DNA TECHNOLOGY AND GENOMICS
... transformation) is used to construct recombinant DNA molecules. e.* Students know how exogenous DNA can be inserted into bacterial cells to alter their genetic makeup and support expression of new protein products. ...
... transformation) is used to construct recombinant DNA molecules. e.* Students know how exogenous DNA can be inserted into bacterial cells to alter their genetic makeup and support expression of new protein products. ...
document
... A selective sweep decreases the number of polymorphisms present in a population surrounding the gene that was driven into fixation due to positive selection. This provides an alternative to dN/dS ratios to detect genes under positive selection. ...
... A selective sweep decreases the number of polymorphisms present in a population surrounding the gene that was driven into fixation due to positive selection. This provides an alternative to dN/dS ratios to detect genes under positive selection. ...
Document
... • Uncertainties associated with gene tests for susceptibilities and complex conditions (e.g., heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease). • Fairness in access to advanced genomic technologies. • Conceptual and philosophical implications regarding human responsibility, free will vs genetic det ...
... • Uncertainties associated with gene tests for susceptibilities and complex conditions (e.g., heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease). • Fairness in access to advanced genomic technologies. • Conceptual and philosophical implications regarding human responsibility, free will vs genetic det ...
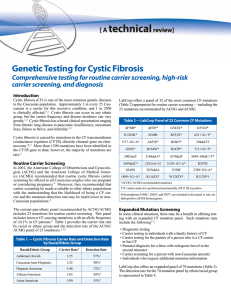
Genetic Testing for Cystic Fibrosis
... Limitations This method does not reliably detect mosaic variants; large deletions; large duplications, inversions, or other rearrangements; or deep intronic variants. It may be affected by allele dropout, it may not allow determination of the exact numbers of T/A or microsatellite repeats, and it do ...
... Limitations This method does not reliably detect mosaic variants; large deletions; large duplications, inversions, or other rearrangements; or deep intronic variants. It may be affected by allele dropout, it may not allow determination of the exact numbers of T/A or microsatellite repeats, and it do ...
Evolutionary Genetics - The Institute for Environmental Modeling
... sometimes alter the structure or number of genes or entire chromosomes. Most mutations are harmful, but some are advantageous. Mutations occur naturally at low rates (10−5 −10−6 per gene per generation). Mutation is considered to be the major factor limiting the speed of evolution. Isolated populati ...
... sometimes alter the structure or number of genes or entire chromosomes. Most mutations are harmful, but some are advantageous. Mutations occur naturally at low rates (10−5 −10−6 per gene per generation). Mutation is considered to be the major factor limiting the speed of evolution. Isolated populati ...
Slide 1
... • Genetic disorder of connective tissue • Due to mutation in one of several genes that encode different types of collagen proteins that are important ingredients of connective tissue of the eye, ear, cartilage, and other tissues. ...
... • Genetic disorder of connective tissue • Due to mutation in one of several genes that encode different types of collagen proteins that are important ingredients of connective tissue of the eye, ear, cartilage, and other tissues. ...
File
... is why there are many variations among species, because not all species can be the same. This is also one of their ways to avoid competition, if they are different then there’s no need for them to be in the same competition. ...
... is why there are many variations among species, because not all species can be the same. This is also one of their ways to avoid competition, if they are different then there’s no need for them to be in the same competition. ...
Understanding Human Genetic Variation
... which allow scientists to compare DNA samples from different sources and to locate specific base sequences within samples; and the automated sequencing techniques that today are allowing workers to sequence the human genome at an unprecedented rate. On the immediate horizon are even more powerful te ...
... which allow scientists to compare DNA samples from different sources and to locate specific base sequences within samples; and the automated sequencing techniques that today are allowing workers to sequence the human genome at an unprecedented rate. On the immediate horizon are even more powerful te ...
Get PDF - Wiley Online Library
... Sex chromosomes can evolve gene contents that differ from the rest of the genome, as well as larger sex differences in gene expression compared with autosomes. This probably occurs because fully sex-linked beneficial mutations substitute at different rates from autosomal ones, especially when fitnes ...
... Sex chromosomes can evolve gene contents that differ from the rest of the genome, as well as larger sex differences in gene expression compared with autosomes. This probably occurs because fully sex-linked beneficial mutations substitute at different rates from autosomal ones, especially when fitnes ...
Word - State of New Jersey
... Students should synthesize information and cite specific evidence from texts, experiments, or simulations to gain a coherent understanding of and support explanations about the relationship between the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding instructions for characteristic traits passed from parents t ...
... Students should synthesize information and cite specific evidence from texts, experiments, or simulations to gain a coherent understanding of and support explanations about the relationship between the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding instructions for characteristic traits passed from parents t ...
Antley-Bixler syndrome or POR deficiency?
... the important coenzyme-cofactor relationship is impaired such that CYPOR can not transfer electrons to its acceptors. Consequently, cytochromes P450 can not function normally and appear deficient. As shown in Fig. 3, several steps in the pathway of steroidogenesis are inhibited by depressed activity ...
... the important coenzyme-cofactor relationship is impaired such that CYPOR can not transfer electrons to its acceptors. Consequently, cytochromes P450 can not function normally and appear deficient. As shown in Fig. 3, several steps in the pathway of steroidogenesis are inhibited by depressed activity ...
