Chapter 9 Clickers
... first two seconds. Then, the force remains constant for four seconds. During the last two seconds, the force linearly decreases to zero newtons. What is the total impulse exerted on the object? a) This cannot be determined because neither the initial momentum nor the final momentum is known. b) This ...
... first two seconds. Then, the force remains constant for four seconds. During the last two seconds, the force linearly decreases to zero newtons. What is the total impulse exerted on the object? a) This cannot be determined because neither the initial momentum nor the final momentum is known. b) This ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... 3. Sum the forces along each axis to get two equations for two unknowns. a) FRADIUS: +FIN FOUT = m(v2)/ r b) FTAN : FFORWARD FBACKWARDS = ma 4. You can generally expect the weight of the object to have components in both equations unless the object is exactly at the top, bottom or sides of t ...
... 3. Sum the forces along each axis to get two equations for two unknowns. a) FRADIUS: +FIN FOUT = m(v2)/ r b) FTAN : FFORWARD FBACKWARDS = ma 4. You can generally expect the weight of the object to have components in both equations unless the object is exactly at the top, bottom or sides of t ...
Section 13.10 Interference of Waves
... motion by rolling it with a speed of 3.00 m/s across a room 12.0 m long between two walls. Assume that the collisions made with each wall are perfectly elastic and that the motion is perpendicular to the two walls. (a) Show that the motion is periodic and determine its period. (b) Is the motion simp ...
... motion by rolling it with a speed of 3.00 m/s across a room 12.0 m long between two walls. Assume that the collisions made with each wall are perfectly elastic and that the motion is perpendicular to the two walls. (a) Show that the motion is periodic and determine its period. (b) Is the motion simp ...
4.4 Wave Characteristics
... Draw a third wave with wavelength 8cme. Draw 3 more waves with the same wavelengths as the first set but with an amplitude of 6 cm. ...
... Draw a third wave with wavelength 8cme. Draw 3 more waves with the same wavelengths as the first set but with an amplitude of 6 cm. ...
Solutions to Homework Set #3 Phys2414 – Fall 2005
... Note: The numbers in the boxes correspond to those that are generated by WebAssign. The numbers on your individual assignment will vary. Any calculated quantities that involve these variable numbers will be boxed as well. 1. GRR1 3.P.001. Two cars, a Porsche and a Honda, are traveling in the same di ...
... Note: The numbers in the boxes correspond to those that are generated by WebAssign. The numbers on your individual assignment will vary. Any calculated quantities that involve these variable numbers will be boxed as well. 1. GRR1 3.P.001. Two cars, a Porsche and a Honda, are traveling in the same di ...
UNIT 2
... Motion is Relative Earth is moving at 100,000 km/hr orbital speed. Looks or feels like barely moving from our perspective. Frames of Reference: We must specify which frame of reference we’re using when describing the motion of a body. 1. In most cases, it will be the Earth itself. 2. When the body ...
... Motion is Relative Earth is moving at 100,000 km/hr orbital speed. Looks or feels like barely moving from our perspective. Frames of Reference: We must specify which frame of reference we’re using when describing the motion of a body. 1. In most cases, it will be the Earth itself. 2. When the body ...
Chapter 7
... orbits by a gravitational pull to the Sun and the other planets in the Solar System. • He went on to conclude that there is a mutual gravitational force between all particles of matter. • From that he saw that the attractive force was universal to all objects based on their mass and the distance the ...
... orbits by a gravitational pull to the Sun and the other planets in the Solar System. • He went on to conclude that there is a mutual gravitational force between all particles of matter. • From that he saw that the attractive force was universal to all objects based on their mass and the distance the ...
Axis
... Freddie swings a 2-kg stone at the end of a thin rope of length 1.2 m. He tugs mightily, swinging the stone so fast that the rope is almost horizontal. If the string tension is 200 N, show that the stone moves at 11 m/s. ...
... Freddie swings a 2-kg stone at the end of a thin rope of length 1.2 m. He tugs mightily, swinging the stone so fast that the rope is almost horizontal. If the string tension is 200 N, show that the stone moves at 11 m/s. ...
12.3 Velocity and Acceleration
... Velocity and Acceleration As an object moves along a curve in the plane, the coordinates x and y of its center of mass are each functions of time t. Rather than using the letters f and g to represent these two functions, it is convenient to write x = x(t) and y = y(t). So, the position vector r(t) ...
... Velocity and Acceleration As an object moves along a curve in the plane, the coordinates x and y of its center of mass are each functions of time t. Rather than using the letters f and g to represent these two functions, it is convenient to write x = x(t) and y = y(t). So, the position vector r(t) ...
Appendix 3.qxd
... inclined plane at regular intervals. Since the car accelerates down the plane, we must determine the distance up the plane from which the car is released in order to increase the velocity at a known rate. Several ways that this may be approached are included here, but it is not intended that all be ...
... inclined plane at regular intervals. Since the car accelerates down the plane, we must determine the distance up the plane from which the car is released in order to increase the velocity at a known rate. Several ways that this may be approached are included here, but it is not intended that all be ...
Lec12
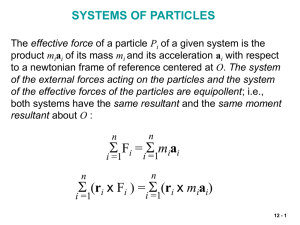
... the flow of air through a jet engine. The principle of impulse and momentum is applied to a system S of particles during a time interval Dt, including particles which enter the system at A during that time interval and those (of the same mass Dm) which leave the system at B. The system formed by the ...
... the flow of air through a jet engine. The principle of impulse and momentum is applied to a system S of particles during a time interval Dt, including particles which enter the system at A during that time interval and those (of the same mass Dm) which leave the system at B. The system formed by the ...
ODU-Mechanics-Questions
... The world downhill skiing speed trial takes place at Les Arcs every year. Describe a method that could be used to find the average speed of the skier over the 1 km run. Your description should include: (a) (b) (c) ...
... The world downhill skiing speed trial takes place at Les Arcs every year. Describe a method that could be used to find the average speed of the skier over the 1 km run. Your description should include: (a) (b) (c) ...