BB30055: Genes and genomes
... (IHGSC) - composite from several different people generated from 10-20 primary samples taken from numerous anonymous donors across racial and ethnic groups (B) Celera Genomics – 5 different donors (one of whom was J Craig Venter himself !!!) ...
... (IHGSC) - composite from several different people generated from 10-20 primary samples taken from numerous anonymous donors across racial and ethnic groups (B) Celera Genomics – 5 different donors (one of whom was J Craig Venter himself !!!) ...
wg: Use primers wg550F and wgABRZ with cycler profile ST
... were deleted prior to alignment. We aligned amino acid translations of CAD and wg genes using MAFFT v7.130b [9,10] and the L-INS-i algorithm with default parameter values. We then shifted nucleotide sequences to match the amino acid alignment using Mesquite [11]. 28S and 18S were also aligned using ...
... were deleted prior to alignment. We aligned amino acid translations of CAD and wg genes using MAFFT v7.130b [9,10] and the L-INS-i algorithm with default parameter values. We then shifted nucleotide sequences to match the amino acid alignment using Mesquite [11]. 28S and 18S were also aligned using ...
Evolutionary Genetics
... In 1952, Frederick Sanger and coworkers determined the complete amino acid sequence of insulin. Since that time, the amount of sequence information has grown exponentially. For example, Genbank contains all publicly available DNA sequences, which amounts to more than 3.8 billion basepairs from 4.8 m ...
... In 1952, Frederick Sanger and coworkers determined the complete amino acid sequence of insulin. Since that time, the amount of sequence information has grown exponentially. For example, Genbank contains all publicly available DNA sequences, which amounts to more than 3.8 billion basepairs from 4.8 m ...
Understanding the Mechanism of Adaptive Evolution and
... From the beginning of my research at 1997, I have been focusing on the adaptive evolution of animals. Especially, the mechanism of morphological diversification in higher vertebrates through adaptive evolution is of my primary interest because the earth is full of interesting creatures in terms of t ...
... From the beginning of my research at 1997, I have been focusing on the adaptive evolution of animals. Especially, the mechanism of morphological diversification in higher vertebrates through adaptive evolution is of my primary interest because the earth is full of interesting creatures in terms of t ...
Clike here - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... fundamental level - the order of bases along the DNA molecule. This method uses DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands in the presence of dideoxy nucleotides. Since these lack a 3’ OH group, whenever one is incorporated into the growing strand, that molecule does not elongate further. ...
... fundamental level - the order of bases along the DNA molecule. This method uses DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands in the presence of dideoxy nucleotides. Since these lack a 3’ OH group, whenever one is incorporated into the growing strand, that molecule does not elongate further. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... fundamental level - the order of bases along the DNA molecule. This method uses DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands in the presence of dideoxy nucleotides. Since these lack a 3’ OH group, whenever one is incorporated into the growing strand, that molecule does not elongate further. ...
... fundamental level - the order of bases along the DNA molecule. This method uses DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands in the presence of dideoxy nucleotides. Since these lack a 3’ OH group, whenever one is incorporated into the growing strand, that molecule does not elongate further. ...
DNA experiments exercise
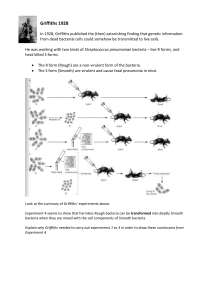
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
Introduction to biological databases
... The 3 databases form an international collaboration. Each of the three groups collects a portion of the total sequence data reported worldwide, and all new and updated database entries are exchanged between the groups on a ...
... The 3 databases form an international collaboration. Each of the three groups collects a portion of the total sequence data reported worldwide, and all new and updated database entries are exchanged between the groups on a ...
DNA, Chromosomes & Genes
... • A specific sequence of bases – Sequences carry the information needed for constructing proteins • Proteins provide the structural components of cells and tissues as well as enzymes for essential biochemical reactions. ...
... • A specific sequence of bases – Sequences carry the information needed for constructing proteins • Proteins provide the structural components of cells and tissues as well as enzymes for essential biochemical reactions. ...
Human Molecular Genetics Section 14–3
... Researchers completed the genomes of yeast and fruit flies during the same time they sequenced the human genome. ...
... Researchers completed the genomes of yeast and fruit flies during the same time they sequenced the human genome. ...
The 5 Kingdom System: R.H. Whittaker Two kinds of cells: simple
... The 5 Kingdoms and the Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote split Microbial Systematics Morphology and other defining characteristics υ Size, shape and arrangement ...
... The 5 Kingdoms and the Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote split Microbial Systematics Morphology and other defining characteristics υ Size, shape and arrangement ...
RichardDurbin_CSI2011
... – 85% of this class in NA12891 are in pilot data 1000 Genomes Project pilot paper ...
