Lecture 6: Genome variation File
... Estimating genetic distance • Genetic distance = the number of substitutions that have accumulated between two homologous sequences after they diverged from a common ancestor • First approximation: proportion of sites that are different between the two sequences – sometimes it is called the p-dista ...
... Estimating genetic distance • Genetic distance = the number of substitutions that have accumulated between two homologous sequences after they diverged from a common ancestor • First approximation: proportion of sites that are different between the two sequences – sometimes it is called the p-dista ...
Biology - Genetics OEQs
... early development normal cell function causation of disease or cell malfunction Scientists can now determine the complete DNA sequences of organisms, including humans. Now that this milestone has been reached, is there a reason to continue learning about Mendel, alleles, and inheritance patt ...
... early development normal cell function causation of disease or cell malfunction Scientists can now determine the complete DNA sequences of organisms, including humans. Now that this milestone has been reached, is there a reason to continue learning about Mendel, alleles, and inheritance patt ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... Genetics — The scientific study of heredity, including the structure and function of genes. ...
... Genetics — The scientific study of heredity, including the structure and function of genes. ...
Mistakes Happen
... • What effect did the sickle cell gene have on the people who were carriers of the mutation? • Why has the sickle cell gene persisted even when sickle cell anemia is so debilitating? • What are the odds that the child of parents who each carry one normal gene and one sickle cell mutation gene will h ...
... • What effect did the sickle cell gene have on the people who were carriers of the mutation? • Why has the sickle cell gene persisted even when sickle cell anemia is so debilitating? • What are the odds that the child of parents who each carry one normal gene and one sickle cell mutation gene will h ...
Slide 1 - Indiana University–Purdue University Indianapolis
... DNA that develop throughout a person's life. In contrast to hereditary mutations, somatic mutations arise in the DNA of individual cells; the genetic errors are passed only to direct descendants of those cells. Mutations are often the result of errors that crop up during cell division, when the cell ...
... DNA that develop throughout a person's life. In contrast to hereditary mutations, somatic mutations arise in the DNA of individual cells; the genetic errors are passed only to direct descendants of those cells. Mutations are often the result of errors that crop up during cell division, when the cell ...
The Human Genome
... data base for comparison; may allow for identification of gene, gene function, and evolutionary relationships • Pharmacogenetics – customizes drugs to match a patient’s genetic makeup in order to reduce chances of side effects • Proteomics – the study of the proteins produced by the individual cell ...
... data base for comparison; may allow for identification of gene, gene function, and evolutionary relationships • Pharmacogenetics – customizes drugs to match a patient’s genetic makeup in order to reduce chances of side effects • Proteomics – the study of the proteins produced by the individual cell ...
Topic 6. Growth & Reproduction of Bacteria
... every 25 years. Because humans have about 30,000 genes per genome that’s about 18 million mutations in 25 years or only ~ 2000 per day, in the entire human population. ...
... every 25 years. Because humans have about 30,000 genes per genome that’s about 18 million mutations in 25 years or only ~ 2000 per day, in the entire human population. ...
Test 2 from 2012
... PART 1: Short Answer. Answer 5 of the following 6 questions. Question 1: Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that is critical to glycolysis. Part of the amino acid sequence for the wild type glucose-6-phosphate isomerase enzyme is shown below, along with the same part of the protein as produc ...
... PART 1: Short Answer. Answer 5 of the following 6 questions. Question 1: Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that is critical to glycolysis. Part of the amino acid sequence for the wild type glucose-6-phosphate isomerase enzyme is shown below, along with the same part of the protein as produc ...
Genetics of AHC - Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood Foundation
... No single genetic cause has been identified for AHC. Diagnosis of exclusion No way for physicians to confirm a child has AHC via a specific ...
... No single genetic cause has been identified for AHC. Diagnosis of exclusion No way for physicians to confirm a child has AHC via a specific ...
Lecture # 5 Mutations
... 3. Harmful (these mutations may disrupt gene function/ protein function) ...
... 3. Harmful (these mutations may disrupt gene function/ protein function) ...
Lecture Slides
... Each colored stripe in this fly embryo shows the expression of a different gene or set of genes. The spatial regulation of these genes allows the embryo to be divided up into different regions that will give rise to the head, the internal organs, the abdomen, etc. ...
... Each colored stripe in this fly embryo shows the expression of a different gene or set of genes. The spatial regulation of these genes allows the embryo to be divided up into different regions that will give rise to the head, the internal organs, the abdomen, etc. ...
Agents of Evolutionary Change
... errors during DNA replication. Mutations can happen in different ways: Substitutions ACTGCGA ACTGCCT ...
... errors during DNA replication. Mutations can happen in different ways: Substitutions ACTGCGA ACTGCCT ...
