in kernel development results in smalle ...
Plant transposons
... (1) At the beginning of kernel development, the Ds transposon is inserted into the colored (C) gene, resulting in colorless tissue. (2) Ds transposition early in kernel development restores the C gene, giving rise to a large colored sector. (3) Transposition later in kernel development results in sm ...
... (1) At the beginning of kernel development, the Ds transposon is inserted into the colored (C) gene, resulting in colorless tissue. (2) Ds transposition early in kernel development restores the C gene, giving rise to a large colored sector. (3) Transposition later in kernel development results in sm ...
Transposable element
A transposable element (TE or transposon) is a DNA sequence that can change its position within the genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell's genome size. Transposition often results in duplication of the TE. Barbara McClintock's discovery of these jumping genes earned her a Nobel prize in 1983.TEs make up a large fraction of the C-value of eukaryotic cells. There are at least two classes of TEs: class I TEs generally function via reverse transcription, while class II TEs encode the protein transposase, which they require for insertion and excision, and some of these TEs also encode other proteins. It has been shown that TEs are important in genome function and evolution. In Oxytricha, which has a unique genetic system, they play a critical role in development. They are also very useful to researchers as a means to alter DNA inside a living organism.