What is Genetic Testing?
... • Can test siblings of affected child to see if they are carriers for the disease (1 in 70 in the general population are carriers) ...
... • Can test siblings of affected child to see if they are carriers for the disease (1 in 70 in the general population are carriers) ...
Basic principles of DT40
... • Good model for genome stability in mammals • Complementation by human genes • Good database ...
... • Good model for genome stability in mammals • Complementation by human genes • Good database ...
: Determining DNA sequences
... host cell. Inside the host cell both the vector and the DNA fragment are cloned (copied). In the example a DNA fragment is inserted into the plasmid. The plasmid is then inserted into the host cells and produces many copies of itself. – The LacZ gene is used as a marker. If markers is disrupted then ...
... host cell. Inside the host cell both the vector and the DNA fragment are cloned (copied). In the example a DNA fragment is inserted into the plasmid. The plasmid is then inserted into the host cells and produces many copies of itself. – The LacZ gene is used as a marker. If markers is disrupted then ...
Quiz 13 Name: 1. Suppose there are two alleles of a gene, called A
... 4. Disorders caused by recessive, sex-linked (X) alleles should be most commonly expressed in: A) male humans (XY) B) female humans (XX) 5. If we assume that in dogs long legs are dominant to short then, if a heterozygous long-legged dog mates with a homozygous short-legged dog, what is the probabil ...
... 4. Disorders caused by recessive, sex-linked (X) alleles should be most commonly expressed in: A) male humans (XY) B) female humans (XX) 5. If we assume that in dogs long legs are dominant to short then, if a heterozygous long-legged dog mates with a homozygous short-legged dog, what is the probabil ...
Heredity and Meiosis - Chaparral Star Academy
... chain, a peptide bond occurs between amino acids to hold the chain together. When a bond has been made the ribosome will then move on down the mRNA to the next active site and continue the process. The used tRNA then returns to the cytoplasm ...
... chain, a peptide bond occurs between amino acids to hold the chain together. When a bond has been made the ribosome will then move on down the mRNA to the next active site and continue the process. The used tRNA then returns to the cytoplasm ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
... Inbreeding: crossing two organisms that are very similar to retain desirable characteristics. ...
... Inbreeding: crossing two organisms that are very similar to retain desirable characteristics. ...
Chapter 12 - Mantachie High School
... Mutations can involve an entire chromosome or a single DNA nucleotide or DNA segment. Mutations can occur in gametes (reproductive cells) or body cells. We don’t know everything that causes gene mutations, but scientists have linked several things to them. Mutagens are external agents that can cause ...
... Mutations can involve an entire chromosome or a single DNA nucleotide or DNA segment. Mutations can occur in gametes (reproductive cells) or body cells. We don’t know everything that causes gene mutations, but scientists have linked several things to them. Mutagens are external agents that can cause ...
BiotechnologySimple
... • occurs in most cells of all organisms • composed of four different nucleotides in different combinations • each cell in the human body contains more than 3 BILLION letters ...
... • occurs in most cells of all organisms • composed of four different nucleotides in different combinations • each cell in the human body contains more than 3 BILLION letters ...
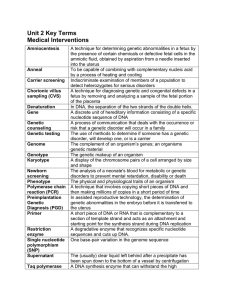
Unit 2 Terms
... disorders to prevent mental retardation, disability or death The physical and physiological traits of an organism A technique that involves copying short pieces of DNA and then making millions of copies in a short period of time In assisted reproductive technology, the determination of genetic abnor ...
... disorders to prevent mental retardation, disability or death The physical and physiological traits of an organism A technique that involves copying short pieces of DNA and then making millions of copies in a short period of time In assisted reproductive technology, the determination of genetic abnor ...
F factor
... - Bacteria are haploid, have only 1 copy of each gene on circular chromosome - There are mechanisms to introduce pieces of DNA from one cell to another to produce a partial diploid - Partial diploids, because usually only small pieces of DNA with only a few genes are transferred - The foreign DNA in ...
... - Bacteria are haploid, have only 1 copy of each gene on circular chromosome - There are mechanisms to introduce pieces of DNA from one cell to another to produce a partial diploid - Partial diploids, because usually only small pieces of DNA with only a few genes are transferred - The foreign DNA in ...
Chapter 15
... -can be a risky practice because it increases the chances that offspring will have two recessive alleles for a genetic defect ...
... -can be a risky practice because it increases the chances that offspring will have two recessive alleles for a genetic defect ...
TECRL: connecting sequence to consequence for a new sudden
... a devastating event. One of the first questions a family will ask is “Why did this happen?” In some cases, the answer may become obvious during a postmortem examination, but in up to 40% of cases, the postmortem is negative (Bagnall et al, 2016). In the last 1–2 decades, an improved understanding of ...
... a devastating event. One of the first questions a family will ask is “Why did this happen?” In some cases, the answer may become obvious during a postmortem examination, but in up to 40% of cases, the postmortem is negative (Bagnall et al, 2016). In the last 1–2 decades, an improved understanding of ...
Gene Mutations Activity
... Background: There are two types of mutations, smallscale gene mutations and largescale chromosomal mutations. In this activity you will be learning about gene mutations. There are two basic types of gene mutations, point (base substitution) and frameshift (insertions and deletions). In frameshi ...
... Background: There are two types of mutations, smallscale gene mutations and largescale chromosomal mutations. In this activity you will be learning about gene mutations. There are two basic types of gene mutations, point (base substitution) and frameshift (insertions and deletions). In frameshi ...
