Advanced Physics Semester 2 Final Study Guide Momentum
... The momentum of an object depends on mass and velocity. Momentum is how hard it is to stop an object that is moving. Momentum is a (vector/scalar) quantity. vector – it has magnitude and direction Write a sentence that uses the word “momentum” that demonstrates that you know the meaning of the word. ...
... The momentum of an object depends on mass and velocity. Momentum is how hard it is to stop an object that is moving. Momentum is a (vector/scalar) quantity. vector – it has magnitude and direction Write a sentence that uses the word “momentum” that demonstrates that you know the meaning of the word. ...
Force & Motion Buckle Down Review
... pairs: For every action, there is a reaction that is equal in magnitude (size) but opposite in direction. This sometimes confuses people: if the forces are equal and opposite, then why don’t they cancel each other out? How does anything move? The key is to remember that the “equal and opposite” forc ...
... pairs: For every action, there is a reaction that is equal in magnitude (size) but opposite in direction. This sometimes confuses people: if the forces are equal and opposite, then why don’t they cancel each other out? How does anything move? The key is to remember that the “equal and opposite” forc ...
CURRICULUM SUMMARY – September to October 2008
... Calculate speed / acceleration from gradient of distance-time speed-time graph Distinguish between speed and velocity Understand deceleration as a negative acceleration Recognise that a force may produce a change in size and shape of a body Recognise that if there is no resultant force on a body it ...
... Calculate speed / acceleration from gradient of distance-time speed-time graph Distinguish between speed and velocity Understand deceleration as a negative acceleration Recognise that a force may produce a change in size and shape of a body Recognise that if there is no resultant force on a body it ...
d = 0.5 gt 2
... Since accelerating objects are constantly changing their velocity, you can say that the distance traveled divided by the time taken to travel that distance is not a constant value. A falling object for instance usually accelerates as it falls. The fact that the distance which the object travels ever ...
... Since accelerating objects are constantly changing their velocity, you can say that the distance traveled divided by the time taken to travel that distance is not a constant value. A falling object for instance usually accelerates as it falls. The fact that the distance which the object travels ever ...
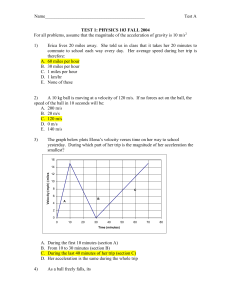
SAMPLE TEST 1: PHYSICS 103
... Elise jumps off a cliff and lands in a lake 20 m below. Neglecting air resistance, the speed with which she hits the water is: A. 5 m/s B. 10 m/s C. 15 m/s D. 20 m/s ...
... Elise jumps off a cliff and lands in a lake 20 m below. Neglecting air resistance, the speed with which she hits the water is: A. 5 m/s B. 10 m/s C. 15 m/s D. 20 m/s ...
Chapter 23
... Fmax = (qVdB)(NAl) where N = number of atoms But, I = NqVdA (from chapter 17) so we simplify our equation into F = BIl (This equation can only be used when the current and the magnetic field are perpendicular to each other) *If the field direction and velocity are not perpendicular F = BIl (sinσ) (u ...
... Fmax = (qVdB)(NAl) where N = number of atoms But, I = NqVdA (from chapter 17) so we simplify our equation into F = BIl (This equation can only be used when the current and the magnetic field are perpendicular to each other) *If the field direction and velocity are not perpendicular F = BIl (sinσ) (u ...
Student Review Sheet Physics Semester A Examination
... BCRs were put on the exam review sheets to encourage appropriate student collaboration and review of concepts in preparation for the entire exam (not just the BCRs). Teachers should not address these BCRs during the course of their instruction nor should they assist in preparing students for the BCR ...
... BCRs were put on the exam review sheets to encourage appropriate student collaboration and review of concepts in preparation for the entire exam (not just the BCRs). Teachers should not address these BCRs during the course of their instruction nor should they assist in preparing students for the BCR ...
