LEDs and Lasers
... Why does a diode carry current only one way? How does an LED produce its light? How does laser light differ from regular light? How does a laser produce coherent light? ...
... Why does a diode carry current only one way? How does an LED produce its light? How does laser light differ from regular light? How does a laser produce coherent light? ...
Exam Review
... 42. An object is pushed from rest across a sheet of ice, accelerating at 5.0 m/s2 over a distance of 80.0 cm. The object then slides with a constant speed for 4.0 s until it reaches a rough section which causes it to stop in 2.5 s. (a) What is the speed of the object when it reaches the rough sectio ...
... 42. An object is pushed from rest across a sheet of ice, accelerating at 5.0 m/s2 over a distance of 80.0 cm. The object then slides with a constant speed for 4.0 s until it reaches a rough section which causes it to stop in 2.5 s. (a) What is the speed of the object when it reaches the rough sectio ...
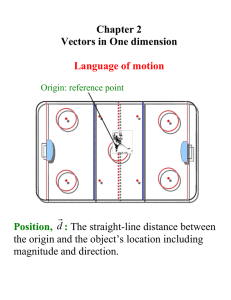
Vectors
... ground. Find the horizontal and vertical components of his applied force. 16. Another man pulls a wagon with his son sitting in it. The man pulls the wagon with a force of 200 N at an angle of 40o with the ground. The sidewalk provides 30 N of friction in the opposite direction of the man’s motion. ...
... ground. Find the horizontal and vertical components of his applied force. 16. Another man pulls a wagon with his son sitting in it. The man pulls the wagon with a force of 200 N at an angle of 40o with the ground. The sidewalk provides 30 N of friction in the opposite direction of the man’s motion. ...
32 From Galileo to Lorentz transformations
... It will be shown, when discussing relativistic dynamics, that an infinite energy is required to accelerate a particle with non-zero mass to the speed of light. Therefore no massive particle can reach the speed of light. On the other hand relativistic dynamics shows that massless particles always tra ...
... It will be shown, when discussing relativistic dynamics, that an infinite energy is required to accelerate a particle with non-zero mass to the speed of light. Therefore no massive particle can reach the speed of light. On the other hand relativistic dynamics shows that massless particles always tra ...
Hyperbolic Geometrodynamic Warp Drives
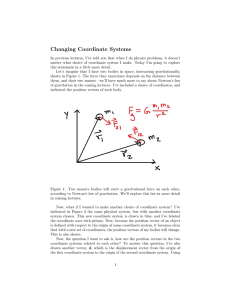
... special relativity applies to ones local geometry). Light speed is the local speed limit, but the broader considerations of general relativity may provide an end-run way of circumventing this local statute. It is possible to change the metrics of a local region of space-time to one in which the loca ...
... special relativity applies to ones local geometry). Light speed is the local speed limit, but the broader considerations of general relativity may provide an end-run way of circumventing this local statute. It is possible to change the metrics of a local region of space-time to one in which the loca ...
Vector Algebra and Velocity
... has dimensions. If the scalar is dimensionless, that is a pure number, than the multiplication simply enlarges (or reduces) the original vector if the scalar is bigger (or less) than 1.0 . If the scalar has dimensions, then the result is a new type of vector because the product will have different d ...
... has dimensions. If the scalar is dimensionless, that is a pure number, than the multiplication simply enlarges (or reduces) the original vector if the scalar is bigger (or less) than 1.0 . If the scalar has dimensions, then the result is a new type of vector because the product will have different d ...
Momentum
... 16. A moving particle is stopped by a single head-on collision with a second, stationary particle, if the moving particle undergoes A) an elastic collision with a second particle of much smaller mass. B) an elastic collision with a second particle of much greater mass. C) an elastic collision with a ...
... 16. A moving particle is stopped by a single head-on collision with a second, stationary particle, if the moving particle undergoes A) an elastic collision with a second particle of much smaller mass. B) an elastic collision with a second particle of much greater mass. C) an elastic collision with a ...
Physics Ch. 7 Rotational Motion
... of a person standing at the equator for 1.0 h? B. Convert this angular displacement to radians. C. What is the arc length traveled by this person? ...
... of a person standing at the equator for 1.0 h? B. Convert this angular displacement to radians. C. What is the arc length traveled by this person? ...
Chapter 33 - KFUPM Faculty List
... 33.8.1. Which one of the following statements relating to index of refraction n is false? a) Values of n are always greater than or equal to one. b) The speed of light in gases is only slightly less than that in a vacuum. c) The index of refraction tends to be larger for solids than for gases. d) V ...
... 33.8.1. Which one of the following statements relating to index of refraction n is false? a) Values of n are always greater than or equal to one. b) The speed of light in gases is only slightly less than that in a vacuum. c) The index of refraction tends to be larger for solids than for gases. d) V ...
Problem Set 9 Angular Momentum Solution
... far from the Sun as Neptune. Sedna has the longest orbital period of any known large object in the Solar System, calculated at approximately 11,400 years. Its maximum speed is 4.64 km ! s "1 . Its orbit is extremely eccentric, with an aphelion (furthest distance form the Sun) estimated at 937 AU and ...
... far from the Sun as Neptune. Sedna has the longest orbital period of any known large object in the Solar System, calculated at approximately 11,400 years. Its maximum speed is 4.64 km ! s "1 . Its orbit is extremely eccentric, with an aphelion (furthest distance form the Sun) estimated at 937 AU and ...
Exam 1 Solutions Kinematics and Newton’s laws of motion
... Can you feel gravity? We previously determined that you can’t. 1) Hanging from a 100 m high diving board – your arms feel stretched by the bending of the board. 2) Standing on a bed – your legs feel compressed by the springs in the mattress. The bent diving board or the compressed springs provide th ...
... Can you feel gravity? We previously determined that you can’t. 1) Hanging from a 100 m high diving board – your arms feel stretched by the bending of the board. 2) Standing on a bed – your legs feel compressed by the springs in the mattress. The bent diving board or the compressed springs provide th ...
Chapter 5: Matter in Motion
... • A plane passes over point A at a velocity of 240 m/s north. Forty seconds later, it passes over point B at a velocity of 260 m/s north. What is the plane’s average acceleration? ...
... • A plane passes over point A at a velocity of 240 m/s north. Forty seconds later, it passes over point B at a velocity of 260 m/s north. What is the plane’s average acceleration? ...
Chapter 1 Describing Motion
... At a swim meet, nervous swimmers position themselves along the starting line. They crouch down, ready to begin the 50-meter race. At the sound of the starter’s gun, the swimmers dive in and swim to the other end of the pool. As the crowd cheers, one swimmer touches the wall to win the race. Swimmers ...
... At a swim meet, nervous swimmers position themselves along the starting line. They crouch down, ready to begin the 50-meter race. At the sound of the starter’s gun, the swimmers dive in and swim to the other end of the pool. As the crowd cheers, one swimmer touches the wall to win the race. Swimmers ...