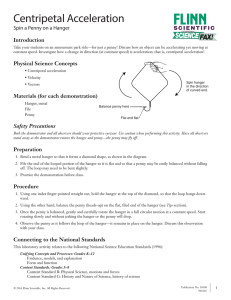
Review for Final Exam - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 55. The closest star to our solar system is Alpha Centauri, which is 4.12 x 1016 m away. How long would it take light from Alpha Centauri to reach our solar system if the speed of light is 3.00 x 108 m/s? Provide an answer in both seconds and in years. {1.37 x 108 s or 4.35 years} 56. A car is trav ...
... 55. The closest star to our solar system is Alpha Centauri, which is 4.12 x 1016 m away. How long would it take light from Alpha Centauri to reach our solar system if the speed of light is 3.00 x 108 m/s? Provide an answer in both seconds and in years. {1.37 x 108 s or 4.35 years} 56. A car is trav ...
6.3 Apparent forces in circular motion
... control of the bike, the rider wants the normal force on the tires at the top of the loop to equal or exceed the riders and the bike’s combined weight. What is the minimum speed at which the rider can take the loop? ...
... control of the bike, the rider wants the normal force on the tires at the top of the loop to equal or exceed the riders and the bike’s combined weight. What is the minimum speed at which the rider can take the loop? ...
Chap2_motion_revised
... stones, big or small Galileo’s experiments showed that if there were NO AIR for them to push their way through, all falling objects near the Earth’s surface would have the same acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 ...
... stones, big or small Galileo’s experiments showed that if there were NO AIR for them to push their way through, all falling objects near the Earth’s surface would have the same acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 ...
Ch 8 Dynamics II Review Problems
... to a 1.0 m long string, then allowing the mass to move in a horizontal circle of radius 20 cm. a. Find the tension is the string and b. the angular speed of the ball in rpm. Analysis: The mass moves in a horizontal circle of radius The acceleration and the net force vector point to the center of the ...
... to a 1.0 m long string, then allowing the mass to move in a horizontal circle of radius 20 cm. a. Find the tension is the string and b. the angular speed of the ball in rpm. Analysis: The mass moves in a horizontal circle of radius The acceleration and the net force vector point to the center of the ...
المحاضرة الثالثة Circular Motion
... a- V=squar root(2*R*g) where R :radius of the planet g :the gravitational acceleration at its surface b- A car with a mass 2500kg moving with velocity 2ookm/hr ,a break force applied on it to stop after 5 sec find The acceleration The distance traveled before it stopa ...
... a- V=squar root(2*R*g) where R :radius of the planet g :the gravitational acceleration at its surface b- A car with a mass 2500kg moving with velocity 2ookm/hr ,a break force applied on it to stop after 5 sec find The acceleration The distance traveled before it stopa ...
Unit 1
... on an object, the greater its change in motion; however, the same amount of force applied to an object with less mass results in a greater acceleration. • While Newton’s second law describes a single object, forces always come in equal and opposite pairs due to interaction between objects. Give exam ...
... on an object, the greater its change in motion; however, the same amount of force applied to an object with less mass results in a greater acceleration. • While Newton’s second law describes a single object, forces always come in equal and opposite pairs due to interaction between objects. Give exam ...
If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its
... A l.0-meter stick and a clock move with speed 0.8 c relative to an observer. 47. If the stick is aligned parallel to the direction of motion, its observed length is most nearly (A) 0.6 m (B) 0.8 m (C) 1.0 m (D) 1/(0.8) m (E) 1/(0.6) m 48. If the stick is aligned perpendicularly to the direction of m ...
... A l.0-meter stick and a clock move with speed 0.8 c relative to an observer. 47. If the stick is aligned parallel to the direction of motion, its observed length is most nearly (A) 0.6 m (B) 0.8 m (C) 1.0 m (D) 1/(0.8) m (E) 1/(0.6) m 48. If the stick is aligned perpendicularly to the direction of m ...
Unit 2: Vector Dynamics
... 25. Which of the following is not a statement of one of Newton’s laws of motion? a. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. b. If no net force acts on an object, the object will remain at rest, or continue to move at a constant velocity. c. The acceleration of freely f ...
... 25. Which of the following is not a statement of one of Newton’s laws of motion? a. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. b. If no net force acts on an object, the object will remain at rest, or continue to move at a constant velocity. c. The acceleration of freely f ...
Physics 101 (F11) Q2A Name: Section: Score: /20
... For the initial 2 seconds, the acceleration is a, so the upward velocity at time 2 s is 2a. Since the fuel is gone, after this, the rocket problem is just the ball thrown upward with the initial velocity 2a. At the highest point the vertical velocity must vanish. v(t) = v(0) + (-g)t, since the accel ...
... For the initial 2 seconds, the acceleration is a, so the upward velocity at time 2 s is 2a. Since the fuel is gone, after this, the rocket problem is just the ball thrown upward with the initial velocity 2a. At the highest point the vertical velocity must vanish. v(t) = v(0) + (-g)t, since the accel ...
H2 PHYSICS SET B PAPER 1 THE PHYSICS CAFE
... A student performing an experiment whirls a rubber bung attached to one end of a string which passes through a glass tube with smooth openings and has a weight W hanging at its other end. The weight of the rubber bung is much smaller than W. The rubber bung is set into a horizontal uniform circular ...
... A student performing an experiment whirls a rubber bung attached to one end of a string which passes through a glass tube with smooth openings and has a weight W hanging at its other end. The weight of the rubber bung is much smaller than W. The rubber bung is set into a horizontal uniform circular ...
Science 20 Unit b Final Test
... front of him and stops in the middle of the highway if it takes Drayton 0.4 seconds to respond and 4 seconds to come to a complete stop will he hit the deer? And if he doesn’t hit the deer how many meters is Drayton away from the deer? a. He hits the deer b. He stops 66.7 m from the deer c. He stops ...
... front of him and stops in the middle of the highway if it takes Drayton 0.4 seconds to respond and 4 seconds to come to a complete stop will he hit the deer? And if he doesn’t hit the deer how many meters is Drayton away from the deer? a. He hits the deer b. He stops 66.7 m from the deer c. He stops ...
Motion in Two Dimensions
... This also means that if the distance between the centers of the objects changes, the gravity will change. Therefore, if you move closer to the center of the earth, you will experience a greater gravity and you will weigh more! Conversely, if you move out into space, you will weigh less! ...
... This also means that if the distance between the centers of the objects changes, the gravity will change. Therefore, if you move closer to the center of the earth, you will experience a greater gravity and you will weigh more! Conversely, if you move out into space, you will weigh less! ...
DO PHYSICS ONLINE SPACE PROJECTILE MOTION
... Galileo’s Analysis of Projectile Motion Our understanding of projectile motion owes a great debt to Galileo, who in his work entitled “Dialogues Concerning Two New Sciences”, presented his classic analysis of such motion. Galileo argued that projectile motion was a compound motion made up of a horiz ...
... Galileo’s Analysis of Projectile Motion Our understanding of projectile motion owes a great debt to Galileo, who in his work entitled “Dialogues Concerning Two New Sciences”, presented his classic analysis of such motion. Galileo argued that projectile motion was a compound motion made up of a horiz ...