Slide 1 - Mother Seton
... opposes the motion? 6.41 The driver of a 1200 kg car notices that the car slows from 20 m/s to 15 m/s as it coasts a distance of 130 m along level ground. How large a force opposes the motion? 6.42 A 2000 kg elevator rises from rest in the basement to the fourth floor, a distance of 25 m. As it pass ...
... opposes the motion? 6.41 The driver of a 1200 kg car notices that the car slows from 20 m/s to 15 m/s as it coasts a distance of 130 m along level ground. How large a force opposes the motion? 6.42 A 2000 kg elevator rises from rest in the basement to the fourth floor, a distance of 25 m. As it pass ...
Final Exam Key Term Review Sheet
... 10. A 67.0 kg block is pushed with an acceleration of 8.9 m/s2 to the left. What is the force in which Block is being pushed? And what law of motion is being applied? ...
... 10. A 67.0 kg block is pushed with an acceleration of 8.9 m/s2 to the left. What is the force in which Block is being pushed? And what law of motion is being applied? ...
Physics Review
... (B) In that period of time, how far has the ship traveled relative to the earth? (C) How long a period of time has it been on the ship? (D) How far does the ship think it is to the Earth from Neptune? As the ship passes an asteroid, it pulls out its super duper destructo beam gun and shoots the 45.0 ...
... (B) In that period of time, how far has the ship traveled relative to the earth? (C) How long a period of time has it been on the ship? (D) How far does the ship think it is to the Earth from Neptune? As the ship passes an asteroid, it pulls out its super duper destructo beam gun and shoots the 45.0 ...
AS Unit G481: Mechanics
... tends to produce rotation only explain that both the net force and net moment on an extended object in equilibrium is zero ...
... tends to produce rotation only explain that both the net force and net moment on an extended object in equilibrium is zero ...
Teacher guide Teacher guide: Turning Points in Physics
... predicts the formation of two fringes corresponding to the two slits. In addition, they should know that Huygens explained refraction by assuming that light travels slower in a transparent substance than in air in contrast with Newton’s assumption that its speed is faster in a transparent substance. ...
... predicts the formation of two fringes corresponding to the two slits. In addition, they should know that Huygens explained refraction by assuming that light travels slower in a transparent substance than in air in contrast with Newton’s assumption that its speed is faster in a transparent substance. ...
MA Syllabus Summary Blank
... present information graphically of: - displacement vs time - velocity vs time - for objects with uniform and non-uniform linear velocity ...
... present information graphically of: - displacement vs time - velocity vs time - for objects with uniform and non-uniform linear velocity ...
pdf file
... the Sun at one of the focal points. ► A line drawn from the Sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. ► The square of the orbital period of any planet is proportional to cube of the average distance from the Sun to the planet. ...
... the Sun at one of the focal points. ► A line drawn from the Sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. ► The square of the orbital period of any planet is proportional to cube of the average distance from the Sun to the planet. ...
Document
... Although the velocity of light is large, it is not infinite. c = 300,000 km/sec or c = 186,000 miles/sec Ordinary matter cannot travel faster than the speed of light. ...
... Although the velocity of light is large, it is not infinite. c = 300,000 km/sec or c = 186,000 miles/sec Ordinary matter cannot travel faster than the speed of light. ...
27. Gravitation
... field for different bodies Gravitational field E due to a spherical shell of mass M and radius R at a point distant r from the centre. (a) When r > R ...
... field for different bodies Gravitational field E due to a spherical shell of mass M and radius R at a point distant r from the centre. (a) When r > R ...
No Slide Title
... • The filament of a normal light bulb is heated to about 2500 celsius to make it give off ‘white’ light • When something is at about 800 celsius: its red hot • When its colder, it gives off only infra-red light. We can’t ‘see’ this light but we can detect it. • IR light is absorbed by molecules in o ...
... • The filament of a normal light bulb is heated to about 2500 celsius to make it give off ‘white’ light • When something is at about 800 celsius: its red hot • When its colder, it gives off only infra-red light. We can’t ‘see’ this light but we can detect it. • IR light is absorbed by molecules in o ...