Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... motion (circular motion at a constant speed) is called centripetal acceleration. An understanding of centripetal acceleration was one of the key elements that led to Newton’s formulation of the law of universal gravitation. Question: How is centripetal acceleration related to radius, mass, and veloc ...
... motion (circular motion at a constant speed) is called centripetal acceleration. An understanding of centripetal acceleration was one of the key elements that led to Newton’s formulation of the law of universal gravitation. Question: How is centripetal acceleration related to radius, mass, and veloc ...
Chapter 7 The Quantum- Mechanical Model of the Atom - NTOU-Chem
... It was observed that many metals emit electrons when a light shines on their surface. – This is called the photoelectric effect. Classic wave theory attributed this effect to the light energy being transferred to the electron. According to this theory, if the wavelength of light is made shorter, or ...
... It was observed that many metals emit electrons when a light shines on their surface. – This is called the photoelectric effect. Classic wave theory attributed this effect to the light energy being transferred to the electron. According to this theory, if the wavelength of light is made shorter, or ...
293) Physics
... 111) Centripetal Force: The force that causes an object moving at constant speed to move in a curved path or circle. 112) The Law of Conservation of Momentum: Momentum can be transferred between objects but the total momentum is never lost. 113) Momentum: Object's mass multiplied by its velocity. P= ...
... 111) Centripetal Force: The force that causes an object moving at constant speed to move in a curved path or circle. 112) The Law of Conservation of Momentum: Momentum can be transferred between objects but the total momentum is never lost. 113) Momentum: Object's mass multiplied by its velocity. P= ...
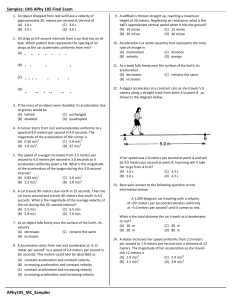
Fall Semester Review - Physics [Regular]
... If some measurements agree closely with each other but differ widely from the actual value, these measurements are a. neither precise nor accurate. b. accurate but not precise. c. acceptable as a new standard of accuracy. d. precise but not accurate. ...
... If some measurements agree closely with each other but differ widely from the actual value, these measurements are a. neither precise nor accurate. b. accurate but not precise. c. acceptable as a new standard of accuracy. d. precise but not accurate. ...
Wells Problem Workbook Pack
... comes to rest on the landing strip. Can this plane land at an airport where the runway is 0.80 km long (Hint, the 0.80 km is not necessarily the distance actually traveled, it is simply the total length of the runway which can be used as a comparison)? ...
... comes to rest on the landing strip. Can this plane land at an airport where the runway is 0.80 km long (Hint, the 0.80 km is not necessarily the distance actually traveled, it is simply the total length of the runway which can be used as a comparison)? ...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach
... drive. If the 140 g ball is movi ng hori zo ntall y at 28 m/s. and the catch is made whe n the ballplayer is at the hi ghest point of hi s leap, what is hi s speed immed iately after stoppin g the ball ? 23. !II A kid at the j unior hi gh cafeteria wants to prope l an e mpty miLk carton along a lu n ...
... drive. If the 140 g ball is movi ng hori zo ntall y at 28 m/s. and the catch is made whe n the ballplayer is at the hi ghest point of hi s leap, what is hi s speed immed iately after stoppin g the ball ? 23. !II A kid at the j unior hi gh cafeteria wants to prope l an e mpty miLk carton along a lu n ...
Physics Packet 2013-2014 - Haverford School District
... b. A driver is in a small town where there is a lot of pedestrian traffic. He drives the speed limit and slows to a stop at the stop sign. After stopping, he begins to drive for a half a block, when a small child runs out from behind a parked car. The driver brakes hard and stops, just in time. Afte ...
... b. A driver is in a small town where there is a lot of pedestrian traffic. He drives the speed limit and slows to a stop at the stop sign. After stopping, he begins to drive for a half a block, when a small child runs out from behind a parked car. The driver brakes hard and stops, just in time. Afte ...
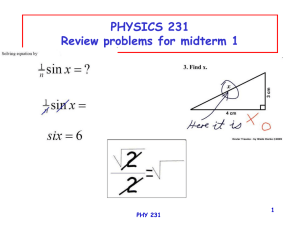
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1 1 PHY 231
... magnitude (speed is decreasing) since the gravitational force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer ...
... magnitude (speed is decreasing) since the gravitational force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer ...
Document
... 5.7.2. A ball on the end of a rope is moving in a vertical circle near the surface of the earth. Point A is at the top of the circle; C is at the bottom. Points B and D are exactly halfway between A and C. Which one of the following statements concerning the tension in the rope is true? a) The tens ...
... 5.7.2. A ball on the end of a rope is moving in a vertical circle near the surface of the earth. Point A is at the top of the circle; C is at the bottom. Points B and D are exactly halfway between A and C. Which one of the following statements concerning the tension in the rope is true? a) The tens ...
FREE Sample Here
... any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part. ...
... any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part. ...












![Fall Semester Review - Physics [Regular]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001475483_1-821ba0594b36cdf9728de3eb9fea5ec6-300x300.png)