Unit 6: DNA and Inheritance
... Students should synthesize information and cite specific evidence from texts, experiments, or simulations to gain a coherent understanding of and support explanations about the relationship between the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding instructions for characteristic traits passed from parents t ...
... Students should synthesize information and cite specific evidence from texts, experiments, or simulations to gain a coherent understanding of and support explanations about the relationship between the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding instructions for characteristic traits passed from parents t ...
how imprinting affects inheritance, boulder 2011
... • Previous concepts: Mendelian inheritance, DNA structure, intro molecular genetics •Reading assignment for class: Text information on epigenetics •This is the first lesson in the unit, but it will be followed by two lessons on mechanism and other epigenetic phenomena. •Since this topic has more cha ...
... • Previous concepts: Mendelian inheritance, DNA structure, intro molecular genetics •Reading assignment for class: Text information on epigenetics •This is the first lesson in the unit, but it will be followed by two lessons on mechanism and other epigenetic phenomena. •Since this topic has more cha ...
Variation of Traits
... simplify things by just focusing on the physical aspect of inherited traits. For example, if both parents exhibit the trait of red hair, their offspring have a greater chance of acquiring the genes that code for red hair. Certain traits are characteristically dominant or recessive, depending on t ...
... simplify things by just focusing on the physical aspect of inherited traits. For example, if both parents exhibit the trait of red hair, their offspring have a greater chance of acquiring the genes that code for red hair. Certain traits are characteristically dominant or recessive, depending on t ...
Ch. 9: Presentation Slides
... fragment of DNA that includes the coding sequence for the wildtype protein, then to use germ-line transformation to introduce this fragment into the genome of an organism that contains a mutation of a gene. If the introduced DNA includes all regulatory sequences necessary for correct gene expression ...
... fragment of DNA that includes the coding sequence for the wildtype protein, then to use germ-line transformation to introduce this fragment into the genome of an organism that contains a mutation of a gene. If the introduced DNA includes all regulatory sequences necessary for correct gene expression ...
Mitochondrial - Reversible infantile respiratory chain deficiency
... Clinically affected patients Carrier or Presymptomatic: Relatives of clinically affected patients Prenatal: At risk of having an affected child REFERRALS o From Hospital Consultants, mainly Clinical Genetics, Neurology, Paediatrics, Hepatology. o Prenatal referrals are only accepted from Clinical Ge ...
... Clinically affected patients Carrier or Presymptomatic: Relatives of clinically affected patients Prenatal: At risk of having an affected child REFERRALS o From Hospital Consultants, mainly Clinical Genetics, Neurology, Paediatrics, Hepatology. o Prenatal referrals are only accepted from Clinical Ge ...
Supplementary
... 5′-GAC TCA GAT TGG TTG CAC TTT-3′; Scramble DNA: TAA TAC GACTCA CTA TAG GGA-3′) were purchased from IDT. 1.2. Detecting Target DNA in the Presence of a DNA Library For the selectivity study, circularized DNA was produced in the presence of a library of non-complementary DNA. The linear DNA, target D ...
... 5′-GAC TCA GAT TGG TTG CAC TTT-3′; Scramble DNA: TAA TAC GACTCA CTA TAG GGA-3′) were purchased from IDT. 1.2. Detecting Target DNA in the Presence of a DNA Library For the selectivity study, circularized DNA was produced in the presence of a library of non-complementary DNA. The linear DNA, target D ...
Chapter 22 MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL GENETICS OF RYR1
... epidemiological evidence indicates that the frequency of MHS in the population is on the order of 1% while MHE frequencies are as high as 5%.823 This suggests that genetic and/or environmental factors have a strong influence on expression of clinical MH. A syndrome essentially identical to human MH ...
... epidemiological evidence indicates that the frequency of MHS in the population is on the order of 1% while MHE frequencies are as high as 5%.823 This suggests that genetic and/or environmental factors have a strong influence on expression of clinical MH. A syndrome essentially identical to human MH ...
Document
... Know what restriction enzymes, “sticky ends” are, their function, and how they are useful in recombinant technology, where restriction enzymes come from Know the functions of promoter, operator, enhancer, regulator sites on DNA Know the different levels of control/their order in gene activity/expres ...
... Know what restriction enzymes, “sticky ends” are, their function, and how they are useful in recombinant technology, where restriction enzymes come from Know the functions of promoter, operator, enhancer, regulator sites on DNA Know the different levels of control/their order in gene activity/expres ...
ANTHR1 - Physical Anthropology
... 3. Anthropology can be defined as the study of a. extinct humans c. all humans in all times & all places b. foreign cultures d. modern humans 4. The structure (remember, I said it was like a factory) that assembles amino acids into proteins is a a. ribosome c. chromosome b. DNA molecule d. allele 5. ...
... 3. Anthropology can be defined as the study of a. extinct humans c. all humans in all times & all places b. foreign cultures d. modern humans 4. The structure (remember, I said it was like a factory) that assembles amino acids into proteins is a a. ribosome c. chromosome b. DNA molecule d. allele 5. ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.