... – 85% of this class in NA12891 are in pilot data 1000 Genomes Project pilot paper ...
Chapter 25
... comparing ingroup species with an outgroup species that does not have the shared derived characteristic ...
... comparing ingroup species with an outgroup species that does not have the shared derived characteristic ...
March 1, 2005 - Ambry Genetics
... rapidly detect the underlying cause in patients afflicted with genetic disease, as 85% of genetic mutations with large clinical consequences occur within the exome. We have seriously considered First, Last Name underlying diagnosis, and while we think that it is highly likely that he/she has an inhe ...
... rapidly detect the underlying cause in patients afflicted with genetic disease, as 85% of genetic mutations with large clinical consequences occur within the exome. We have seriously considered First, Last Name underlying diagnosis, and while we think that it is highly likely that he/she has an inhe ...
DNA switches
... The findings have immediate applications for understanding how alterations in the nongene parts of DNA contribute to human diseases, which may in turn lead to new drugs. They can also help explain how the environment can affect disease risk. In the case of identical twins, small changes in environm ...
... The findings have immediate applications for understanding how alterations in the nongene parts of DNA contribute to human diseases, which may in turn lead to new drugs. They can also help explain how the environment can affect disease risk. In the case of identical twins, small changes in environm ...
PPTX - UT Computer Science
... Marker-based profiling can produce more accurate taxonomic profiles (distributions) than techniques that attempt to classify all fragments. ...
... Marker-based profiling can produce more accurate taxonomic profiles (distributions) than techniques that attempt to classify all fragments. ...
Fundamental Principles of Variation
... According to Futuyama, “Genetic variation is the foundation of evolution, for the great changes in organisms that have transpired over time and the differences that have developed among species as they diverged from theif common ancestors all originated as genetic variants within species.” Review of ...
... According to Futuyama, “Genetic variation is the foundation of evolution, for the great changes in organisms that have transpired over time and the differences that have developed among species as they diverged from theif common ancestors all originated as genetic variants within species.” Review of ...
ASPM
... FOXP2 differs in just one amino acid from these three species. Human FOXP2 differs from gorilla & chimp in two further amino acids (and thus differs from mouse in three amino acids). ...
... FOXP2 differs in just one amino acid from these three species. Human FOXP2 differs from gorilla & chimp in two further amino acids (and thus differs from mouse in three amino acids). ...
3.1.8 The causes of sickle cell anemia, including a
... • Scientists are still in the process of decoding these sequences to ID specific genes • ~23,000 genes were identified (much fewer than predicted!) • Discovered much of the genome is NOT transcribed • Highly-repetitive sequences originally-called “junk DNA” but now recognized as having a number of k ...
... • Scientists are still in the process of decoding these sequences to ID specific genes • ~23,000 genes were identified (much fewer than predicted!) • Discovered much of the genome is NOT transcribed • Highly-repetitive sequences originally-called “junk DNA” but now recognized as having a number of k ...
lecture25_DarkMatter..
... encodes a noncoding RNA; two primary transcripts share a 5’ untranslated region, but they are considered different genes because the translated regions (D and E do not overlap; there is a noncoding RNA, but the fact it shares its genomic sequence (X and Y) with the protein-coding genomic segments A ...
... encodes a noncoding RNA; two primary transcripts share a 5’ untranslated region, but they are considered different genes because the translated regions (D and E do not overlap; there is a noncoding RNA, but the fact it shares its genomic sequence (X and Y) with the protein-coding genomic segments A ...
Mitochondrial - Reversible infantile respiratory chain deficiency
... Clinically affected patients Carrier or Presymptomatic: Relatives of clinically affected patients Prenatal: At risk of having an affected child REFERRALS o From Hospital Consultants, mainly Clinical Genetics, Neurology, Paediatrics, Hepatology. o Prenatal referrals are only accepted from Clinical Ge ...
... Clinically affected patients Carrier or Presymptomatic: Relatives of clinically affected patients Prenatal: At risk of having an affected child REFERRALS o From Hospital Consultants, mainly Clinical Genetics, Neurology, Paediatrics, Hepatology. o Prenatal referrals are only accepted from Clinical Ge ...
genome
... Figure 3.6 ~20% of Drosophila genes code for proteins concerned with maintaining or expressing genes, ~20% for enzymes, <10% for proteins concerned with the cell cycle or signal transduction. Half of the genes of Drosophila code for products of unknown function. ...
... Figure 3.6 ~20% of Drosophila genes code for proteins concerned with maintaining or expressing genes, ~20% for enzymes, <10% for proteins concerned with the cell cycle or signal transduction. Half of the genes of Drosophila code for products of unknown function. ...
Genetics
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
Metagenomics

Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics or community genomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Recent studies use either ""shotgun"" or PCR directed sequencing to get largely unbiased samples of all genes from all the members of the sampled communities. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater scale and detail than before.