Representation and Manipulation of 3D Molecular Structures
... • Data mining for conformational properties and intermolecular interactions (CSD & PDB) • Data mining for information about intermolecular interactions (CSD & PDB) • Further understanding of the nature of protein structure and its relationship to amino acid sequence (PDB) • Homology modeling (compar ...
... • Data mining for conformational properties and intermolecular interactions (CSD & PDB) • Data mining for information about intermolecular interactions (CSD & PDB) • Further understanding of the nature of protein structure and its relationship to amino acid sequence (PDB) • Homology modeling (compar ...
Cell Standards
... forms and functions. For example, all organisms require an outside source of energy to sustain life processes; all organisms demonstrate patterns of growth and, in many cases, senescence, the process of becoming old; and the continuity of all species requires reproduction. All organisms are construc ...
... forms and functions. For example, all organisms require an outside source of energy to sustain life processes; all organisms demonstrate patterns of growth and, in many cases, senescence, the process of becoming old; and the continuity of all species requires reproduction. All organisms are construc ...
Amino Acid Starter Kit in Brief
... Notice that some of the side chains have a YELLOW band around the bottom. These side chains are hydrophobic and DO NOT LIKE water. Notice that some of the side chains have a WHITE band around the bottom. These side chains are hydrophilic and DO LIKE water. Notice that some side chains have a RED ban ...
... Notice that some of the side chains have a YELLOW band around the bottom. These side chains are hydrophobic and DO NOT LIKE water. Notice that some of the side chains have a WHITE band around the bottom. These side chains are hydrophilic and DO LIKE water. Notice that some side chains have a RED ban ...
Chemistry 464 Biochemistry First Hour Exam
... metabolites, cofactors, proteins, and ribosomes Ways they are different: Eukariotic cells are generally larger and contain a much large and more complex DNA. Eukariots have membrane bound organelles like the nucleus, the mitochondria, choroplasts, etc that prokariots lack. The DNA in prokariots is a ...
... metabolites, cofactors, proteins, and ribosomes Ways they are different: Eukariotic cells are generally larger and contain a much large and more complex DNA. Eukariots have membrane bound organelles like the nucleus, the mitochondria, choroplasts, etc that prokariots lack. The DNA in prokariots is a ...
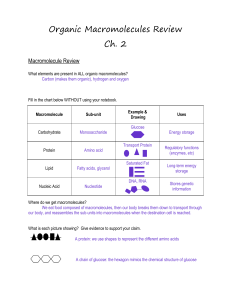
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
Protein Digestion and Absorption
... Proteins are sequences of amino acids (AA) linked by peptide bonds. There are twenty amino acids of which nine are essential and eleven are non-essential. Essential amino acids include phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, leucine, lysine, and histidine. These AA are ...
... Proteins are sequences of amino acids (AA) linked by peptide bonds. There are twenty amino acids of which nine are essential and eleven are non-essential. Essential amino acids include phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, leucine, lysine, and histidine. These AA are ...
gelbank
... the sequence of amino acids that will appear in the final protein. In translation codons of three nucleotides determine which amino acid will be added next in the growing protein chain. But you will need to decide on which nucleotide to start translation, and when to stop, this is called an open rea ...
... the sequence of amino acids that will appear in the final protein. In translation codons of three nucleotides determine which amino acid will be added next in the growing protein chain. But you will need to decide on which nucleotide to start translation, and when to stop, this is called an open rea ...
Protein /amino acids deficiency causes
... - Protein entering rumen will be digested into ammonia for microbial growth protein synthesis ...
... - Protein entering rumen will be digested into ammonia for microbial growth protein synthesis ...
Transcription - Effingham County Schools
... If you really need this information, you can make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the nucleus. ...
... If you really need this information, you can make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the nucleus. ...
VIII. PROTEINS, continued
... V. THE BIOMOLECULES • Most are ____________ made up of single units called ____________ • The different classes of macromolecules differ in the nature of their monomers, but the chemical mechanisms that cells use to make and break polymers are basically the same. ...
... V. THE BIOMOLECULES • Most are ____________ made up of single units called ____________ • The different classes of macromolecules differ in the nature of their monomers, but the chemical mechanisms that cells use to make and break polymers are basically the same. ...
Document Here - What is BioInformatics?
... same structure • Organism has many similar genes • Single gene may have multiple functions • Genes and proteins function in genetic and regulatory pathways • How do we organize all this information so that we can make sense of it? ...