1 Early concepts of the gene. Pseudoalleles. Demise of the bead
... 9. What appears to be Miescher's principal interest in undertaking the purification and characterization of "nuclein"? What are the main conclusions stated by Miescher? What evidence and arguments does he present in support of these conclusions? 10. Avery et al. cite the view of Dobzhansky that tran ...
... 9. What appears to be Miescher's principal interest in undertaking the purification and characterization of "nuclein"? What are the main conclusions stated by Miescher? What evidence and arguments does he present in support of these conclusions? 10. Avery et al. cite the view of Dobzhansky that tran ...
DNA Sequencing
... Synthesis of new strand starts at 3’ end of primer and continues until dideoxyribonucleotide is inserted- stops synthesis Separate labeled strands through a polyacrylamide gel Placed on x-ray film Because of florescent tag, different length fragments are revealed on film and read manually ...
... Synthesis of new strand starts at 3’ end of primer and continues until dideoxyribonucleotide is inserted- stops synthesis Separate labeled strands through a polyacrylamide gel Placed on x-ray film Because of florescent tag, different length fragments are revealed on film and read manually ...
Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom
... Natural selection increases the frequency of beneficial mutations in a population Adaptation—a favored trait that evolves through natural selection Adaptation also describes the process that produces the trait. Individuals with deleterious mutations are less likely to survive, reproduce, and pass t ...
... Natural selection increases the frequency of beneficial mutations in a population Adaptation—a favored trait that evolves through natural selection Adaptation also describes the process that produces the trait. Individuals with deleterious mutations are less likely to survive, reproduce, and pass t ...
Classification of genetic disorders
... be protected against unnecessary exposure of the gonads to radiation. X-ray examination of the pregnant uterus to determine the presence of twins or the lie of the foetus is to be strongly deprecated. Rh haemolytic disease of the newborn which is a genetically determined immunological disorder is no ...
... be protected against unnecessary exposure of the gonads to radiation. X-ray examination of the pregnant uterus to determine the presence of twins or the lie of the foetus is to be strongly deprecated. Rh haemolytic disease of the newborn which is a genetically determined immunological disorder is no ...
Brooker Chapter 16
... parent to offspring without mutation However, in persons with TNRE disorders, the length of a trinucleotide repeat has increased above a certain critical size ...
... parent to offspring without mutation However, in persons with TNRE disorders, the length of a trinucleotide repeat has increased above a certain critical size ...
DNA, Genes, and Proteins EOC Review Describe the chemical and
... 1. Identify possible external causes (e.g., heat, radiation, certain chemicals) and effects of DNA mutations (e.g., altered proteins which may affect chemical reactions and structural development) A strand of DNA is exposed to intense heat. Which of these best describes what will happen to the stran ...
... 1. Identify possible external causes (e.g., heat, radiation, certain chemicals) and effects of DNA mutations (e.g., altered proteins which may affect chemical reactions and structural development) A strand of DNA is exposed to intense heat. Which of these best describes what will happen to the stran ...
protein synthesis
... (Note: There are 3 kinds of RNA transcribed in the nucleus; Messenger, Transfer and Ribosomal. Transfer and Ribosomal are stable, and reused so it is mostly mRNA that is being continuously transcribed) 3. The mRNA then moves out through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm where it is translated int ...
... (Note: There are 3 kinds of RNA transcribed in the nucleus; Messenger, Transfer and Ribosomal. Transfer and Ribosomal are stable, and reused so it is mostly mRNA that is being continuously transcribed) 3. The mRNA then moves out through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm where it is translated int ...
Socrative Modern Genetics - Manhasset Public Schools
... B) They only involve changes in the chromosome structure. C) They involve changes in the chromosome number or the chromosome structure. D) They never involve changes in the chromosome number or the chromosome structure. 47. An analysis of chromosomes may show the loss of a portion of a chromosome. T ...
... B) They only involve changes in the chromosome structure. C) They involve changes in the chromosome number or the chromosome structure. D) They never involve changes in the chromosome number or the chromosome structure. 47. An analysis of chromosomes may show the loss of a portion of a chromosome. T ...
11-2 Genetics and Probability
... resistance of crops to pests and herbicides, pollution control, designer species ...
... resistance of crops to pests and herbicides, pollution control, designer species ...
dihybrid cross: a genetic cross which examines the transmission of
... nitrogenous bases in a gene or a chromosome. There are two types of mutation – chromosome mutation (e.g. Down’s syndrome) and gene mutation (e.g. Sickle cell anaemia). phenotype: physical appearance of an individual as a result of the interaction of the genotype with the environment. recessive (alle ...
... nitrogenous bases in a gene or a chromosome. There are two types of mutation – chromosome mutation (e.g. Down’s syndrome) and gene mutation (e.g. Sickle cell anaemia). phenotype: physical appearance of an individual as a result of the interaction of the genotype with the environment. recessive (alle ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... 13. Environmental substances that can cause cancer are called A. tumors. B. carcinogens. C. mutations. D. poisons. 14. Environmental factors like ultraviolet light, asbestos fibers, and cigarette smoke are A. harmless and do not cause lasting cellular damage. B. only temporarily damaging to cellular ...
... 13. Environmental substances that can cause cancer are called A. tumors. B. carcinogens. C. mutations. D. poisons. 14. Environmental factors like ultraviolet light, asbestos fibers, and cigarette smoke are A. harmless and do not cause lasting cellular damage. B. only temporarily damaging to cellular ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.