Finding disease genes
... “The production of billions of NGS reads has also challenged the infrastructure of existing information technology systems in terms of data transfer, storage and quality control, computational analysis to align or assemble read data….” “Advances in bioinformatics are ongoing, and improvements are n ...
... “The production of billions of NGS reads has also challenged the infrastructure of existing information technology systems in terms of data transfer, storage and quality control, computational analysis to align or assemble read data….” “Advances in bioinformatics are ongoing, and improvements are n ...
BSC 219
... 1) ( 3 points) Describe the main ways that eukaryotic transcription initiation is different from prokaryotic transcription initiation. Eukaryotic initiation involves a large number of proteins to form an initiation complex that recruits RNA Polymerase to the promoter region. The DNA sequences and so ...
... 1) ( 3 points) Describe the main ways that eukaryotic transcription initiation is different from prokaryotic transcription initiation. Eukaryotic initiation involves a large number of proteins to form an initiation complex that recruits RNA Polymerase to the promoter region. The DNA sequences and so ...
1st
... Store information Replicate (when cells divide) Express information (as proteins) Mutate at a low frequency (less than 1 in a million) ...
... Store information Replicate (when cells divide) Express information (as proteins) Mutate at a low frequency (less than 1 in a million) ...
Ch 020 DNA Technology II
... segments of DNA cut by restriction enzymes in a reproducable way Sticky end: short extensions of restriction fragments DNA ligase: enzyme that can join the sticky ends of DNA fragments Cloning vector: DNA molecule that can carry foreign DNA into a cell and replicate there (usually bacterial plasmids ...
... segments of DNA cut by restriction enzymes in a reproducable way Sticky end: short extensions of restriction fragments DNA ligase: enzyme that can join the sticky ends of DNA fragments Cloning vector: DNA molecule that can carry foreign DNA into a cell and replicate there (usually bacterial plasmids ...
What is a gene? - Ecology and Evolution Unit
... Other studies, one by Guigo’s team4, and one carry the instructions for making proteins, are interspersed with non-coding introns. In alter- by geneticist Rotem Sorek5, now at Tel Aviv native splicing, the cell snips out introns and University, Israel, and his colleagues, have sews together the exon ...
... Other studies, one by Guigo’s team4, and one carry the instructions for making proteins, are interspersed with non-coding introns. In alter- by geneticist Rotem Sorek5, now at Tel Aviv native splicing, the cell snips out introns and University, Israel, and his colleagues, have sews together the exon ...
Genetics Online Scavenger Hunt
... What is a Gene? What is a Chromosome? What is a protein? What is Heredity? What is a Trait? 3. As you go from one tutorial to the next answer the corresponding questions for each topic. ...
... What is a Gene? What is a Chromosome? What is a protein? What is Heredity? What is a Trait? 3. As you go from one tutorial to the next answer the corresponding questions for each topic. ...
cummings and clegg - nucleotide sequence diversity at the
... 4. Describe the relationship between diversity and recombination? 5. What is the relationship between selection intensity and recombination on the breadth of selection sweep? What is the relationship between background selection and reduced diversity? 6. What is alcohol dehydrogenase a good gene for ...
... 4. Describe the relationship between diversity and recombination? 5. What is the relationship between selection intensity and recombination on the breadth of selection sweep? What is the relationship between background selection and reduced diversity? 6. What is alcohol dehydrogenase a good gene for ...
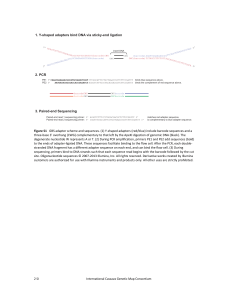
Figure S1 - G3: Genes | Genomes | Genetics
... degenerate nucleotide W represents A or T. (2) During PCR amplification, primers PE1 and PE2 add sequences (bold) to the ends of adapter‐ligated DNA. These sequences facilitate binding to the flow cell. After the PCR, each double‐ stranded DNA fragment has a different adapter sequence on each end, ...
... degenerate nucleotide W represents A or T. (2) During PCR amplification, primers PE1 and PE2 add sequences (bold) to the ends of adapter‐ligated DNA. These sequences facilitate binding to the flow cell. After the PCR, each double‐ stranded DNA fragment has a different adapter sequence on each end, ...
Gene rearrangements occur via various mechanisms
... without the donating chromosome being changed. Gene conversion occurs at high frequency at the actual site of the recombination event during meiosis. It is a process by which a DNA sequence is copied from one DNA helix (which remains unchanged) to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered. Gene c ...
... without the donating chromosome being changed. Gene conversion occurs at high frequency at the actual site of the recombination event during meiosis. It is a process by which a DNA sequence is copied from one DNA helix (which remains unchanged) to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered. Gene c ...
Chapter 20 Terms to Know
... Gel Electrophoresis: used to separate DNA molecules on basis of size and charge using an electrical current (DNA + pole) ...
... Gel Electrophoresis: used to separate DNA molecules on basis of size and charge using an electrical current (DNA + pole) ...
What is DNA?
... • Half of every strand of your DNA comes from your mom and half comes from your dad. • It doesn’t matter who you look like more, you are 50/50 mom and dad! ...
... • Half of every strand of your DNA comes from your mom and half comes from your dad. • It doesn’t matter who you look like more, you are 50/50 mom and dad! ...
Document
... ___ 2. A certain mutant bacterial cell cannot produce substance 3. stimulate immunity X. 4. control a disorder The mutation was most likely the result of a change in the 1. structure of the cell membrane ___ 7. The type of molecule represented in the accompanying 2. ability of the DNA to replicate d ...
... ___ 2. A certain mutant bacterial cell cannot produce substance 3. stimulate immunity X. 4. control a disorder The mutation was most likely the result of a change in the 1. structure of the cell membrane ___ 7. The type of molecule represented in the accompanying 2. ability of the DNA to replicate d ...
Linking recombinant genes sequence to protein
... number of important operations which we can perform without thinking of them.” (Alfred North Whitehead) ...
... number of important operations which we can perform without thinking of them.” (Alfred North Whitehead) ...
AIR Genetics Review PPT
... – tRNA, that contains an amino acid (anticodon), base pairs with mRNA strand (codon). Amino acids are linked together. – Stop codon reached and amino acid sequence is released to fold (protein) ...
... – tRNA, that contains an amino acid (anticodon), base pairs with mRNA strand (codon). Amino acids are linked together. – Stop codon reached and amino acid sequence is released to fold (protein) ...
BC2004
... Restriction endonucleases are bacterial enzymes that act as defense mechanisms in these organisms. Restriction endonucleases cleave double-stranded DNA internally, cutting both strands at regions of specific nucleotide sequences that vary from one enzyme to another. The sequence cut by a restriction ...
... Restriction endonucleases are bacterial enzymes that act as defense mechanisms in these organisms. Restriction endonucleases cleave double-stranded DNA internally, cutting both strands at regions of specific nucleotide sequences that vary from one enzyme to another. The sequence cut by a restriction ...
epigenetic webquest 2014
... 5. When a gene is inactive – describe the amount of methyl molecules and the mRNA transcripts? ...
... 5. When a gene is inactive – describe the amount of methyl molecules and the mRNA transcripts? ...
Genetic Engineering PowerPoint
... manufacture alcohol and other chemicals process minerals. Make human proteins. There is concern about possible risks to the environment and the general population as genetically engineered bacteria are introduced. ...
... manufacture alcohol and other chemicals process minerals. Make human proteins. There is concern about possible risks to the environment and the general population as genetically engineered bacteria are introduced. ...