... same structure • Organism has many similar genes • Single gene may have multiple functions • Genes and proteins function in genetic and regulatory pathways • How do we organize all this information so that we can make sense of it? ...
How to interpretate results from shotgun MS analysis
... which sequence(s) in the database contain(s) a given set of peptides. This can yield very univocal identifications if there are enough unique sequences matched. However several database sequences are often matched by the same set of peptides. This can happen because: i) highly homologous protein fam ...
... which sequence(s) in the database contain(s) a given set of peptides. This can yield very univocal identifications if there are enough unique sequences matched. However several database sequences are often matched by the same set of peptides. This can happen because: i) highly homologous protein fam ...
Macromolecules - Essentials Education
... M14. DNA and protein sequences usually show greater similarity between closely related groups of organisms than between distantly related groups M15. Change in the base sequence of DNA can lead to the alteration or absence of proteins, and to the appearance of new characteristics in the descendants ...
... M14. DNA and protein sequences usually show greater similarity between closely related groups of organisms than between distantly related groups M15. Change in the base sequence of DNA can lead to the alteration or absence of proteins, and to the appearance of new characteristics in the descendants ...
Supplementary Information (docx 4776K)
... Mn(III) was also monitored during Mn(II) oxidation by the co-culture of strain Arthrobacter and strain Sphingopyxis. Ligand-binding complex P2O74- (PP) was selected to complex Mn(III) by forming stable Mn(III)-PP complex, which has max absorbance at 258 nm (ε = 6,750 M-1). The co-culture was first c ...
... Mn(III) was also monitored during Mn(II) oxidation by the co-culture of strain Arthrobacter and strain Sphingopyxis. Ligand-binding complex P2O74- (PP) was selected to complex Mn(III) by forming stable Mn(III)-PP complex, which has max absorbance at 258 nm (ε = 6,750 M-1). The co-culture was first c ...
Honors Biology Unit 6 Ch. 10 “DNA, RNA & Protein synthesis”
... I can describe what happens during transcription. I can describe what happens during translation. I can explain how transcription and translation work together to make a protein. b. I can identify how each type of RNA is involved in protein synthesis. c. I can describe the functions of protein ...
... I can describe what happens during transcription. I can describe what happens during translation. I can explain how transcription and translation work together to make a protein. b. I can identify how each type of RNA is involved in protein synthesis. c. I can describe the functions of protein ...
Genome sequence and gene compaction of the eukaryote parasite
... composed of more than two CDSs (for example, histones H3 and H4 on chrIX). Genome compaction can also be related to gene shortening, as indicated by the length distribution of all potential proteins (Fig. 2a). The mean and median lengths of all potential E. cuniculi proteins are only 359 and 281 ami ...
... composed of more than two CDSs (for example, histones H3 and H4 on chrIX). Genome compaction can also be related to gene shortening, as indicated by the length distribution of all potential proteins (Fig. 2a). The mean and median lengths of all potential E. cuniculi proteins are only 359 and 281 ami ...
Honors Biology Unit 6 Ch. 10 “DNA, RNA & Protein synthesis”
... I can describe what happens during transcription. I can describe what happens during translation. I can explain how transcription and translation work together to make a protein. b. I can identify how each type of RNA is involved in protein synthesis. c. I can describe the functions of protein ...
... I can describe what happens during transcription. I can describe what happens during translation. I can explain how transcription and translation work together to make a protein. b. I can identify how each type of RNA is involved in protein synthesis. c. I can describe the functions of protein ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription
... ribosomes outside the nucleus? A molecular cousin of DNA – RNA – is used to carry these messages. ...
... ribosomes outside the nucleus? A molecular cousin of DNA – RNA – is used to carry these messages. ...
Protein Building Activity Lesson
... 5. What kinds of conditions may cause a protein to denature? Would the protein still function after this change? Why not? 6. Why is the biological concept of “Structure and Function” extremely important to building proteins? Slide #8 – Pick any protein found in the body. The title should be the name ...
... 5. What kinds of conditions may cause a protein to denature? Would the protein still function after this change? Why not? 6. Why is the biological concept of “Structure and Function” extremely important to building proteins? Slide #8 – Pick any protein found in the body. The title should be the name ...
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening (also known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the binding domain (BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the domain responsible for binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation assay.