Document
... Have focused on changes in bp sequence of genes. This can actually lead to changes in gene function if the bp sequence changes are nonsynonymous and result in changes in amino acids. But in course of evolution, more complex organisms have arisen with increased number of genes. Genes with old functio ...
... Have focused on changes in bp sequence of genes. This can actually lead to changes in gene function if the bp sequence changes are nonsynonymous and result in changes in amino acids. But in course of evolution, more complex organisms have arisen with increased number of genes. Genes with old functio ...
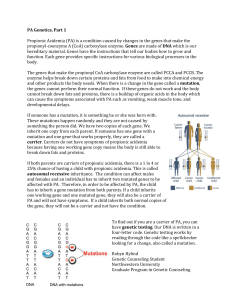
Propionic-Acidemia-G.. - Propionic Acidemia Foundation
... and other products the body needs. When there is a change in the gene called a mutation, the genes cannot perform their normal function. If these genes do not work and the body cannot break down fats and proteins, there is a buildup of organic acids in the body which can cause the symptoms associate ...
... and other products the body needs. When there is a change in the gene called a mutation, the genes cannot perform their normal function. If these genes do not work and the body cannot break down fats and proteins, there is a buildup of organic acids in the body which can cause the symptoms associate ...
dna_notes - KScience
... Mutations are sometimes beneficial because they generate variability, which is the basis of natural selection. Mutations are more often deleterious because selection in a species has selected for the genome it now has and changes are therefore more likely to be less useful. Mutations can lead to sev ...
... Mutations are sometimes beneficial because they generate variability, which is the basis of natural selection. Mutations are more often deleterious because selection in a species has selected for the genome it now has and changes are therefore more likely to be less useful. Mutations can lead to sev ...
Review for Final Exam
... 1. What is the study of heredity called? 2. Who is considered the father of genetics? 3. What is a gene that is fully expressed when 2 different alleles are present called? 4. What is a gene that is not fully expressed when 2 different alleles are present called? 5. What is a gene pair in which the ...
... 1. What is the study of heredity called? 2. Who is considered the father of genetics? 3. What is a gene that is fully expressed when 2 different alleles are present called? 4. What is a gene that is not fully expressed when 2 different alleles are present called? 5. What is a gene pair in which the ...
From Gene to Protein Protein Synthesis
... http://library.thinkquest.org/20465/g_DNATranscription.html ...
... http://library.thinkquest.org/20465/g_DNATranscription.html ...
Tumour-Suppressor Genes
... Restriction enzyme digestion of DNA, gel electrophoresis and “blotting” to a suitable membrane. DNA fragments are hybridised to a probe complementary to the gene of interest. If the probe recognises a segment within the boundaries of a single fragment one band is identified. If the gene has been tra ...
... Restriction enzyme digestion of DNA, gel electrophoresis and “blotting” to a suitable membrane. DNA fragments are hybridised to a probe complementary to the gene of interest. If the probe recognises a segment within the boundaries of a single fragment one band is identified. If the gene has been tra ...
The process represented in the diagram below occurs in many cells
... (1) cloning (2) inducing mutations (3) genetic engineering (4) selective breeding ...
... (1) cloning (2) inducing mutations (3) genetic engineering (4) selective breeding ...
Gen.1303 Genome: The total genetic content contained in a haploid
... A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes. Chromatin: A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nuc ...
... A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes. Chromatin: A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nuc ...
Progenika obtains the CE Mark for the first DNAchip to detect
... in order to reduce mortality and morbidity. The LPLchip® can precisely, quickly and economically detect more than 120 mutations in the LPL gene. The test uses Progenika’s pioneering advanced DNAchip technology, which offers reliable and fast diagnosis. All that is required for analysis using the LPL ...
... in order to reduce mortality and morbidity. The LPLchip® can precisely, quickly and economically detect more than 120 mutations in the LPL gene. The test uses Progenika’s pioneering advanced DNAchip technology, which offers reliable and fast diagnosis. All that is required for analysis using the LPL ...
level two biology: gene expression
... I can define the term “mutagen” and can name some examples. I can explain the difference between phenotype and genotype. I can show that I understand the difference between a mutagen and an environmental factor by comparing: ...
... I can define the term “mutagen” and can name some examples. I can explain the difference between phenotype and genotype. I can show that I understand the difference between a mutagen and an environmental factor by comparing: ...
mutation as a source of variation
... Genetic variation is essential for Darwin’s theory of natural selection and all genetic variation must come, ultimately, from mutations. A mutation is any hereditary change in the DNA sequence or in chromosome number, form or structure. Most mutations arise from errors during DNA replication that fa ...
... Genetic variation is essential for Darwin’s theory of natural selection and all genetic variation must come, ultimately, from mutations. A mutation is any hereditary change in the DNA sequence or in chromosome number, form or structure. Most mutations arise from errors during DNA replication that fa ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.