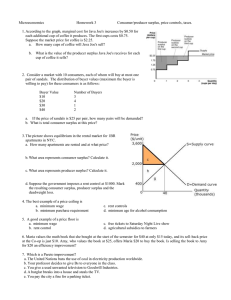
Econ 300- Second Graded Problem Set
... a. If this market has a very elastic supply and a very inelastic demand, how would the burden of a tax on rubber bands be shared between consumers and producers? Use table and graph measuring consumer surplus and producer surplus similar to the one developed in class. b. If this market has very inel ...
... a. If this market has a very elastic supply and a very inelastic demand, how would the burden of a tax on rubber bands be shared between consumers and producers? Use table and graph measuring consumer surplus and producer surplus similar to the one developed in class. b. If this market has very inel ...
Ed Dolan, Soda Taxes, April 13, 2010
... usually extended to cover all sweetened beverages. The popularity of a Soda tax is driven by two factors Rising budget deficits at both the federal and state levels Increased concern about obesity and its associated health-care costs Several states have instituted soda taxes and a national s ...
... usually extended to cover all sweetened beverages. The popularity of a Soda tax is driven by two factors Rising budget deficits at both the federal and state levels Increased concern about obesity and its associated health-care costs Several states have instituted soda taxes and a national s ...
Chapter 9
... elasticities of S and D. – Pass-through fraction = Es/(Es-Ed) • Tells fraction of tax “passed thru” to buyers in form of higher prices. ...
... elasticities of S and D. – Pass-through fraction = Es/(Es-Ed) • Tells fraction of tax “passed thru” to buyers in form of higher prices. ...
Practice problems on Chapter 8
... 4. The benefit to buyers of participating in a market is measured by a. the price elasticity of demand. b. consumer surplus. c. the amount buyers are willing to pay for the good. d. the equilibrium price. 5. The benefit that government receives from a tax is measured by a. the change in the equilibr ...
... 4. The benefit to buyers of participating in a market is measured by a. the price elasticity of demand. b. consumer surplus. c. the amount buyers are willing to pay for the good. d. the equilibrium price. 5. The benefit that government receives from a tax is measured by a. the change in the equilibr ...
Chapter 8 Questions
... both John and Willa will still benefit from the lawn-mowing arrangement. If the tax is $10, a price can be set which will leave John and Willa neither better off nor worse off from the lawn-mowing arrangement. If the tax is greater than $10, all possible prices will leave at least one of the parties ...
... both John and Willa will still benefit from the lawn-mowing arrangement. If the tax is $10, a price can be set which will leave John and Willa neither better off nor worse off from the lawn-mowing arrangement. If the tax is greater than $10, all possible prices will leave at least one of the parties ...
Price Controls - Gore High School
... Indirect tax = A tax on consumption or spending e.g. GST ( Goods and Services Tax) Sales tax will affect supply as the tax effectively increases the producers costs of production. Therefore producers are willing to supply less which will cause supply curve to shift UP (vertically) to reach this new ...
... Indirect tax = A tax on consumption or spending e.g. GST ( Goods and Services Tax) Sales tax will affect supply as the tax effectively increases the producers costs of production. Therefore producers are willing to supply less which will cause supply curve to shift UP (vertically) to reach this new ...
Who is economically hurt when the following person is taxed…
... • When a good is taxed, the quantity sold is smaller. • Buyers and sellers share the tax burden. ...
... • When a good is taxed, the quantity sold is smaller. • Buyers and sellers share the tax burden. ...
Ch.31 Public Choice Theory and the Economics of Taxation
... in the dominant position to determine the outcome of an election. Implications -The size of government will be largely determined by the median preference -Some people may “vote with their feet” by moving into political jurisdictions where the median voter’s preferences are closer to their own. ...
... in the dominant position to determine the outcome of an election. Implications -The size of government will be largely determined by the median preference -Some people may “vote with their feet” by moving into political jurisdictions where the median voter’s preferences are closer to their own. ...
Homework 3
... deadweight loss. 4. The best example of a price ceiling is a. minimum wage b. minimum purchase requirement ...
... deadweight loss. 4. The best example of a price ceiling is a. minimum wage b. minimum purchase requirement ...
Quiz5
... b) [3 mark] Now suppose the government imposes an excise tax of $10 per unit. What will the new equilibrium quantity be? What price will the buyer pay? What price will the seller receive? Answer: With an excise tax, two conditions must hold. First, the market must clear so that Q d Q s . Second, t ...
... b) [3 mark] Now suppose the government imposes an excise tax of $10 per unit. What will the new equilibrium quantity be? What price will the buyer pay? What price will the seller receive? Answer: With an excise tax, two conditions must hold. First, the market must clear so that Q d Q s . Second, t ...
indirect taxes and subsidies File
... The product below (corn) receives a generous government subsidy. Show the effect on the diagram. ...
... The product below (corn) receives a generous government subsidy. Show the effect on the diagram. ...
Taxation, Incidence, Distribution
... above and beyond the tax revenues collected. • also refer as welfare cost or deadweight loss • Other Key Concepts: – Consumer surplus, social surplus ...
... above and beyond the tax revenues collected. • also refer as welfare cost or deadweight loss • Other Key Concepts: – Consumer surplus, social surplus ...
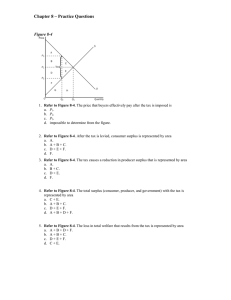
Figure 8-4
... c. the supply of the product is more elastic than the demand for the product. d. the demand for the product is more elastic than the supply of the product. ...
... c. the supply of the product is more elastic than the demand for the product. d. the demand for the product is more elastic than the supply of the product. ...
Has your clicker response been recorded properly in the last 2
... The effect on price of a sales tax collected from buyers is the same as the effect of 1. An upward shift of the demand curve. 2. A downward shift of the demand curve . 3. An upward shift of the supply curve. 4. A downward shift of the supply curve. ...
... The effect on price of a sales tax collected from buyers is the same as the effect of 1. An upward shift of the demand curve. 2. A downward shift of the demand curve . 3. An upward shift of the supply curve. 4. A downward shift of the supply curve. ...
Homework: October 7, 2015 Tax Incidence and Deadweight Loss
... Homework: October 7, 2015 Tax Incidence and Deadweight Loss - Read pages 416-419 1. Explain what is meant by tax incidence. 2. What does the phrase “division of burden” mean when applied to a sales or excise tax? 3. Explain how elasticities of supply and demand affect the incidence of a sales or exc ...
... Homework: October 7, 2015 Tax Incidence and Deadweight Loss - Read pages 416-419 1. Explain what is meant by tax incidence. 2. What does the phrase “division of burden” mean when applied to a sales or excise tax? 3. Explain how elasticities of supply and demand affect the incidence of a sales or exc ...